Aging-US: A pro-diabetogenic mtDNA polymorphism in mitochondrial-derived peptide
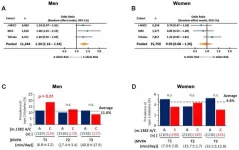
'The m.1382A>C polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to T2D in men, possibly interacting with exercise, and contributing to the risk of T2D in sedentary males by reducing the activity of MOTS-c'
2021-02-03
(Press-News.org) C polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to T2D in men, possibly interacting with exercise, and contributing to the risk of T2D in sedentary males by reducing the activity of MOTS-c.
Dr. Noriyuki Fuku from The Juntendo University and Dr. Pinchas Cohen from The University of Southern California said, "The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is growing dramatically."
While diabetes syndromes directly caused by mutations in mtDNA are extremely rare, several genetic analyses reveal that mtDNA polymorphisms contribute to T2D risk in both European and Asian populations.
MOTS-c levels are correlated with insulin resistance, and circulating MOTS-c levels are reduced in obese male children.
MOTS-c levels are inversely correlated with markers of insulin resistance and obesity including BMI, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, fasting insulin level, HOMA-IR, HbA1c.
Although that study suggested an association between the haplogroup that includes mtDNA SNP at the MOTS-c region and T2D, the relation between the m.1382A>C polymorphism and human T2D pathophysiology was not explored.
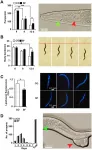
Here, they elucidated the association between T2D and m.1382A>C in Japanese individuals and established the abnormal biological effects of the K14Q MOTS-c peptide variant - a consequence of the m.1382A>C polymorphism - on insulin action and adiposity in vitro and in vivo.
The Fuku/Cohen Research Team concluded in their Aging-US Research Paper, "we found that the C allele of the m.1382A>C polymorphism changes body composition and increases the risk of T2D in Japanese men, especially in sedentary individuals. This polymorphism causes an amino acid replacement from Lys (K) to Gln (Q) at amino acid 14 in the MOTS-c peptide, which renders it a less potent insulin-sensitizer compared to WT MOTS-c. A deeper understanding the effects of this genetic polymorphism will provide a basis for developing physical activity strategies to maximize the benefits of exercise in T2D."
INFORMATION:
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article
DOI - https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202529
Full Text - https://www.aging-us.com/article/202529/text
Correspondence to: Noriyuki Fuku email: noriyuki.fuku@nifty.com and Pinchas Cohen email: hassy@usc.edu
Keywords: diabetes, mitochondrial DNA, polymorphism, MOTS-c insulin resistance
About Aging-US
Launched in 2009, Aging-US publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research as well as topics beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, cancer, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
To learn more about Aging-US, please visit http://www.Aging-US.com or connect with @AgingJrnl
Aging-US is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit http://www.ImpactJournals.com or connect with @ImpactJrnls
Media Contact
18009220957x105
MEDIA@IMPACTJOURNALS.COM
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-03
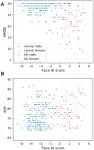
Aging-US published "Screening of Alzheimer's disease by facial complexion using artificial intelligence" which reported that despite the increasing incidence and high morbidity associated with dementia, a simple, non-invasive, and inexpensive method of screening for dementia is yet to be discovered.
This study aimed to examine whether artificial intelligence could distinguish between the faces of people with cognitive impairment and those without dementia.
121 patients with cognitive impairment and 117 cognitively sound participants were recruited for the study.
The binary differentiation of dementia / non-dementia facial image was expressed as a "Face AI score".
However, MMSE score showed significantly stronger ...
2021-02-03
Aging-US published "Sulforaphane promotes C. elegans longevity and healthspan via DAF- 16/DAF-2 insulin/IGF-1 signaling" which reported that the broccoli-derived isothiocyanate sulforaphane inhibits inflammation, oxidative stress and cancer, but its effect on healthspan and longevity are unclear.
The authors used the C. elegans nematode model and fed the wildtype and 9 mutant strains ±sulforaphane.
Sulforaphane increased the lifespan and promoted a health-related phenotype by increasing mobility, appetite and food intake and reducing lipofuscin accumulation.
Mechanistically, sulforaphane inhibited DAF-2-mediated insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling and its downstream targets AGE-1, AKT-1/AKT-2. This was associated with increased nuclear translocation of ...
2021-02-03
Amsterdam, NL, February 3, 2021 - Patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and healthcare professionals caring for them have expressed concerns about the COVID-19 vaccine's efficacy and safety in the specific context of PD and its symptomatic treatment. In a END ...
2021-02-03
WHAT:
An experimental single-dose, intranasal influenza vaccine was safe and produced a durable immune response when tested in a Phase 1 study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation. The investigational vaccine, called Ad4-H5-VTN, is a recombinant, replicating adenovirus vaccine designed to spur antibodies to hemagglutinin, a protein found on the surface of influenza viruses that attaches to human cells.
The investigational vaccine was developed by Emergent Biosolutions Inc., (Gaithersburg, Maryland). It was administered intranasally (28 study participants), as an oral capsule (10 participants) and via a tonsillar swab (25 participants) to ...
2021-02-03
BATON ROUGE, LOUISIANA - In patients with type 2 diabetes, big swings in blood sugar levels between doctors' visits are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
The study, published in the journal Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism, looked at more than 29,000 patients with type 2 diabetes over a two-year period. Patients who already had heart disease were excluded.
The American Diabetes Association recommends adults with diabetes maintain an A1c, the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, of less than 7 percent to reduce complications from diabetes, such ...
2021-02-03
A study published in the journal Applied Ergonomics compared the standardised processes set out for community pharmacists to follow when dispending medication to what happens in reality. A gap was revealed and researchers also looked at the reasons for this.
The research, "Mind the gap: Examining work-as-imagined and work-as-done when dispensing medication in the community pharmacy setting"*, was conducted by the National Institute for Health Research Greater Manchester Patient Safety Translational Research Centre (NIHR GM PSTRC). The Centre is a partnership between The University of Manchester and Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust.
The research involved observing pharmacists and pharmacy staff as they conducted the task of dispensing, ...
2021-02-03
Sneakers can be about style, history and even community. A new study reveals that for "Sneakerheads," sneakers are an important facet of their identities, particularly for African-American men who grew up in the 1970s and '80s coveting sneakers popularized by hip-hop stars and basketball legends.
In the journal Fashion and Textiles, researchers report new insights into the motivations, brand preferences and identity considerations of Sneakerheads. The findings were drawn from interviews with 12 men in the mid-Atlantic region of the United States, many whom are African-American, and ...
2021-02-03
Researchers have developed a computerized adaptive screener to identify youth at risk for attempting suicide. The screener, called the computerized adaptive screen for suicidal youth (CASSY), consists of 11 questions on average and correctly identified 82.4% of youth who went on to attempt suicide in the three months following screening. The results suggest this screener could serve as an easy-to-use way for providers to detect youth suicide risk in emergency department settings. The findings, funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), ...
2021-02-03
Today, neuroscience and robotics are developing hand in hand. Mikhail Lebedev, Academic Supervisor at HSE University's Centre for Bioelectric Interfaces, spoke about how studying the brain inspires the development of robots.
Robots are interesting to neuroscience and neuroscience is interesting to robots - this is what the article 'Neuroengineering challenges of fusing robotics and neuroscience' was about in the journal Science Robotics. Such collaborative development contributes to progress in both fields, bringing us closer to developing more advanced android robots and a deeper understanding ...
2021-02-03
Among the many avenues that viruses can use to infect humans, drinking water may pose only a tiny risk for spreading certain viruses like the novel coronavirus. However, in cases where there is unauthorized wastewater disposal or other events of inadvertent mixing of wastewater with water sources, the possibility of transmission through drinking water remains unknown.
Using a surrogate of the coronavirus that only infects bacteria, researchers at Texas A&M University have now presented strong evidence that existing water purification plants can easily reduce vast quantities of the virus thereby protecting our household water from such contagions. In particular, the researchers showed that the water purification step called coagulation could alone get rid of 99.999% of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aging-US: A pro-diabetogenic mtDNA polymorphism in mitochondrial-derived peptide
'The m.1382A>C polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to T2D in men, possibly interacting with exercise, and contributing to the risk of T2D in sedentary males by reducing the activity of MOTS-c'