Hospital hygiene: A closer look reveals realistic frequency of infection
2021-02-18
(Press-News.org) The incidence of surgical site infections after an operation is an important quality indicator for hospitals. An overview from six European countries published in 2017 documented increased costs and, in some cases, significantly poorer surgical outcomes due to SSIs. The European Center for Disease Control (ECDC) and authorities in the U.S. have therefore defined criteria for recording and documenting the rate of surgical site infections per procedure. Swissnoso has issued binding guidelines for Switzerland based on these criteria. The study investigated to what extent surgical site infection rates correlate with the audit results in Swiss hospitals.
Seek and you shall find: low SSI rates with low audit score
The study was able to establish a clear correlation between a low surgical site infection rate and the results from on-site surveillance quality audits (audit score). The better a hospital scored on the 50-point audit, the more infection cases had been detected or reported. This was true for all three surgeries studied (knee and hip implants as well as colorectal surgeries). According to the study's lead author Andrew Atkinson: "The study shows that the quality of the respective surveillance systems must be systematically considered when interpreting surgical site infections - and this independently of the type of surgery and infection rate."
What exactly was measured?
The study analyzed 81 957 hip and knee surgeries from 125 hospitals and 33 315 colorectal surgeries from 110 hospitals. At least two external audits per hospital were carried out to assess surveillance quality. The study was based on the Swissnoso guidelines. The detailed audit results were ranked in an overall score between 1 and 50. The audits were carried out by three specifically trained investigators.
Results in detail
The following values refer to the median of the results. The SSI rate for knee and hip implants was 1.0% with an audit score of 37. As expected the infection rate for colorectal surgery was much higher at 12.7% with a slightly higher audit score of 38. It appeared that higher infection rates correlated with higher audit scores. A discernible range of scores among hospital types could be observed, with private hospitals forming a cluster in the lower range of audit scores and infection rates.
How can a possible systematic error be corrected?
The research team makes a specific proposal for future evaluations and national comparisons of surgical site infection rates. A computational correction (normalization) and inclusion of the audit score are proposed for discussion. Prof. Jonas Marschall summarizes: "For the first time, this study provides us with a basis for rendering the number of infections more comparable and better understood throughout Switzerland. Now we have to work hard to establish regular comparisons among Swiss hospitals even more meaningful and the incentive to be at the forefront even greater."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-18
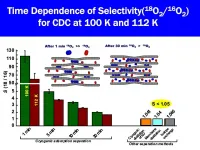
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) plays a major role in the early detection of various types of cancer. A research group led by Specially Appointed Professor Katsumi Kaneko of the Research Initiative for Supra-Materials (RISM), Shinshu University have discovered a method to separate oxygen-18 from oxygen-16, an essential isotope for PET diagnosis, at high speed and high efficiency. The results of this research were recently published online in the journal Nature Communications.
The novel method for the rapid and efficient separation of O-18 from O2-16, which ...
2021-02-18
Covid-19 has not made people any less concerned about climate change - despite the pandemic disrupting and dominating many aspects of their lives, a study suggests.
Over a period of 14 months - including the first three months of the Covid-19 lockdown - neither concern about climate change nor belief in the severity of the problem declined in the UK, the research found.
Researchers compared responses to the pandemic with the financial crisis of 2008 to better understand how worries and priorities can change in a crisis.
In contrast to the economic collapse of 2008, which led to reduced concern with environmental issues, the pandemic has not decreased people's belief in the severity of climate change.
The findings shed light on how a concept called the finite pool ...
2021-02-18
A team of researchers has devised a method using smartphones in order to measure food consumption--an approach that also offers new ways to predict physical well-being.
"We've harnessed the expanding presence of mobile and smartphones around the globe to measure food consumption over time with precision and with the potential to capture seasonal shifts in diet and food consumption patterns," explains Andrew Reid Bell, an assistant professor in New York University's Department of Environmental Studies and an author of the paper, which appears in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Food consumption ...
2021-02-18
Menopause is associated with several physiological changes, including loss of skeletal muscle mass. However, the mechanisms underlying muscle wasting are not clear. A new study conducted in collaboration between the universities of Minnesota (USA) and Jyväskylä (Finland) reveals that estrogen deficiency alters the microRNA signalling in skeletal muscle, which may activate signalling cascades leading to loss of muscle mass.
Menopause leads to an estrogen deficiency that is associated with decreases in skeletal muscle mass and strength. This is likely due to changes in both muscle function and the size of muscle cells commonly referred to as fibers.
"The mechanistic role of estrogen in the loss of muscle mass had not been established. In our study, we focused on signaling cascades ...
2021-02-18
PHILADELPHIA--A significant number of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients in a Penn Medicine-initiated clinical trial continue to be in remission five years after receiving the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy Kymriah™, researchers in Penn's Abramson Cancer Center reported today in the END ...
2021-02-18
Tsukuba, Japan - Scientists at the University of Tsukuba demonstrated the possibility of electrons moving as if they were massless when certain materials called "topological insulators" are irradiated with laser beams. This work may lead to a new class of highly efficient electronic devices and photonic crystals.
Conventional electronic devices rely primarily on silicon crystals. From the point of view of electrons that make up the electrical signals coursing through these materials, the systems are so big as to be practically endless. This causes most of the electronic structures ...
2021-02-18
A unique brain protein measured in the blood could be used to diagnose Alzheimer's disease decades before symptoms develop, according to new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research.
Published in Nature journal Translational Psychiatry, the study is the first to find that people with elevated glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the blood also have increased amyloid beta in the brain, a known indicator of Alzheimer's disease.
GFAP is a protein normally found in the brain, but it is released into the blood when the brain is damaged by early Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer's disease affects more than 340,000 Australians and more than 35 million people in the world. Current ...
2021-02-18
Scientists at EMBL Heidelberg and at the Zentrum für Infektiologie at Heidelberg University Hospital have succeeded for the first time in imaging HIV during transport into the nucleus of an infected cell. The electron tomographic images show the protein envelope of the virus passing through one of the nuclear pores - the openings in the membrane around the nucleus that allow molecules in and out. The scientists found that the virus passes through the nuclear pore intact, only breaking apart inside the nucleus, where it releases its genetic information. This clarifies an important mechanism by which the virus's genetic material is integrated into the genome of the infected cell.
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) - which was ...
2021-02-18
A highly porous metal organic framework, assembled from molecular building blocks designed to lock together in a specific orientation, has been developed by researchers at KAUST.
Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are crystalline materials made from metal ions connected by organic linkers. Their internal structure is like a repeating array of tiny identical cages, which are ideal for hosting various molecules. MOFs have found potential uses from gas sensing to molecular separations to storage, depending on the dimensions and structure of their pores.
One family of MOFs has been inspired by inorganic porous materials called zeolites. Zeolites are a special class of porous material with ...
2021-02-18
One of the most intriguing features in all living beings is the "biological clock", an internal time-keeping mechanism that governs our behavioral pattern (such as the sleep-wake cycle). In fact, the biological clock dictates the developmental timing of various processes, such as when flowers bloom and insects reproduce. Biologists refer to these activities collectively as "circadian rhythms," owing to the rhythmic pattern in which they occur.
Since their discovery, circadian rhythms have been studied extensively, and today we know a great deal about how they work. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Hospital hygiene: A closer look reveals realistic frequency of infection