Acute breakdown of the glial network in epilepsy
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) Tohoku University scientists and their colleagues in Germany have revealed that a first-time exposure to only a brief period of brain hyperactivity resulted in an acute breakdown of the inter-cellular network of glial cells. Pharmacological intervention of the glial plasticity may provide a new preventative strategy for fighting epilepsy.
The findings were detailed in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by neuronal hyper-excitation and a progression of seizures with each episode. Anti-epileptic drugs are mostly aimed at suppressing hyperactivity, but approximately 30% of patients worldwide show drug-resistance.
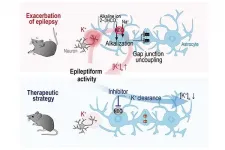
Half of the brain is occupied by non-neuronal glial cells. Astrocytes are star-shaped glial cells that are connected to each other via gap junctions. Neuronal excitation leads to potassium extrusion from neurons. The excess potassium is picked up by astrocytes and diluted in the astrocyte network. Efficacy of the potassium clearance can affect neuronal signal processing.
"Astrocytes have a strong control over neuronal activity," says professor Ko Matsui of the Super-network Brain Physiology lab at Tohoku University, who led the research. "Plasticity of the neuronal network underlies learning and memory but apparently astrocyte function is also susceptible to plastic change."
A collaborative research group led by Matsui, doctoral student Mariko Onodera and researchers at Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, studied the plastic change of astrocytes associated with epileptogenesis in mice.
In response to hyperactivity of the surrounding neurons, Na+/HCO3- co-transporter (NBC) in astrocytes was activated. The resulting intracellular alkalization led to gap junction uncoupling and impairment of prompt potassium clearance. Pharmacological blockade of the NBC suppressed the plastic change of the astrocyte network and prevented intensification of epileptiform activity.
"Astrocytes play a crucial role in taking control of neuronal activity in healthy brains as well, said Matsui. "Our research reveals the presence of glial plasticity and suggests a future therapeutic strategy can be aimed to control the glial function for treating disease."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
Results of a 2018 multirocket launch at Poker Flat Research Range north of Fairbanks, Alaska, will help scientists better understand the impact of more water vapor accumulating near the fringe of the Earth's atmosphere.
"This is the first time anyone has experimentally demonstrated that cloud formation in the mesosphere is directly linked to cooling by water vapor itself," said Irfan Azeem, space physicist at Astra LLC in Louisville, Colorado, and principal investigator of the Super Soaker mission.
The NASA-funded project, named Super Soaker, ...
2021-03-01
In recent years, European forests have suffered greatly from extreme climate conditions and their impacts. More than half of Europe's forests are potentially at risk from windthrow, forest fire, insect attacks or a combination of these. This is the main result of a study by an international team of scientists with the participation of Henrik Hartmann from the Max Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry in Jena, Germany. Using satellite data and artificial intelligence, the scientists studied vulnerability to disturbances in the period between 1979 and 2018. In the light of ongoing climate change, their findings are very important for improving mitigation and adaptation strategies ...
2021-03-01
Materials called perovskites can be more readily incorporated into silicon-based semiconducting platforms by using a microfluidic pumping technology developed at KAUST.
The perovskites currently being explored for many applications in new technologies are diverse materials sharing the same crystalline structure as the natural mineral perovskite. These semiconducting materials show great promise in a variety of optoelectronic applications, such as light emitters, sensors and solar cells.
Compared to traditional semiconductors, perovskites are soft and unstable. "This makes it difficult to pattern them using standard lithography methods," says materials scientist Iman Roqan at KAUST.
The challenge tackled by Roqan and her colleagues was to adapt microfluidic technologies to manipulate ...
2021-03-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Parents may fear that if their high school student isn't motivated to do well in classes, there's nothing that will change that.
But a new study that followed more than 1,600 students over two years found that students' academic motivation often did change - and usually for the better.
Results showed that increasing students' sense of "belongingness" in school was one key way of increasing academic motivation.
"Our results point to a more hopeful picture for students who start out with lower levels of motivation - they tend to shift toward more adaptive ...
2021-03-01
March 1, 2021 - A new paper published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society discusses how smoking may affect risk for COVID-19 and the types of research that are needed to better understand the link between smoking and COVID-19 risk.
In "Smoking and COVID-19: The Real Deal," Enid Neptune, MD, and Michelle N. Eakin, PhD, of the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, discuss research to date on this topic and propose areas of research that can help clarify this relationship.
Studies have shown that current smokers with COVID-19 have twice the ...
2021-03-01
New research has determined the prevalence of private security systems may be robbing the general public of the police services they need.
Dr. Ross Hickey is an economist in UBC Okanagan's Faculty of Management and the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences. Along with a team of researchers, Hickey examined data from a social survey of Canada victimization, where people answered whether they had added security measures to their homes to protect themselves from crime.
"We are seeing more expenditures on private security systems installed in homes and, as economists, we have to ask why. We know that crime rates are down and expenditure on police is up," says Hickey. "But private security purchases are at an all-time ...
2021-03-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Selectively cutting trees in riparian zones to aid forest restoration can be done without adversely affecting streams' water temperature as long as the thinning isn't too intensive, new research by Oregon State University shows.
Published in PLOS One, the study led by OSU College of Agricultural Sciences graduate student David Roon is one of the few to quantify restorative thinning's effects on forest streams.
"We don't know much about what happens with the more subtle changes in shade and light that come with thinning," Roon said. "Most of the research so far has looked at the effects of clearcutting with no stream-side buffer at all, or harvests outside of an untouched buffer area. And regulatory requirements ...
2021-03-01
Around 2.5 billion years ago, our planet experienced what was possibly the greatest change in its history: According to the geological record, molecular oxygen suddenly went from nonexistent to becoming freely available everywhere. Evidence for the "great oxygenation event" (GOE) is clearly visible, for example, in banded iron formations containing oxidized iron. The GOE, of course, is what allowed oxygen-using organisms - respirators - and ultimately ourselves, to evolve. But was it indeed a "great event" in the sense that the change was radical and sudden, or were the organisms alive at the time already using free oxygen, just at lower levels?
Prof. Dan Tawfik of the Weizmann Institute of Science's Biomolecular Sciences Department explains that the dating of the GOE ...
2021-03-01
HOUSTON - (March 1, 2021) - Rice University physicists have discovered a way to trap the world's coldest plasma in a magnetic bottle, a technological achievement that could advance research into clean energy, space weather and astrophysics.
"To understand how the solar wind interacts with the Earth, or to generate clean energy from nuclear fusion, one has to understand how plasma -- a soup of electrons and ions -- behaves in a magnetic field," said Rice Dean of Natural Sciences Tom Killian, the corresponding author of a published study about the work in Physical Review Letters.
Using laser-cooled strontium, ...
2021-03-01
Europeans spend more than £700 billion (€800bn) a year on recreational visits to water bodies - but perceived poor water quality costs almost £90 billion (€100bn) in lost visits, a new study has found.
The new research - led by a European collaboration involving the University of Exeter and the University of Stirling - used data from 11,000 visits in 14 different countries to analyse the economic value of water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, waterfalls, beaches and seaside promenades.
The research team estimated that people spend an average of £35 (€40) travelling to and from these sites, with a typical family making 45 such trips each year.
The team also found ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Acute breakdown of the glial network in epilepsy




