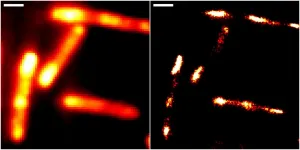
Virus detection method is versatile and accessible
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) A safe, fast and cheap testing method that uses magnetic nanoparticles to detect viruses in both clinical and wastewater samples has been developed by KAUST researchers. The centrifuge-free approach is compatible with magnetic bead-based automated systems that are already used to process hundreds of samples.
"Our silica magnetic nanoparticle-based workflow can be assembled from scratch by any researcher," says lead author Gerardo Ramos-Mandujano. "It rivals commercial viral-RNA extraction kits while lowering the risk of handling potentially infectious samples."
To diagnose COVID-19, clinicians extract SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA from different types of clinical samples, such as nasopharyngeal swabs, and detect the virus using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays.
But the sheer scale of the pandemic could lead to shortages in essential supplies for diagnostic testing, such as commercial reagents and laboratories that satisfy biosafety requirements. Conventional chemical supplies are also expensive, making them less accessible to low-income countries and remote healthcare facilities.
As the virus has been detected in wastewater before community outbreaks, keeping a close eye on its presence in sewage is becoming an important public health measure. Due to the risk of handling infectious samples, this will require an approach that is safe and easy to perform, while using cheap chemicals that are readily available.
To address these challenges, Ramos-Mandujano and Mo Li, Assistant Professor of bioscience, developed an open-source protocol for detecting viral RNA in clinical and environmental samples using magnetic nanoparticles, which isolate nucleic acids without centrifuging or expensive reagents.
"Our method enables any basic biology lab to make homemade silica magnetic nanoparticles from readily available materials," says Li
The technique works in TRIzol, a common reagent that completely inactivates viruses, allowing clinicians to safely handle infectious samples. At just 0.3 US cents per RNA extraction, the protocol is cheaper than commercial diagnostic kits and produces high-quality RNA.
Their method also works efficiently on other human pathogenic viruses, including influenza A and B and respiratory syncytial virus. When the researchers tested the protocol on wastewater samples, they were able to recover 88 percent of the input synthetic SARS-CoV-2 RNA, making it an effective tool for detecting the virus in sewage.
The versatile technique could become a useful tool for widespread community testing of different viral threats and wastewater monitoring during future pandemics. It could also be used by liquid-handling robots to extract RNA from a large number of samples.
"We hope to move the method from research laboratories to real-world testing sites so that it can improve capacity and decrease the cost of COVID-19 testing," says Li.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
Air pollution from fuel combustion is one of the greatest environmental problems, especially in urban environments. In densely populated cities, the presence of nitrogen oxides, very small carbon particles, and carbon monoxide (CO) in the air seriously harms the human health and increases mortality. A collaboration between researchers from the University of Barcelona and from the Boreskov Institute of Catalysis of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Novosibirsk (Russia) opens the way for reducing emissions of automotive pollutants. In a recent study, the scientists ...
2021-02-25
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is key to various fundamental biological processes. It transfers genetic information, translates it into proteins or supports gene regulation. To achieve a more detailed understanding of the precise functions it performs, researchers based at Heidelberg University and at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have devised a new fluorescence imaging method which enables live-cell RNA imaging with unprecedented resolution.
The method is based on a novel molecular marker called Rhodamine-Binding Aptamer for Super-Resolution Imaging Techniques (RhoBAST). This RNA-based fluorescence marker is used in combination with the dye rhodamine. Due to their distinctive properties, marker and dye interact in a very specific way, which makes individual RNA molecules ...
2021-02-25
Similar to the fact that a person would act differently when being alone, materials can also obtain unique qualities when being separated in atom-level, among which is the enhanced catalyzing ability.
Single-atom catalysts have shown enormous catalyzing capability since its first appearance. By preparing 2-dimensional (2D) single-atom monolayer crystals, scientists can expect to get catalysts with high loading density of active sites as well as great stability. However, the question herein is that only the edge atoms in the 2D monolayer have shown this effect while most of the atoms are inside the basal plane, which is critically limiting the efficiency ...
2021-02-25
One of the main culprits of global warming is the vast amount of carbon dioxide pumped out into the atmosphere mostly from burning fossil fuels and the production of steel and cement. In response, scientists have been trying out a process that can sequester waste carbon dioxide, transporting it into a storage site, and then depositing it at a place where it cannot enter the atmosphere.
The problem is that capturing carbon from power plants and industrial emissions isn't very cost-effective. The main reason is that waste carbon dioxide isn't emitted pure, but is mixed with nitrogen and other gases, and extracting it from industrial emissions ...
2021-02-25
NUI Galway study finds problem and non-problem gamblers differ in the gratifications they seek from mobile gambling
Non problematic mobile gambling is associated with positive mood
Advice for regulators and mobile gamblers on how to avoid gambling harms
A study carried out by the J.E. Cairnes School of Business and Economics at NUI Galway has examined how the different gratifications sought from mobile gambling explain problematic versus non-problematic patterns in highly involved gamblers.
For a subgroup of vulnerable individuals, gambling involvement can be pathological and reflects a personality disorder. ...
2021-02-25
Previous research from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) has shown that people with anxiety disorders can benefit from two types of therapy. But in a new NTNU study, the same patients also exhibited major changes on a scientific personality test.
The treatment resulted in patients scoring lower on the neuroticism personality trait, and thereby perhaps having a lower risk of relapse. In general, the patients' personality profiles also normalized.
"Our findings might apply to treatment in general. The risk of relapse could be less if we manage to reduce patients' neuroticism," says Professor Leif Edward Ottesen Kennair at NTNU's Department of Psychology.
Two effective methods
People ...
2021-02-25
PHILADELPHIA - Heart attack, kidney failure, stroke. These are just a few of the life-threatening complications that patients are at risk for following surgery. Now Jefferson researchers have developed an easy-to-use, web-based tool that predicts the risk of post-surgical complications such as kidney failure and stroke. The model may help medical professionals put preventive measures in place before the need for emergency intervention.
"We need to be able to assess the risk of life-threatening, post-surgical complications so we can then come up with individualized ways to ...
2021-02-25
Amsterdam, February 25, 2021 - COVID-19 has wrought havoc on the global economy and the world's public health systems. People with disabilities are more likely to suffer severe cases of the disease. Experts advocate in this special issue of the Journal of Vocational Rehabilitation that vocational rehabilitation across the major life phases of health, work, and education must focus on access to technology and home-based employment and ensure people with disabilities are prepared for the new global workplace.
To date, 500,000 Americans who have acquired COVID-19 have died, making it the current leading cause of death in the United States with over 2.4 million deaths worldwide. Individuals with some types of disabilities, especially those with multiple ...
2021-02-25
People's teeth-chattering experiences in the dentist's chair could be improved by fresh insights into how tiny, powerful bubbles are formed by ultra-fast vibrations, a study suggests.
The physics of how so-called nanobubbles are generated could have a range of clinical and industrial applications, including in dental hygiene devices used to remove plaque, experts say.
The findings could also inform the development of other technologies - such as devices to selectively target tumour cells - that harness the energy released when the bubbles burst.
Engineers at the University of Edinburgh ran complex ...
2021-02-25
Herndon, Va. (February 25, 2021) - Climate services are vital tools for decision makers addressing climate change in developing countries. Science-based seasonal forecasts and accompanying materials can support climate risk management in agriculture, health, water management, energy, and disaster risk reduction.
But in East Africa, natural resource managers have been slow to use climate information services, partly because they are difficult to understand and may not feel relevant for their local planning purposes. A new study published by the journal Risk Analysis suggests that one way to encourage policymakers in East Africa to use climate services more often is to appeal to the motivational factors that influence their professional actions on climate change.
Researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Virus detection method is versatile and accessible