SLAS Technology special collection on AI in process automation available now
The February edition of SLAS Technology is a special collection of articles focused on 'Artificial Intelligence in Process Automation' by guest editor Cenk Ündey, Ph.D. (Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA)
2021-02-02
(Press-News.org) Oak Brook, IL - The February edition of SLAS Technology is a special collection of articles focused on "Artificial Intelligence in Process Automation" by Guest Editor Cenk Ündey, Ph.D. (Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA).
This SLAS Technology special collection targets the use of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques and technologies as applied specifically to drug discovery, automated gene editing and machine learning. As AI becomes increasingly more prevalent in research, medicine and even everyday life, laboratory automation has gone beyond hardware advancements toward new levels of precision and complexity. Beyond research, AI serves as a powerful tool for clinicians diagnosing and treating patients in a medical setting. The AI advancements presented in this issue highlight the wide spectrum of medical AI breakthroughs.
This month's issue of SLAS Technology also celebrates the top 10 most-cited articles within the journal's history. Over the past decade, the publication's priority has been to provide a platform for researchers to share technological advancements as well as a resource to continually share the impact of technology on life sciences and biomedical research.
The February issue of SLAS Discovery includes nine articles of original research in addition to the cover article.
Articles of Original Research include:
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells on a Chip: A Self-Contained, Accessible, Pipette-less iPSC Culturing and Differentiation Kit
Core Hairpin Structure of SpCas9 sgRNA Functions in a Sequence- and Spatial Conformation-Dependent Manner
Performance Comparison of Massively Parallel Sequencing (MPS) Instruments Using Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Panels for Ancestry
Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision Strategies for Automated Gene Editing with a Nanofountain Probe Electroporation (NFP-E) System
Other articles include:
Artificial Intelligence Effecting a Paradigm Shift in Drug Development
Artificial Intelligence (AI) to the Rescue: Deploying Machine Learning to Bridge the Biorelevance Gap in Antioxidant Assays
SLAS Celebrates the Top 10 Most-Cited SLAS Technology Articles
The Diagnostic Accuracy of Liquid Biopsy in EGFR-Mutated NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 40 Studies
Point-of-Need Diagnostics for Foodborne Pathogen Screening
An Automated Tube Labeler for High-Throughput Purification Laboratories
INFORMATION:
Access to February's SLAS Technology issue is available at http://journals.sagepub.com/toc/jlad/26/1.
For more information about SLAS and its journals, visit http://www.slas.org/journals. Access a "behind the scenes" look at the latest issue with SLAS Technology Authors Talk Tech podcast. Tune into February's episode by visiting https://slastechnology.buzzsprout.com/.
SLAS (Society for Laboratory Automation and Screening) is an international professional society of academic, industry and government life sciences researchers and the developers and providers of laboratory automation technology. The SLAS mission is to bring together researchers in academia, industry and government to advance life sciences discovery and technology via education, knowledge exchange and global community building.
SLAS Discovery: Advancing the Science of Drug Discovery, 2019 Impact Factor 2.195. Editor-in-Chief Robert M. Campbell, Ph.D., Twentyeight-Seven Therapeutics, Boston, MA (USA).
SLAS Technology: Translating Life Sciences Innovation, 2019 Impact Factor 2.174. Editor-in-Chief Edward Kai-Hua Chow, Ph.D., National University of Singapore (Singapore).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-01
Risk for a severe form of retinopathy of prematurity, which can cause blindness in extremely premature babies, was halved when the newborns were given a new supplement combining various fatty acids. This was shown in a Swedish study led from the University of Gothenburg.
The study, now published in JAMA Pediatrics, is described as groundbreaking in its field. It documents a clear fall in retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) among extremely premature (EP) infants (born before 28 weeks' gestation), whose retinal blood vessels are not fully developed. The condition can cause ...
2021-02-01
When the body's immune response to an infection gets out of control, the result can be sepsis, a life-threatening condition in which an overwhelming inflammatory response can lead rapidly to failure of multiple organs and death.
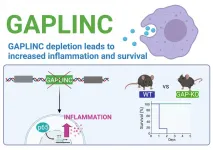
In a new study, researchers at UC Santa Cruz have identified a long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) molecule that regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes in immune system cells called macrophages and affects the susceptibility of mice to septic shock.
This lncRNA, called GAPLINC, was previously studied for its role in cancer, but it turns out to be the most highly expressed lncRNA in macrophages, which play a central role in inflammation. ...
2021-02-01
A previously unknown root trait allows some cereal plants to grow deeper roots capable of punching through dry, hard, compacted soils, according to Penn State researchers, who suggest that harnessing the inherited characteristic could lead to crops better able to deal with a changing climate.
"This discovery bodes well for American and global agriculture because the trait helps corn, wheat and barley grow deeper roots, which is important for drought tolerance, nitrogen efficiency and carbon sequestration," said Jonathan Lynch, distinguished professor in plant science. "Breeding for this trait should be helpful in developing new crops for climate mitigation."
Called multiseriate cortical sclerenchyma by the researchers -- or MCS -- the phenotype is ...
2021-02-01
New research from North Carolina State University reveals that probiotic Lactobacillus bacteria use enzymes situationally to manipulate bile acids and promote their own survival in the gut. These findings further elucidate the complicated relationship between bile acids and gut bacteria and could eventually enable researchers to design lactobacilli with therapeutic properties, thereby engineering a healthier human gut environment.
Bile acids are key players in digestion and overall gut health. Produced in the liver and released after we eat, these acids not ...
2021-02-01
Just as plants and animals on land are keenly attuned to the hours of sunlight in the day, life in the oceans follows the rhythms of the day, the seasons and even the moon. A University of Washington study finds the biological light switches that make this possible.
Single-celled organisms in the open ocean use a diverse array of genetic tools to detect light, even in tiny amounts, and respond, according to a study published Feb. 1 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"If you look in the ocean environment, all these different organisms have this day-night cycle. They are very in tune with each other, even as they get moved around. How do they know when it's day? How do they know when it's night?" said lead ...
2021-02-01
There are fossils, found in ancient marine sediments and made up of no more than a few magnetic nanoparticles, that can tell us a whole lot about the climate of the past, especially episodes of abrupt global warming. Now, researchers including doctoral student Courtney Wagner and associate professor Peter Lippert from the University of Utah, have found a way to glean the valuable information in those fossils without having to crush the scarce samples into a fine powder. Their results are published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"It's so fun to be a part of a discovery like this, something that can be used ...
2021-02-01
Most snakes get from A to B by bending their bodies into S-shapes and slithering forward headfirst. A few species, however -- found in the deserts of North America, Africa and the Middle East -- have an odder way of getting around. Known as "sidewinders," these snakes lead with their mid-sections instead of their heads, slinking sideways across loose sand.
Scientists took a microscopic look at the skin of sidewinders to see if it plays a role in their unique method of movement. They discovered that sidewinders' bellies are studded with tiny pits and have few, if any, of the tiny spikes found on the bellies of other snakes.
The Proceedings ...
2021-02-01
CAMBRIDGE -- The temperature of a planet is linked with the diversity of life that it can support. MIT geologists have now reconstructed a timeline of the Earth's temperature during the early Paleozoic era, between 510 and 440 million years ago -- a pivotal period when animals became abundant in a previously microbe-dominated world.
In a study appearing today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers chart dips and peaks in the global temperature during the early Paleozoic. They report that these temperature variations coincide with the planet's ...
2021-02-01
In a new study led by Yale Cancer Center, researchers have discovered a novel metabolic gatekeeper mechanism for leukemia. This mechanism depends on a molecule called PON2, which could lead to a new treatment for the disease. The findings were published online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
B cells are effector cells of the adaptive immune system and are marked by low energy levels, which prevent transformation to leukemia. In this study, Yale scientists identified high expression levels of the detoxifying lactonase ...
2021-02-01
Philadelphia, February 1, 2021 - Researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have demonstrated that autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be caused by defects in the mitochondria of brain cells. The findings were published online by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Multiple studies have revealed hundreds of mutations associated with autism spectrum disorder, but there is no consensus as to how these genetic changes cause the condition. Biochemical and physiological analyses have suggested that deficiencies in mitochondria, the "batteries" of the cell that produce ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SLAS Technology special collection on AI in process automation available now
The February edition of SLAS Technology is a special collection of articles focused on 'Artificial Intelligence in Process Automation' by guest editor Cenk Ündey, Ph.D. (Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA, USA)