Including racial/ethnic minorities, females, older adults in vaccine trials
2021-02-19
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did:
Using data from completed interventional vaccine trials from 2011 to 2020, researchers examined whether racial/ethnic minority groups, females and older adults were underrepresented in U.S.-based vaccine clinical trials.
Authors:
Steven A. Pergam, M.D., M.P.H., of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, and Julie K. Silver, M.D., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study:
Visit our For The Media website at this link
https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37640)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory:
The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article
This link will be live at the embargo time
http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.37640?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=021921
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-19
Women of minority races and ethnicities and with less education and income have had relatively lower access to 3D mammography, a technology that can improve breast cancer detection and decrease false alarms, according to research published today.
"This study was about whether adoption of this technology is equitable. We're showing that it has not been, even though it has been FDA-approved for a decade now," said END ...
2021-02-19
Recreational hunting -- especially hunting of charismatic species for their trophies --raises ethical and moral concerns. Yet recreational hunting is frequently suggested as a way to conserve nature and support local people's livelihoods.
In a new article published in the journal One Earth, scientists from the University of Helsinki in Finland and Flinders University in Australia have reviewed more than 1,000 studies on recreational hunting -- the first such attempt to summarize the scientific literature examining the biodiversity and social effects of recreational hunting globally.
Co-lead author University of Helsinki Associate Professor Enrico ...
2021-02-19
Creating "super soldiers" of specific white blood cells to boost an anti-tumour response has been shown in a series of elegant experiments by Princess Margaret researchers.
Research led by Ph.D. candidate Helen Loo Yau, Post-doctoral fellow Dr. Emma Bell and Senior Scientist Dr. Daniel D. De Carvalho describes a DNA modifying epigenetic therapy that can transform immune killer T-cells into "super soldiers" by boosting their ability to kill cancer cells.
Their findings could potentially enhance immunotherapy, a new paradigm in cancer treatment currently effective for a minority of cancer patients. Some patients respond well to immunotherapy, with their tumours drastically shrinking in size, but others respond only partially or not at all. Clinicians and scientists around ...
2021-02-19
At some point, microvehicles that are small enough to navigate our blood vessels will enable physicians to take biopsies, insert stents and deliver drugs with precision to sites that are difficult to reach, all from inside the body. Scientists around the world are currently researching and developing suitable microvehicles. In most cases, they are powered and controlled by acoustic and magnetic fields or using light. However, until now, propelling microvehicles against a fluid flow had proved to be a major challenge. This would be necessary for the micromachines to be able to navigate in blood vessels against the direction of blood flow. Researchers at ETH Zurich have now developed microvehicles ...
2021-02-19
The latest observations from Insight-HXMT were published online in Nature Astronomy on Feb. 18. Insight-HXMT has discovered the very first X-ray burst associated with a fast radio burst (FRB) and has identified that it originated from soft-gamma repeater (SGR) J1935+2154, which is a magnetar in our Milky Way.
Insight-HXMT is the first to identify the double-spike structure of this X-ray burst as the high energy counterpart of FRB 200428. This discovery, together with results from other telescopes, proves that FRBs can come from magnetar bursts, thus resolving ...
2021-02-19
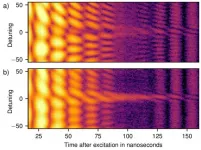
From atomic clocks to secure communication to quantum computers: these developments are based on the increasingly better control of the quantum behaviour of electrons in atomic shells with the help of laser light. Now, for the first time, physicists at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics in Heidelberg have succeeded in precisely controlling quantum jumps in atomic nuclei using X-ray light. Compared with electron systems, nuclear quantum jumps are extreme - with energies up to millions of times higher and incredibly short zeptosecond processes. A zeptosecond is one trillionth of a billionth of a second. The rewards include profound insight into the quantum world, ultra-precise nuclear clocks, ...
2021-02-19
Before life emerged on Earth, many physicochemical processes on our planet were highly chaotic. A plethora of small compounds, and polymers of varying lengths, made up of subunits (such as the bases found in DNA and RNA), were present in every conceivable combination. Before life-like chemical processes could emerge, the level of chaos in these systems had to be reduced. In a new study, LMU physicists led by Dieter Braun show that basic features of simple polymers, together with certain aspects of the prebiotic environment, can give rise to selection processes that reduce disorder.
In previous publications, Braun's research group explored how spatial order could have developed in narrow, water-filled chambers ...
2021-02-19
Epileptic activity originating from one or more diseased brain regions in the temporal lobe is difficult to contain. Many patients with so-called temporal lobe epilepsy often do not respond to treatment with anti-epileptic drugs, and the affected brain areas must therefore be surgically removed. Unfortunately, this procedure only gives seizure freedom to about one third of patients, so the development of alternative therapeutic approaches is of great importance. Scientists led by neurobiologist Prof. Dr. Carola Haas, head of the research group at the Department of Neurosurgery at Medical Center - University of ...
2021-02-19
The major direct and indirect effects of covid-19 have forced the authorities to implement policies that strike a balance between minimizing the immediate health impact of the pandemic and containing the long-term damage to society arising from protective policies.
One parameter that is crucial for calculating how restrictive policies might be warranted is the mortality impact of covid-19, which has led to large-scale international collaborations in order to collect data that records deaths attributable to the pandemic.
Despite the limitations, each of these research avenues and associated health measures (infection rate, deaths and excess deaths) is important in order to inform the public and policymakers about the mortality impact of covid-19.
"Our results confirm that the mortality ...
2021-02-19
When can tuberculosis therapy be stopped without risk of relapse? Doctors are faced with this question time and again, because the lack of detection of the tuberculosis pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis is no guarantee for a permanent cure of the lung infection. Patients who respond to the standard therapy may be out of treatment after six months. But for resistant cases, more than 18 months of treatment duration is currently advised. "This is a very long time for those affected, who often have to take more than four antibiotics every day and suffer from side effects", explains Prof. Dr. Christoph Lange, Clinical Director at the Research Center Borstel and director of the study, conducted at the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) in cooperation with the German Center for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Including racial/ethnic minorities, females, older adults in vaccine trials