SARS-CoV-2 infection among migrant workers in Singapore
2021-02-09
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did:
Researchers examined how common SARS- CoV-2 infection was among migrant workers in Singapore.
Authors:
Vernon J. Lee, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the Ministry of Health in Singapore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study:
Visit our For The Media website at this link
https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24071)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory:
The full article is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article
This link will be live at the embargo time
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2020.24071?guestAccessKey=e5b5e747-139a-4ba0-a2ea-717ad66dfa7f&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=020921
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- The detailed physical processes and pathways involved in the transmission of COVID-19 are still not well understood. Researchers decided to use advanced computational fluid dynamics tools on supercomputers to deepen understanding of transmission and provide a quantitative assessment of how different environmental factors influence transmission pathways and airborne infection risk.
A restaurant outbreak in China was widely reported as strong evidence of airflow-induced transmission of COVID-19. But it lacked a detailed investigation about exactly how transmission occurred.
Why did some people get infected while others within the same area did not? ...
2021-02-09
What The Viewpoint Says: The missteps and miscommunications that have stymied a more effective U.S. and global response to the COVID-19 pandemic bring into sharp focus the deficiencies in governance systems of the U.S. public health and scientific institutions.
Authors: K. M. Venkat Narayan, M.D., M.Sc., of the Rollins School of Public Health and School of Medicine at Emory University in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.23479)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
2021-02-09
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- School closures, the loss of public spaces, and having to work remotely due to the coronavirus pandemic have caused major disruptions in people's social lives all over the world.
Researchers from City University of Hong Kong, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute suggest a reduction in fatal coronavirus cases can be achieved without the need for so much social disruption. They discuss the impacts of the closures of various types of facilities in the journal Chaos, from AIP Publishing.
After running thousands of simulations of the pandemic response in New York City with variations in social distancing behavior at home, in schools, at public facilities, and in the workplace ...
2021-02-09
What The Study Did: To mitigate subsequent waves of COVID-19, allocating testing resources to locations of greatest need is important. Researchers in this study examined the alignment of testing to epidemic intensity in Massachusetts.
Authors: Scott Dryden-Peterson, M.D., M.Sc., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37067)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
2021-02-09
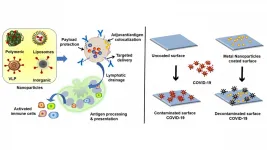
WASHINGTON, February 9, 2021 -- Advances in the fields of biomaterials and nanotechnology could lead to big breakthroughs in the fight against dangerous viruses like the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Indian Institute of Science describe two possibilities being explored by scientists in the field to make vaccines more effective and build surfaces that could fight and kill viruses on their own.
"It is important not just in terms of COVID," said author Kaushik Chatterjee. "We've seen SARS, ...
2021-02-09
FOLSOM, Calif., February 9, 2021 - A new animal study, published in the Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, suggests regular walnut consumption may be a promising intervention for reducing negative outcomes associated with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection, a widespread bacterial infection that affects more than half of the world's population.
Using mice models, researchers from the CHA Cancer Prevention Research Center in Korea found preliminary evidence that eating a diet rich in walnuts may help protect against negative outcomes associated with H. pylori infection. Specifically, the research found that walnut extracts, formed from ...
2021-02-09
Within the constellation Cygnus, an elderly star and its massive companion are having one last hurrah, flinging off mass at an incredible rate before they explode as supernovae and collapse into a black hole.
Now, researchers including recent Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University graduate Laura M. Lee have mapped the elderly star's orbit around its oversized and equally ancient partner. In a scientific first, they have also determined the dynamical mass of both stars that make up a binary system called Wolf-Rayet 133.
The team's findings, published Feb. 9, 2021 by Astrophysical Journal ...
2021-02-09
While the World Health Organization (WHO) continues its mission to Wuhan investigating the origin and early transmission of SARS-CoV-2, a new study led by scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, and Chulalongkorn University, Thailand, shows that SARS-CoV-2-related coronaviruses (SC2r-CoVs) are circulating in animals as far away as Thailand. The study, published in Nature Communications today, reported that high levels of neutralising antibodies against the virus were present in both bats and pangolins found in the Southeast Asian country. The study further indicates that more SC2r-CoVs are likely to be discovered ...
2021-02-09
Amsterdam, NL, February 9, 2021 - Globally, nearly 300,000 babies are born with neural tube defects including spina bifida (SB) each year. This openly available special issue of the Journal of Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine (JPRM) provides 20 important evidence- and consensus-based updates to key sections of the 2018 "Guidelines for the Care of People with Spina Bifida" issued by the Spina Bifida Association (SBA). These reflect current recommendations for the care of patients with SB across the entire lifespan, from prenatal counseling to adult care.
As a result of research advancements and improved team-based patient care, approximately 80%-90% of children with SB now live to adulthood in the United ...
2021-02-09
A study of women who were new mothers in the late 1970s found that those who were given longer, paid maternity leave lived healthier lives as they entered middle age.
While universal paid maternity leave is now available in many Western European nations, this has not always been the case. A new study by University of Georgia economist Meghan Skira looked at the health of Norwegian mothers before and after paid maternity leave became law in 1977. She found that the health benefits of leave continued for years after their children were born.
Skira, an associate professor in the Terry College of Business, worked with economist Aline Bütikofer of the Norwegian School of Economics and Julie Riise of the University of Bergen on the study. Their paper, "The Impact of Paid ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] SARS-CoV-2 infection among migrant workers in Singapore