INFORMATION:
This research was conducted with the grant from the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology, the Mid-career Researcher Program, the Global Frontier Program, the Regional Leading Research Center program, and the Future Materials Discovery Project of the Ministry of Science and ICT, a fellowship from the Hyundai Motors Chung Mong-Koo Foundation, and the Next Generation Researchers Initiative of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Move over heavy goggles, here come the ultra-high refractive index lenses
2021-02-16
(Press-News.org) A POSTECH research team has developed a transparent amorphous silicon that transmits visible light - which permits us to distinguish the colors of objects - enabling the development of paper-thin lenses usable in head-mounted displays (HMD) that show virtual and augmented reality images in real time.
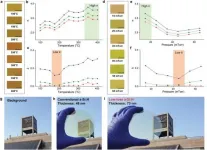
A research team - led by Professor Junsuk Rho of POSTECH's mechanical engineering and chemical engineering departments, and Ph.D. candidate Younghwan Yang and Dr. Gwanho Yoon of the Department of Mechanical Engineering - has developed visibly transparent amorphous silicon by improving the plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) method, a practice widely used by Korean display manufacturers. The researchers also succeeded in effectively controlling the light in the visible region using the newly developed silicon. This research was recently published in Advanced Materials, the most respected international journal on materials science.
Since light bends more with higher refractive index, a material with high refractive index is essential in designing devices for virtual and augmented reality. However, most highly refractive materials tend to absorb light and when used in a device that produces an image by controlling the light - such as an ultra-thin lens or a hologram - their performance deteriorates. The optical materials presented so far have high transmittance with low refractive index, or, conversely, high refractive index and low transmittance, thereby limiting the production of lightweight and highly efficient optical devices.
To this, the research team utilized the PECVD method, a common technique to develop the amorphous silicon. While depositing the silicon using the PECVD method, the team explored each parameter of the process, such as temperature, pressure, plasma power, and hydrogen ratio, and uncovered the effect of each variable on the intermolecular bonds.
Moreover, the team discovered a method to increase the regularity between silicon atoms by inserting hydrogen atoms between strained silicon atomic bonds, and through this, the atomic structure of amorphous silicon that possesses a high refractive index and significant transmittance was identified. In addition, the researchers succeeded in steering red, green, and blue lights in the desired direction, which could not be controlled with the conventional silicon before.
Transparent amorphous silicon has the advantage of producing hologram devices or ultra-thin lenses that are one thousandth of the thickness of conventional lenses at a fraction of the cost. The applicability of the silicon has also been expanded in that the amorphous silicon, which has been used only in thermal infrared cameras, can now be used as an optical device in the visible light region.
"The discovery of an optical element capable of controlling all visible light has revealed clues about the relationship between the atomic bonding structure and the visible light region, which has not been of interest until now," explained Professor Junsuk Rho, the corresponding author who led the study. "As we can produce optical devices that can control all colors at low cost, we are now one step closer to commercializing virtual and augmented reality and hologram technologies only seen in movies."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clues for improving sleep in visually impaired athletes
2021-02-16
Tsukuba, Japan - Sleep is very important for athletes, and sleep loss can affect physical performance and cognitive ability. But now, researchers from the University of Tsukuba have identified the prevalence of sleep disorders in visually impaired athletes, as well as specific risk factors associated with lower sleep quality.
In a study published last November in Sleep Medicine, researchers from the University of Tsukuba conducted a survey of 99 visually impaired athletes in Japan and analyzed data from 81 respondents. They found that approximately one-third of the respondents had sleep disorders. Further, higher levels of stress regarding interpersonal relationships ...
Melanoma patients respond to immunotherapy after changes to gut microbiome
2021-02-16
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Statistical modeling developed by Oregon State University researchers has confirmed that changes to melanoma patients' gut microbiome led them to respond to a type of treatment capable of providing long-term benefit.
Findings were published in Science.
The modeling technique invented by Andrey Morgun of the OSU College of Pharmacy and Natalia Shulzenko of Oregon State's Carlson College of Veterinary Medicine is known as transkingdom network analysis.
The human gut microbiome is a community of more than 10 trillion microbial cells from about 1,000 different bacterial species, and transkingdom network analysis integrates ...
Water is a probable vector for mammalian virus transmission
2021-02-16
Water is a necessity for all life but its availability can be limited. In geographical areas experiencing dry seasons, animals congregate near the few freshwater sources, often reaching large densities. At these sites many animals from different species come to the same spots to drink, potentially operating as key locations for pathogen transmission within and between species. An international team of scientists lead by the German Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (Leibniz-IZW) suggests that viruses can use restricted freshwater sources as a vector to be spread among animals. The key prediction of this idea is that animal viruses remain stable and infectious in water. The team ...
Method for temporal monitoring of microplastic sedimentation
2021-02-16
The effects of microplastics on our health and the environment are being rigorously studied all across the world. Researchers are identifying microplastic sources and their potential routes to the environment by examining rainwater, wastewater, and soil.
Microplastics have been found in nearly all organisms and habitats everywhere in the world. However, factors contributing to the influx and accumulation of microplastics in water ecosystems aren't fully understood yet. The focus of microplastics research has, for a long time, been on the age of microplastics found in sediments, and on the ...
New discovery may enable accurate prediction of cancer spread before cancer develops
2021-02-16
The researchers analysed cells, mouse models, and human patient samples using biochemical, mathematical, and biophysical methods. They identified a protein present in the mesh-like membrane structure (the basement membrane) associated with tumour and vessel softness, and good survival of cancer patients. The researchers tested if removing this protein from the basement membrane would enhance the spread of cancer, which it did, and if supply of this protein would reduce cancer spread, which it did. They proceeded to show that the levels of this protein (netrin-4) already present in basement membrane of organs may determine cancer spread even before cancer develops, ...
New microscopy analysis allows discovery of central adhesion complex
2021-02-16
Cells of organisms are organized in subcellular compartments that consist of many individual molecules. How these single proteins are organized on the molecular level remains unclear, because suitable analytical methods are still missing. Researchers at the University of Münster together with colleagues from the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry (Munich, Germany) have established a new technique that enables quantifying molecular densities and nanoscale organizations of individual proteins inside cells. The first application of this approach reveals a complex of three adhesion proteins that appears to be crucial for the ability of cells to adhere to the surrounding tissue. The research results have been published in the journal Nature ...
The water surface is a fantastic place for chemical reactions
2021-02-16
Using an advanced technique, scientists from the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research have demonstrated that a chemical reaction powered by light takes place ten thousand times faster at the air-water interface--what we usually call the water surface--than in the bulk of the water, even when the light has equivalent energy. This finding could help our understanding of the many important chemical and biological processes that take place at the water surface.
Water is the most important liquid in nature, and research has shown that there is in fact something special about the interface. For reasons that were not well understood, it appears that some chemical reactions take place readily when the molecules are partly in the water, but not when they are fully ...
People with and without AD have a different threshold for elective revascularisation
2021-02-16
The risk of both mortality and rehospitalisation after an elective revascularisation procedure for coronary artery disease is similar for people with and without Alzheimer's disease (AD), but people with AD had worse outcomes after an emergency procedure, according to a new study from the University of Eastern Finland.
Previous studies have investigated the effectiveness of revascularisation in persons with cognitive disorders, but only in terms of short-term outcomes and in acute care settings, and they also have not accounted for electivity. Similar to previous ...
Challenge to anorexia nervosa treatment guidelines
2021-02-16
New analysis published in The Lancet Psychiatry has shown a lack of strong evidence to support current guidance on psychological therapies for treating anorexia nervosa over expert treatment as usual.
The findings highlight a need for further research and support a call for individual trial data to be made available so the benefits of treatments in specific patient populations can be better understood.
Conducted by an international team of clinical experts and researchers, the analysis included 13 randomised controlled trials and a total of 1049 patients. The studies compared psychological therapies to treatment as usual in adults receiving outpatient treatment for anorexia. The trials measured eating disorder ...
First humans in Tasmania must have seen spectacular auroras
2021-02-16
Drilling a 270,000-year old core from a Tasmanian lake has provided the first Australian record of a major global event where the Earth's magnetic field 'switched '- and the opportunity to establish a precedent for developing new paleomagnetic dating tools for Australian archaeology and paleosciences.
"This is the first study of this kind in Australia since pioneering studies in the 1980s," said author Dr Agathe Lisé-Provonost, a McKenzie Fellow from the School of Earth Sciences at the University of Melbourne.
"Just two lakes in north-east Australia previously provided such "full-vector" record, where both the past directions and the past intensity of the Earth magnetic field are obtained from the same cores."
Published in the journal Quaternary Geochronology, Chronostratigraphy ...