Study reveals how a longevity gene protects brain stem cells from stress
2021-02-19
(Press-News.org) A gene linked to unusually long lifespans in humans protects brain stem cells from the harmful effects of stress, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
Studies of humans who live longer than 100 years have shown that many share an unusual version of a gene called Forkhead box protein O3 (FOXO3). That discovery led Dr. Jihye Paik, associate professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, and her colleagues to investigate how this gene contributes to brain health during aging.
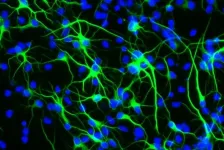
In 2018, Dr. Paik and her team showed that mice who lack the FOXO3 gene in their brain are unable to cope with stressful conditions in the brain, which leads to the progressive death of brain cells. Their new study, published Jan. 28 in Nature Communications, reveals that FOXO3 preserves the brain's ability to regenerate by preventing stem cells from dividing until the environment will support the new cells' survival.
"Stem cells produce new brain cells, which are essential for learning and memory throughout our adult lives," said Dr. Paik, who is also a member of the Sandra and Edward Meyer Cancer Center at Weill Cornell Medicine. "If stem cells divide without control, they get depleted. The FOXO3 gene appears to do its job by stopping the stem cells from dividing until after the stress has passed."
Many challenges like inflammation, radiation or a lack of adequate nutrients can stress the brain. But Dr. Paik and her colleagues looked specifically what happens when brain stem cells are exposed to oxidative stress, which occurs when harmful types of oxygen build up in the body.
"We learned that the FOXO3 protein is directly modified by oxidative stress," she said. This modification sends the protein into the nucleus of the stem cell where it turns on stress response genes.
The resulting stress response leads to the depletion of a nutrient called s-adenosylmethionine (SAM). This nutrient is needed to help a protein called lamin form a protective envelope around the DNA in the nucleus of the stem cell.
"Without SAM, lamin can't form this strong barrier and DNA starts leaking out," she said.
The cell mistakes this DNA for a virus infection, which triggers an immune response called the type-I interferon response. This causes the stem cell to go dormant and stop producing new neurons.
"This response is actually very good for the stem cells because the outside environment is not ideal for newly born neurons," Dr. Paik explained. "If new cells were made in such stressful conditions they would be killed. It's better for stem cells to remain dormant and wait until the stress is gone to produce neurons."
The study may help explain why certain versions of the FOXO3 are linked to extraordinarily long and healthy lives--they may help people keep a good reserve of brain stem cells. It may also help explain why regular exercise, which boosts FOXO3 helps preserve mental sharpness. But Dr. Paik cautioned it is too early to know whether this new information could be used to create new therapies for brain diseases.
"It could be a double-edged sword," Dr. Paik explained. "Over activating FOXO3 could be very harmful. We don't want to keep this on all the time."
To better understand the processes involved, she and her colleagues will continue to study how FOXO3 is regulated and whether briefly turning it on or off would be beneficial for health.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-19
How much personal information can our phone apps gather through location tracking? To answer this question, two researchers - Mirco Musolesi (University of Bologna, Italy) and Benjamin Baron (University College London, UK) - carried out a field study using an app specifically developed for this research. Through the app employed in the study - published in Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies - researchers were able to identify which kind of personal information the app extracted and its privacy sensitivity according to users.
"Users are largely unaware of the privacy implications ...
2021-02-19
The University of Leeds has coordinated a study with 170 experts from 35 countries, including E.T.S. Agronomic Engineering lecturer Luis Perez Urrestarazu. The study conclusions have just been published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
The researchers highlighted opportunities to improve the way green spaces are monitored and maintained and helping people to interact with and appreciate the natural world around them. Similarly, as autonomous vehicles become more widely used in cities, pollution and traffic congestion are set to fall.
But they also warn that advances in robotics and automation could be harmful to the environment. They may, for example generate new sources of waste and pollution, with potentially substantial negative implications for urban nature. Cities may ...
2021-02-19
Social identity is a factor linked to wellbeing and community participation. Various studies have demonstrated the link existing between ethnic identity and empowerment and that the interaction between both of them leads to a rise in the indices of wellbeing and community participation. However, the nature of these relationships may be determined by the fact that the individual perceives his or her own group as a minority one and/or one that is subject to discrimination. In fact, these relations emerge mostly in groups that find themselves in a minority situation and/or one of discrimination, but not in groups that are more hegemonic or in the majority.
To further ...
2021-02-19
Parent education programs and interventions that begin shortly after the birth of a child have shown to significantly impact parenting behaviors that support social and academic engagement for children growing up in poverty, according to a study led by pediatricians and psychologists across the country, including NYU Grossman School of Medicine, NYU Steinhardt, and the University of Pittsburgh.
The study, published today in the journal Pediatrics, examines the Smart Beginnings Project, a first-of-its-kind comprehensive approach to the promotion of school readiness in low-income families. This model addresses one of the most important causes of inequity - that many children from ...
2021-02-19
Researchers at the Institut de Neurociències of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (INc-UAB) obtained a highly accurate recreation of human glioblastoma's features using a novel 3D microscopy analysis. The study, published in the journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications, provides new information to help with the diagnose, by finding therapeutical targets and designing immunotherapeutical strategies.
This new analysis of 3D images and quantitative data "will help to appreciate from within how the tumor is built in its full dimensionality, and to identify where different cell types are located", explains George Paul Cribaro, first author of the study. "It provides more complete information than the usual 2D analyses performed for ...
2021-02-19
Prion diseases are a group of rapidly progressive, fatal and infectious neurodegenerative disorders affecting both humans and animals: Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) or 'mad cow' disease is one of the most famous since in 1996 scientists found that the agent responsible for the disease in cows, is the same agent responsible for the so-called variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD), a disease affecting humans.
A new study carried out by SISSA - Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati in collaboration with other institutions including Genos Glycoscience ...
2021-02-19
DURHAM, N.H.-- A new report from the University of New Hampshire's Crimes against Children Research Center (CCRC), using data collected by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, showed a marked increase in the share of child maltreatment cases resulting in fatalities as well as a decline in cases of physical abuse and neglect in 2019.
The report, which highlights 2019 statistics from the National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System (NCANDS), showed that fatalities rose 4%. The statistics gathered from child protection agencies in each state indicated that the uptick in child maltreatment fatalities was broadly distributed, with 25 states reporting an increase of 10% or more. This increase in fatalities continues an already upward trend ...
2021-02-19
The first global-scale assessment of the role ecosystems play in providing sanitation finds that nature provides at least 18% of sanitation services in 48 cities worldwide, according to researchers in the United Kingdom and India. The study, published February 19 in the journal One Earth, estimates that more than 2 million cubic meters of the cities' human waste is processed each year without engineered infrastructure. This includes pit latrine waste that gradually filters through the soil--a natural process that cleans it before it reaches groundwater.
"Nature can, and does, take the role of sanitation infrastructure," said Alison Parker, a Senior Lecturer in International Water and Sanitation at Cranfield University in the United ...
2021-02-19
SEATTLE -- February 19, 2021 -- A team of scientific experts from across the U.S. and Puerto Rico are advocating for increased diversity in vaccine trials after publishing a new report that highlights a decade's worth of disparities. The new study, published in JAMA Network Open, found that among U.S.-based vaccine clinical trials, people who are Black/African American, American Indian/Alaska Native, Hispanic/Latino and age 65 and older were the most underrepresented groups. Conversely, adult women were overrepresented.
The research team examined 230 U.S.-based vaccine trials of all ...
2021-02-19
What The Study Did: Persistent symptoms among adults with COVID-19 up to nine months after illness onset were analyzed in this study.
Authors: Helen Y. Chu, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0830)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals how a longevity gene protects brain stem cells from stress