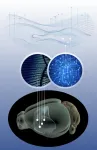
Beta blockers can repair malformed blood vessels in the brain
2021-02-23
(Press-News.org) Peer review/Experimental study/Animals
Propranolol, a drug that is efficacious against infantile haemangiomas ("strawberry naevi", resembling birthmarks), can also be used to treat cerebral cavernous malformations, a condition characterised by misshapen blood vessels in the brain and elsewhere. This has been shown by researchers at Uppsala University in a new study published in the scientific journal Stroke.
"Up to now, there's been no drug treatment for these patients, so our results may become hugely important for them," says Peetra Magnusson of the University's Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology, who headed the study.
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs, also called cavernous angiomas or cavernomas) are vascular lesions on blood vessels in the brain and elsewhere, caused by genetic changes that may be hereditary or arise spontaneously. Today, an operation to remove these lesions is the only possible treatment. However, surgical interventions in the brain are highly risky. Since the vascular malformations, moreover, recur in the hereditary form of the condition, a drug treatment for CCMs is urgently required instead.
The uses of propranolol, a beta blocker, include treating cardiovascular diseases and conditions, such as high blood pressure. But it can also be used to treat a haemangioma ("strawberry naevus"), a common blood-vessel malformation in children. There are some indications that the preparation might work against CCMs as well.
The new study is a collaboration involving researchers at Uppsala University, the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences and, in Italy, IFOM - The FIRC Institute of Molecular Oncology and the Mario Negri Institute of Pharmacological Research. The researchers have been investigating how propranolol affects the emergence of vascular lesions in the form of CCMs.
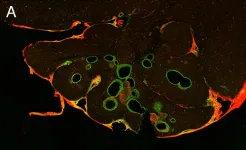
"We examined mice with vascular malformations in the brain - cavernomas or CCMs, as they're called - that corresponded to the hereditary form of the condition in humans. The mice were given propranolol in their drinking water, and we were able to see that the cavernomas were becoming fewer and smaller. The blood vessels functioned better, too, with less leaking and improved contacts between their cells," Magnusson says.
The propranolol dose administered to the animals was equivalent to the dose used to treat diseases in humans. Using an electron microscope, the researchers were able to study in detail how the drug affected the cavernomas.
The results show that propranolol can be used to shrink and stabilise vascular lesions, and may be a potential medicine for treating CCMs.
"What makes the study especially interesting is that right now, in Italy, a clinical study is under way in which CCM patients are to get two years' treatment with propranolol. During this period, they're being monitored by means of magnetic resonance imaging of the blood vessels, to see how the malformations are developing," says Professor Elisabetta Dejana of Uppsala University's Department of Immunology, Genetics and Pathology and IFOM in Italy.
INFORMATION:
Dejana heads the research group at Uppsala University that has been working on the new study, and is also taking part in the ongoing clinical study in Italy.
Oldenburg. J. et al. (2021), Propranolol Reduces the Development of Lesions and Rescues Barrier Function in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations, Stroke.DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029676
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-23
DALLAS, Feb. 23, 2021 — Women face many female-specific risks for heart disease and stroke, including pregnancy, physical and emotional stress, sleep patterns and many physiological factors, according to multiple studies highlighted in this year’s Go Red for Women® special issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association, published online today.
“Although cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in men and women, women are less likely to be diagnosed and receive preventive care and aggressive treatment compared to men,” said Journal of the American Heart Association Editor-in-Chief Barry London, M.D., Ph.D., Ph.D., the Potter Lambert Chair in Internal Medicine, director of the division ...
2021-02-23
Using an innovative computational approach to analyze vast brain cell gene expression datasets, researchers at MIT and Sorbonne Université have found that Huntington's disease may progress to advanced stages more because of a degradation of the cells' health maintenance systems than because of increased damage from the disease pathology itself.
The analysis yielded a trove of specific gene networks governing molecular pathways that disease researchers may now be able to target to better sustain brain cell health amid the devastating neurodegenerative ...
2021-02-23
The use of the polymeric flame retardant PolyFR in "eco-friendly" foam plastic building insulation may be harmful to human health and the environment, according to a new commentary in Environmental Science & Technology. The authors' analysis identifies several points during the lifecycle of foam insulation that may expose workers, communities, and ecosystems to PolyFR and its potentially toxic breakdown products.
With the climate crisis fueling demand for energy-efficient insulation, the production of PolyFR is increasing rapidly. That's because this flame retardant is added to all foam plastic building insulation in North America to comply with flammability codes, replacing the flame retardant ...
2021-02-23
HSE University researchers have become the first in the world to discover genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19. The results of the study were published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology.
T-cell immunity is one of the key mechanisms used by the human body to fight virus infections. The staging ground for cell immunity development is the presentation of virus peptides on the surface of infected cells. This is followed by activation of T lymphocytes, which start to kill the infected cells.
The ability to successfully present virus peptides is largely determined by genetics. In human cells, human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) molecules are responsible for this presentation. The set of six such molecules is unique in every ...
2021-02-23
Young novice drivers who speak into hand-held smartphones while driving are also likely to drive while under the influence of drink or drugs, according to researchers at Lero, the Science Foundation Ireland Research Centre for Software.
The study "Smartphone Use While Driving: An Investigation of Young Novice Driver (YND) Behaviour," also found that speaking on a hand-held phone is strongly correlated with high-risk driving behaviours such as overtaking on the inside of the car ahead, speeding, driving without a valid licence and driving while intoxicated.
Lero researchers, surveyed 700 German Young Novice Drivers ...
2021-02-23
COVID-19 infection in pregnancy is not associated with stillbirth or early neonatal death, according to a new study.
However the research, from over 4000 pregnant women with suspected or confirmed COVID-19, also found women who had a positive test were more likely to have a premature birth.
The research, led by scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, used data from the UK and the USA.
The study team looked at data from 4004 pregnant women who had suspected or confirmed COVID-19. Of these women, ...
2021-02-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - Critics claim environmental regulations hurt productivity and profits, but the reality is more nuanced, according to an analysis of environmental policies in China by a pair of Cornell economists.
The analysis found that, contrary to conventional wisdom, market-based or incentive-based policies may actually benefit regulated firms in the traditional and "green" energy sectors, by spurring innovation and improvements in production processes. Policies that mandate environmental standards and technologies, on the other hand, may broadly harm output and profits.
"The conventional wisdom is not entirely ...
2021-02-22
As electronic devices saturate all corners of public and personal life, engineers are scrambling to find lightweight, mechanically stable, flexible, and easily manufactured materials that can shield humans from excessive electromagnetic radiation as well as prevent electronic devices from interfering with each other.
In a breakthrough report published in Advanced Materials--the top journal in the field-- engineers at the University of California, Riverside describe a flexible film using a quasi-one-dimensional nanomaterial filler that combines excellent electromagnetic shielding with ease of manufacture.
"These novel films are promising for high-frequency communication technologies, which require electromagnetic ...
2021-02-22
A federally approved heart medication shows significant effectiveness in interfering with SARS-CoV-2 entry into the human cell host, according to a new study by a research team from Texas A&M University and The University of Texas Medical Branch (UTMB).
The medication bepridil, which goes by the trade name Vascor, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat angina, a heart condition.
The team's leaders are College of Science professor Wenshe Ray Liu, professor and holder of the Gradipore Chair in the Department of Chemistry at Texas A&M, and Chien-Te Kent Tseng, professor ...
2021-02-22
Climate change impacts are broad and far reaching. A new study by University of Oklahoma researchers from the Institute for Environmental Genomics explores the impacts of climate warming on microbial network complexity and stability, providing critical insights to ecosystem management and for projecting ecological consequences of future climate warming.
"Global climate change is one of the most profound anthropogenic disturbances to our planet," said Jizhong Zhou, IEG's director, a George Lynn Cross Research Professor in the College of Arts and Sciences and an adjunct professor in the Gallogly College of Engineering. "Climate warming can alter soil microbial community diversity, structure and activities, but it remains uncertain whether and how it impacts network complexity and its relationships ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Beta blockers can repair malformed blood vessels in the brain