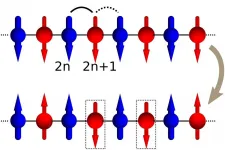
Salmon scales reveal substantial decline in wild salmon population & diversity
Researchers from Simon Fraser University analyzed 100-year-old salmon scales to assess the health of wild salmon populations
2021-02-22
(Press-News.org) The diversity and numbers of wild salmon in Northern B.C. have declined approximately 70 per cent over the past century, according to a new Simon Fraser University study.
Researchers drawing on 100-year-old salmon scales report that recent numbers of wild adult sockeye salmon returning to the Skeena River are 70 per cent lower than 100 years ago. Wild salmon diversity in the Skeena watershed has similarly declined by 70 per cent over the last century.
The research undertaken by Simon Fraser University (SFU) and Fisheries and Oceans Canada was published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology.
The research team applied modern genetic tools to salmon scales collected from commercial fisheries during 1913-1947 to reconstruct historical abundance and diversity of populations for comparison with recent information.
The analysis revealed that Canada's second largest salmon watershed - the Skeena River - once hosted a diverse sockeye salmon portfolio composed of many populations that fluctuated from year to year, yet overall remained relatively stable. However, the Skeena sockeye portfolio has largely eroded over the last century, such that it now is dominated by a single population that primarily is supported by artificial production from spawning channels.
"Our study provides a rare example of the extent of erosion of within-species biodiversity over the last century of human influence," says Michael Price, an SFU PhD candidate and lead author. "That loss in abundance and diversity from wild populations has weakened the adaptive potential for salmon to survive and thrive in an increasingly variable environment influenced by climate change."
Life-cycle diversity also has shifted: populations are migrating from freshwater at an earlier age, and spending more time in the ocean.
"Rebuilding a diversity of abundant wild populations - that is, maintaining functioning portfolios - should help ensure that important salmon watersheds like the Skeena are robust to global change," says John Reynolds, co-author, SFU professor, and Tom Buell BC Leadership Chair in Aquatic Conservation.
This research can help inform status assessments and rebuilding plan discussions for threatened salmon populations by expanding our understanding of historical diversity and production potential.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-22
Boston, Mass. - Even with more than 1.5 million Americans receiving a COVID vaccine each day, officials estimate it will take many more months before enough people are protected from the deadly virus. Until then, and potentially beyond, experts agree that opening up schools, restaurants and other public places as safely as possible will rely on widespread testing for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
As of June 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted emergency use authorization for more than 85 different viral DNA test kits -- or assays -- each with widely varying degrees of sensitivity and unknown rates of accuracy. However, with no existing gold standard test for the novel coronavirus, there's little data on which ...
2021-02-22
A paper recently published in the scientific journal Stem Cells and Development shares an important advancement in conservation -- one that may make the difference between survival and extinction for wildlife species that have been reduced to very small population sizes. Using fibroblast cells that have been preserved in San Diego Zoo Global's Frozen Zoo®, scientists have been able to generate induced pluripotent stem cells of northern and southern white rhinoceroses. This important breakthrough is the first step in a complex process for generating gametes from deceased and non-reproductive individuals of these two subspecies.
"For the northern white rhino, which is functionally extinct, the only hope for survival may be in the ...
2021-02-22
ITHACA, N.Y. - Cornell University scientists have identified a new contender when it comes to quantum materials for computing and low-temperature electronics.
Using nitride-based materials, the researchers created a material structure that simultaneously exhibits superconductivity - in which electrical resistance vanishes completely - and the quantum Hall effect, which produces resistance with extreme precision when a magnetic field is applied.
"This is a beautiful marriage of the two things we know, at the microscale, that give electrons the most startling ...
2021-02-22
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., Feb. 22, 2021--A team of quantum theorists seeking to cure a basic problem with quantum annealing computers--they have to run at a relatively slow pace to operate properly--found something intriguing instead. While probing how quantum annealers perform when operated faster than desired, the team unexpectedly discovered a new effect that may account for the imbalanced distribution of matter and antimatter in the universe and a novel approach to separating isotopes.
"Although our discovery did not the cure the annealing time restriction, it brought a class of new physics problems that can now be studied with quantum annealers without requiring they be too slow," said Nikolai Sinitsyn, a theoretical physicist at Los Alamos National ...
2021-02-22
HOUSTON - (Feb. 22, 2021) - Governments with strong female representation are more likely to deliver on campaign promises, according to new research from Rice University.
"The Effects of Women's Descriptive Representation on Government Behavior" by author Jonathan Homola, an assistant professor of political science at Rice, examines campaign promises and subsequent policymaking by parties in power in 10 European countries, the United States and Canada along with data on women in party leadership and elected offices.
The study also showed that promises are even more likely to be kept when women in government assume leadership roles.
Homola said the research demonstrates the importance of women playing part in the ...
2021-02-22
Researchers at the Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) found that transitioning land enrolled in the Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) to bioenergy agriculture can be advantageous for American landowners, the government, and the environment.
Land enrolled in the CRP cannot currently be used for bioenergy crop production, wherein high-yielding plants (like miscanthus and switchgrass) are harvested for conversion into marketable bioproducts that displace fossil fuel- and coal-based energy. Established by the U.S. Department of Agriculture in 1985, the CRP incentivizes landowners to retire environmentally ...
2021-02-22
A new study by an international team of researchers found that adults with Down syndrome are more likely to die from COVID-19 than the general population, supporting the need to prioritize vaccinating people with the genetic disorder.
Investigators found that adults with Down syndrome were roughly three times more likely to die from COVID-19 than the general population. This increased risk was especially apparent in from fifth decade of life: A 40-year-old with Down syndrome had a similar risk of dying from COVID-19 as someone 30 years older in the general population.
The study was published this week in The Lancet's ...
2021-02-22
Strokes are a leading cause of poor quality of life or even death in Japan and the world over. Since its characterization, several researchers have been working tooth and nail to identify drug-accessible and effective therapeutic targets for this debilitating condition. One such region of interest for drug targets is the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
The BBB is a structure located around the brain, which prevents the entry of unnecessary circulating cells and biomolecules into the brain. The blood vessels in the BBB are coated with a distinct and protective layer of sugar, called the endothelial glycocalyx, which prevents their entry. However, in the event of a stroke, which results in the blockage or severance of blood vessels in the brain, studies have shown that this ...
2021-02-22
Skoltech researchers have designed a software-based algorithm for synchronizing time across smartphones that can be used in practical tasks requiring simultaneous measurements. This algorithm can essentially help turn several devices into a full-fledged network of sensors. The paper was published in the journal Sensors.
If you want a network of intelligent devices - say, an array of cameras capturing a dynamic scene or another kind of network of sensors - to work properly, one of the fundamental tasks you have to solve is clock synchronization: all devices should have the same timeline, often up to sub-millisecond for the more challenging tasks. Modern smartphones can easily be used as multipurpose ...
2021-02-22
Female physicians have better patient outcomes compared with their male peers, while female patients are less likely to receive guideline-recommended care when treated by a male physician, according to a systematic review from the American College of Cardiology's Cardiovascular Disease in Women section published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
While women make up over 50% of internal medicine residents, only 12.6% of cardiologists are female. A dedicated effort to increase diversity in the cardiovascular field could help to lower implicit bias, often considered an important factor in health care disparities.
In a detailed systematic review, researchers looked at 13 studies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Salmon scales reveal substantial decline in wild salmon population & diversity
Researchers from Simon Fraser University analyzed 100-year-old salmon scales to assess the health of wild salmon populations