INFORMATION:
'Classic triad' of symptoms misses positive COVID-19 cases, study finds
2021-02-18
(Press-News.org) Extending the symptoms that trigger a PCR test for COVID-19 could help detect around a third more cases of the disease.
New research led by researchers at King's College London and published in the Journal of Infection suggests that restricting testing to the 'classic triad' of cough, fever and loss of smell which is required for eligibility for a PCR test through the NHS may have missed cases. Extending the list to include fatigue, sore throat, headache and diarrhoea would have detected 96% of symptomatic cases.
A team of researchers at King's College London and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) analysed data from more than 122,000 UK adult users of the ZOE COVID Symptom Study app. These users reported experiencing any potential COVID-19 symptoms, and 1,202 of those reported a positive PCR test within a week of first feeling ill.
While PCR swab testing is the most reliable way to tell whether someone is infected with the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the analysis suggests the limited list of three does not catch all positive cases of COVID-19.
Testing people with any of the three 'classic' symptoms would have spotted 69% of symptomatic cases, with 46 people testing negative for every person testing positive. However, testing people with any of seven key symptoms - cough, fever, anosmia, fatigue, headache, sore throat and diarrhoea - in the first three days of illness would have detected 96% of symptomatic cases. In this case, for every person with the disease identified, 95 would test negative.
Researchers also found users of the Symptom Study App were more likely to select headache and diarrhoea within the first three days of symptoms, and fever during the first seven days, which reflects different timings of symptoms in the disease course. Data from the ZOE app shows that 31% of people who are ill with COVID-19 don't have any of the triad of symptoms in the early stages of the disease when most infectious.
The researchers applied a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm (MOEA) to generate a set of optimal symptom combinations, each characterised by a good trade-off between specificity and sensitivity. MOEA starts generating a population of random symptom combinations and then evolves that population towards better combinations ending with a set of optimal symptom combinations. The choice of the optimal combination to use depends on the testing capacity.
Cough or dyspnoea (shortness of breath) were reported by 46% of individuals positive for COVID-19 within the first three days of symptom onset. When users reported fever, the sensitivity increased to 60%, while logging anosmia/ageusia increased sensitivity to 69%. When headache and fatigue was added the proportion of COVID-19 cases increased to 92% but the tests per case doubled.
The findings may be valuable in situations where there is a limited testing capacity. Researchers suggest a range of optimal symptom combinations that could be used in vaccine efficacy trials or in public health settings, when assessing financial and logistical resources.
Professor Sebastien Ourselin from King's College London said: ""The identification of this combination of symptoms through the COVID Symptom Study app is another prime demonstration of the value of big data analytics and mobile health technology to support the management of this pandemic. Daily self-reported symptoms from a mobile application at the scale of an entire country has offered a new perspective for public health research and response towards the rapid spread of infectious diseases such as COVID-19."
Dr Claire Steves, Reader at King's College London, said: "There are many symptoms which occur in acute COVID, including some like fatigue and headache which are also common in other conditions. Depending on the testing available, different symptom combinations can be used to be as sensitive or specific as possible. We hope these models are of use in a range of settings - from vaccine trials to detecting and treating COVID outbreaks going forward."
Professor Tim Spector from King's College London said: "We've known since the beginning that just focusing testing on the classic triad of cough, fever and anosmia misses a significant proportion of positive cases. We identified anosmia as a symptom back in May and our work led to the government adding it to the list, it is now clear that we need to add more. By inviting any users who log any new symptoms to get a test, we confirmed that there are many more symptoms of COVID-19. This is especially important with new variants that may cause different symptoms. For us, the message for the public is clear: if you're feeling newly unwell, it could be COVID and you should get a test."
Dr Jakob Cramer, Head of Clinical Development, at the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, said: "Accurate diagnosis of COVID-19 cases is crucial when assessing the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccine candidates in large-scale studies, especially since the signs and symptoms associated with the disease are extensive and overlap with other common viral infections. The findings of this study provide important insights that will help optimise the choice of triggering symptoms for diagnostic work-up in COVID-19 vaccine-efficacy trials. We hope the findings of this study will not only aid CEPI's COVID-19 vaccine-development partners but also the wider R&D community."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving stroke treatment with a modified therapeutic molecule
2021-02-18
A research team from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) has improved the protective effect of a molecule against ischemic stroke, which is caused by an interruption of blood flow to the brain. The results of the study, conducted in collaboration with a Spanish team, were published in the Communications Biology of Nature Research journal.
Every year in Quebec, about 20,000 people have a stroke. Also known as a "cerebral infarction", this sudden neurological deficit can lead to psychological and physical after-effects. These effects result from an increase in glutamate in the brain, which destroys neurons. "Glutamate is an essential neurotransmitter for neuronal communication, learning and memory ...
D-Wave demonstrates performance advantage in quantum simulation of exotic magnetism
2021-02-18
BURNABY, BC - (February 18, 2021) -- D-Wave Systems Inc., the leader in quantum computing systems, software, and services, today published a milestone study in collaboration with scientists at Google, demonstrating a computational performance advantage, increasing with both simulation size and problem hardness, to over 3 million times that of corresponding classical methods. Notably, this work was achieved on a practical application with real-world implications, simulating the topological phenomena behind the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physics. This performance advantage, exhibited in a complex quantum simulation of materials, is a meaningful step in the journey toward applications advantage in quantum computing.
The work by scientists at D-Wave ...
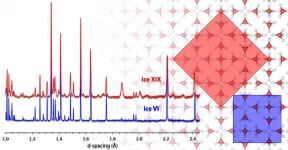
New crystalline ice form
2021-02-18
Ice is a very versatile material. In snowflakes or ice cubes, the oxygen atoms are arranged hexagonally. This ice form is called ice one (ice I). "Strictly speaking, however, these are not actually perfect crystals, but disordered systems in which the water molecules are randomly oriented in different spatial directions," explains Thomas Loerting from the Institute of Physical Chemistry at the University of Innsbruck, Austria. Including ice I, 18 crystalline forms of ice were known so far, which differ in the arrangement of their atoms. The different types of ice, known as polymorphs, form depending on pressure and temperature and have very different properties. For example, their melting points differ by several ...
Gulf war illness not caused by depleted uranium from munitions, study shows
2021-02-18
DALLAS - Feb. 18, 2021 - Inhalation of depleted uranium from exploding munitions did not lead to Gulf War illness (GWI) in veterans deployed in the 1991 Persian Gulf War, a new study co-authored by a leading researcher of the disease at UT Southwestern suggests. The findings, published today in Scientific Reports, help eliminate a long-suspected cause of GWI that has attracted international concern for three decades.
Using high-precision multicollector mass spectrometry for the first time in such a study, END ...
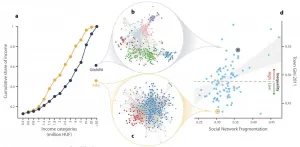
(Re)Shaping cities to combat inequality
2021-02-18
[Vienna, Feb 18, 2021] Communities worldwide are trying to address inequality. One promising approach could be to look at the design of a city, according to research with real-world data in the journal Nature Communications.
An international team of scientists, including members of the Complexity Science Hub Vienna (CSH), show that urban planning directly influences the formation of social networks in a city and subsequently the socio-economic equality or inequality of its citizens.
"We know how important social networks are for our social and economic outcomes," explains CSH researcher Johannes Wachs, one of the authors of the paper. Social relations provide individuals with essential access to resources, information, economic opportunities and other forms ...
Irregular sleep schedules connected to bad moods and depression, study shows
2021-02-18
An irregular sleep schedule can increase a person's risk of depression over the long term as much as getting fewer hours of sleep overall, or staying up late most nights, a new study suggests.
Even when it comes to just their mood the next day, people whose waking time varies from day to day may find themselves in as much of a foul mood as those who stayed up extra late the night before, or got up extra early that morning, the study shows.
The study, conducted by a team from Michigan Medicine, the University of Michigan's academic medical center, uses data from direct measurements of the sleep and mood of more than 2,100 early-career ...
Two distinct pathways leading to the development of septic shock pave the way for personalized medicine in sepsis
2021-02-18
Researchers have published new insights into the causes of mortality in sepsis
Loss of endothelial function is induced through two different pathophysiological processes and is a major driver of septic shock, a life-threatening drop in blood pressure
The first pathway originates in the loss of the endothelial barrier triggering an increased production of the repair hormone bioactive Adrenomedullin (bio-ADM), which also has the undesired side effect of vasodilation
The second threat acting on the endothelial function is the release of the protease DPP3 into the bloodstream which degrades angiotensin II, a process resulting in decreased vascular tone and cardiac output
The different ...
First COVID-19 lockdown cost UK hospitality and high street £45 billion in turnover, researchers estimate
2021-02-18
The UK's first national lockdown from March 2020 and its immediate aftermath saw a massive shift in consumer habits that was initially mandated but then lingered as shops and restaurants opened but risks from the virus remained.
A new study from the universities of Cambridge and Newcastle used data from the ONS to compare retail, hospitality and online sales in the UK between March and August 2020 with average figures for the same months for the years 2010-2019.
Researchers took an approach normally used to estimate cumulative excess deaths to try and measure the impact of the COVID-19 shock on sales of UK retailers and restaurants.
They say their economic models suggest that shops predominantly selling food, such as supermarkets, saw ...
New recommendations aim to eliminate racial bias in myeloma trials
2021-02-18
Researchers from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) are releasing recommendations designed to address the under-representation of African Americans in clinical trials for multiple myeloma (MM), a blood cancer that is twice as deadly in this demographic as in whites.
The initiative, publishing today in the AACR journal Blood Cancer Discovery, is a "road map" for designing myeloma clinical trials to eliminate racial bias by including more African American patients, as well as gathering "real-world" data from health records about the effects of drugs in African American patients. Through this joint workshop initiated by ...
Setting hospital prices would save more than increasing competition or price transparency
2021-02-18
Among strategies to curb hospital prices among the commercially insured population in the U.S., direct price regulations such as setting rates are likely to achieve greater savings than other approaches like increasing competition or improving price transparency, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
But price regulations face the greatest political obstacles and historically have been strongly opposed by medical providers, according to the report.
Setting prices for all commercial health care payers could reduce hospital spending by $61.9 billion to $236.6 billion annually if the rates were set as high as 150% to as low as 100% of the amounts paid by the federal Medicare program, ...