Periodontal disease increases risk of major cardiovascular events
2021-02-22
(Press-News.org) People with periodontitis are at higher risk of experiencing major cardiovascular events, according to new research from Forsyth Institute and Harvard University scientists and colleagues.
In a longitudinal study published recently in the Journal of Periodontology, Dr. Thomas
Van Dyke, Senior Member of Staff at Forsyth, Dr. Ahmed Tawakol of Massachusetts General Hospital, and their collaborators showed that inflammation associated with active gum disease was predictive of arterial inflammation, which can cause heart attacks, strokes, and other dangerous manifestations of cardiovascular disease.
For the study, researchers performed positron emission tomography and computer tomography (PET and CT) scans on 304 individuals to view and quantify inflammation in the arteries and gums of each patient. In follow-up studies approximately four years later, 13 of those individuals developed major adverse cardiovascular events. Presence of periodontal inflammation was shown to be predictive of cardiovascular events, even after researchers controlled for all other risk factors, such as smoking, high blood pressure, obesity, and diabetes.
Importantly, researchers found that bone loss from prior periodontal disease was not associated with cardiovascular events. Patients that did not have actively inflamed gums had a lower risk of cardiovascular disease--even if those individuals had a prior history of periodontal disease as evidenced by periodontal bone loss in their CT scans.
"This is very definitely related to people who have currently active inflammatory disease," said Van Dyke, who is also Vice President of Clinical and Translational Research at Forsyth.
Researchers hypothesize that local periodontal inflammation activates and mobilizes cells signaling through bone marrow, which triggers the inflammation of arteries, leading to adverse cardiac events.
While the study sample size is relatively small, Van Dyke said the observation is significant and should be studied in a much larger population. And for people with active gum disease, seeking treatment could potentially prevent a dangerous a cardiac event.
"If you're in the age zone for cardiovascular disease or have known cardiovascular disease, ignoring your periodontal disease can actually be dangerous and may increase your risk for a heart attack," Van Dyke said.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-22
Despite deaths and hospitalisations linked to many new psychoactive substances (NPS), an international wastewater study led by the University of South Australia shows just how prevalent 'party pills' and 'bath salts' are in different parts of the world.
In a new paper published in Water Research, the world's most comprehensive wastewater analysis of NPS shows the pattern of designer drug use in the 2019/2020 New Year in 14 sites across Australia, New Zealand, China, The Netherlands, Spain, Italy, Norway and the United States.
UniSA analytical chemist Dr Richard Bade says samples were collected over the New Year in each country and ...
2021-02-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University and U.S. Department of Agriculture researchers have significantly expanded the understanding of the hop genome, a development with important implications for the brewing industry and scientists who study the potential medical benefits of hops.
"This research has the unique ability to impact several different fields," said David Hendrix, an associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics and the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at Oregon State. "If you're talking to beer drinkers, they will be excited about the brewing side. If you are talking to the medical field, they are going to be excited about the pharmaceutical potential."
The findings are outlined in ...
2021-02-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Scientists at Oregon State University and the U.S. Forest Service have demonstrated that DNA extracted from water samples from rivers across Oregon and Northern California can be used to estimate genetic diversity of Pacific salmon and trout.
The findings, just published in the journal Molecular Ecology, have important implications for conservation and management of these species, which are threatened by human activities, including those exacerbating climate change.
"There has been a dearth of this kind of data across the Northwest," said Kevin Weitemier, a postdoctoral fellow at Oregon State and lead author of the paper. "This allows us to get a quick snapshot of multiple populations and species all at once."
In addition to demonstrating ...
2021-02-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Desert bighorn sheep in the Mojave National Preserve in California and surrounding areas appear to be more resilient than previously thought to a respiratory disease that killed dozens of them and sickened many more in 2013, a new study has found.
Clint Epps, a wildlife biologist at Oregon State University, and several co-authors, found that exposure to one of the bacteria associated with the disease is more widespread among bighorn sheep populations in the Mojave, and that its presence dates further back, than scientists thought. But they also found that the overall number of infected bighorn has declined since 2013 in the populations surveyed.
Epps and his colleagues, including Nicholas Shirkey, an environmental scientist with ...
2021-02-22
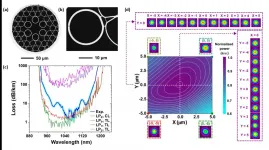
Recent spotlights on IC-HCPCFs are due to the recently demonstrated outstanding ultralow-loss performances and their application capabilities. Nevertheless, while their attenuation achieves impressive figures, the challenge of accomplishing a low loss, single-mode (SM), and polarization-maintaining HCPCF perseveres.
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Applications, a team of scientists, led by Professor Fetah Benabid from the University of Limoges, France, and in collaboration of the University of Modena, Italy and the company GLOphotonics, proposed and ...
2021-02-22
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Dogs synchronize their behavior with the children in their family, but not as much as they do with adults, a new study from Oregon State University researchers found.
The findings are important because there is a growing body of evidence that dogs can help children in many ways, including with social development, increasing physical activity, managing anxiety or as a source of attachment in the face of changing family structures, the researchers said. Yet, very little research has focused on how dogs perceive and socially engage with children.
"The great news is that ...
2021-02-22
In the course of a new and groundbreaking study, led by Dr, Natalia Freund and the doctoral candidate Avia Waston at the Sackler Medical Faculty, the research group succeeded in isolating monoclonal antibodies, which hindered the growth of tuberculosis germs in laboratory mice. The antibodies were isolated from a patient who had succumbed to active tuberculosis disease but had since recovered. This is, in fact, the first time in history that researchers have managed to develop a "biological antibiotic" and demonstrate that human monoclonal antibodies can act as a substitute for the traditional chemical antibiotics and protect mice from pathogenic bacterial challenge. The study was carried out in a collaboration with two additional laboratories from the US ...
2021-02-22
At the heart of most electronics today are rechargeable lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). But their energy storage capacities are not enough for large-scale energy storage systems (ESSs). Lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) could be useful in such a scenario due to their higher theoretical energy storage capacity. They could even replace LIBs in other applications like drones, given their light weight and lower cost.
But the same mechanism that is giving them all this power is keeping them becoming a widespread practical reality. Unlike LIBs, the reaction pathway in LSBs leads to an accumulation of solid lithium sulfide (Li2S6) and liquid lithium polysulfide (LiPS), causing a loss of active material from the sulfur cathode (positively charged electrode) and corrosion of the lithium ...
2021-02-22
In civil engineering, flexural beams are used to control the effect of vibrations that can cause cracks to appear in surfaces (concrete slabs) and beams. This is particularly important in buildings that require high tensile strength and where the use of machinery can cause a lot of vibrations that can disturb structural integrity. One metric to determine the reliability of beams is the deflection value, which should be appropriately low relative to the structure the beams are used in. Engineering codes such as ACI codes include provisions for such values and there are a number of methods to calculate them. Deflection is altered practically by reinforcing the construction materials with concrete or steel.
In this review, engineers ...
2021-02-22
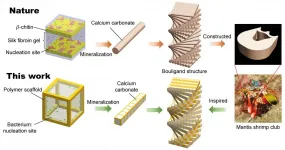
Biological systems can harness their living cells for growth and regeneration, but engineering systems cannot. Until now.
Qiming Wang and researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering are harnessing living bacteria to create engineering materials that are strong, tolerant, and resilient. The research is published in Advanced Materials.
"The materials we are making are living and self-growing," said Wang, the Stephen Schrank Early Career Chair in Civil and Environmental Engineering and assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering in the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Periodontal disease increases risk of major cardiovascular events