(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- Cardiovascular disease remains the number one cause of death globally. Unfortunately, the heart cannot regenerate new tissue, because the cardiomyocytes, or heart muscle cells, do not divide after birth.
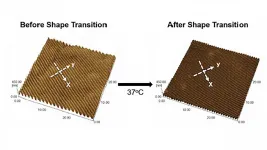
In their paper, published in APL Bioengineering by AIP Publishing, Syracuse researchers developed a shape memory polymer to grow cardiomyocytes. Raising the material's temperature from 30 degrees Celsius to 37 degrees Celsius turned the polymer's flat surface into nanowrinkles, which promoted cardiomyocyte alignment.
The research is part of the growing field of mechanobiology, which investigates how physical forces between cells and changes in their mechanical properties contribute to development, cell differentiation, physiology, and disease.
The researchers provide an overview in their paper of how some of the latest stimuli-responsive biomaterials (SRBs), which include the shape memory polymer, are used to mimic the dynamic microenvironment during heart development and disease progression.
Such research could provide better insight into the biomolecular and regulatory mechanisms that promote cell maturation, the final stages of cell differentiation, and spur the onset of disease.
Scientists have developed cardiac microenvironments by incorporating external stimulations, such as pressure or stretching, to promote cardiomyocyte growth and maturation. But, they haven't been able to control these microenvironments enough to reproduce the step-by-step gradual changes that occur in the body to understand the processes of rebuilding or remodeling heart tissue.
To address this challenge, researchers are using SRBs to learn more about how the microenvironment operates during heart development. SRBs, which are highly tunable, respond to temperature, pressure, electricity, and other external stimuli to provide cues for cell and tissue growth. SRBs undergo property switches in response to external stimuli, which means they can deliver on-demand changes that occur over time to affect the behaviors of cultured cells.
The ideal situation researchers are striving for is the creation of a synthetic 3D SRB-based cell culture platform that can change its material properties to mimic the natural progression of heart development. The platform could also help them learn more about the chemical and physical properties that lead to heart disease.
"It is crucial to understand how time-dependent biophysical cues affect cells during tissue formation," said author Zhen Ma. "However, conceptual models are still based largely on results from studies of static, 2D experimental platforms in which biophysical cues remain constant over time."
Ma suggests there should be a sharper focus on SRB electrical properties to expand the understanding of cardiac responses to extracellular changes. Embedding carbon nanotubes to enhance the conductivity of different polymer scaffolds, for instance, has been shown to improve intercellular communication and cardiomyocyte growth.
INFORMATION:
The article "Stimuli-responsive biomaterials for cardiac tissue engineering and dynamic mechanobiology" is authored by Huaiyu Shi, Chenyan Wang, and Zhen Ma. The article will appear in APL Bioengineering on March 2, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0025378). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0025378.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Bioengineering is an open access journal publishing significant discoveries specific to the understanding and advancement of physics and engineering of biological systems. See http://aip.scitation.org/journal/apb.
A 'Fish DJ' at The University of Queensland has used her knowledge of cool beats to understand brain networks and hearing in baby fish.
The DJ-turned-researcher used her acoustic experience to design a speaker system for zebrafish larvae and discovered that their hearing is considerably better than originally thought.
PhD candidate Rebecca Poulsen from the Queensland Brain Institute said that combining this new speaker system with whole-brain imaging showed how larvae can hear a range of different sounds they would encounter in the wild.
"For many years ...
[LAKEWOOD, CO; BRIDGEWATER, NJ; March 2, 2021] Two of the world's leading veterinary organizations are proud to announce updated recommendations in the 2021 AAHA/AAFP Feline Life Stage Guidelines. The American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) and the American Association of Feline Practitioners (AAFP) convened a Task Force of experts in feline medicine to define distinct feline life stages and provide a framework for individualized healthcare plans.
Understanding a cat's life stage and lifestyle greatly impacts healthcare strategies. Veterinary professionals have a responsibility to stress ...
New energy tariffs could leave people on bad deals even worse off despite the potential benefits for everyone, research has found.
The study, led by the University of Leeds, found new types of energy contracts designed for a low carbon future could benefit all types of customer, with opportunities to sell excess energy from solar panels or incentives for using energy at off-peak times.
However, many people were unlikely to choose them because they were disengaged from the energy market, didn't trust energy companies, or already feel satisfied with their current tariffs. ...
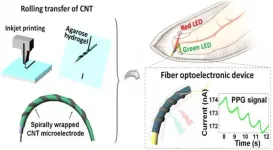
Advances in wearable devices have enabled e-textiles, which fuse lightweight and comfortable textiles with smart electronics, and are garnering attention as the next-generation wearable technology. In particular, fiber electronic devices endowed with electrical properties, while retaining the specific characteristics of textiles, are key elements in manufacturing e-textiles.
Optoelectronic devices are generally constructed using layers of semiconductors, electrodes, and insulators; their performance is greatly affected by the size and structure of the electrodes. Fiber electronic components for e-textiles need to be fabricated on thin, pliable threads; since these ...
The agricultural cultivation of the staple food of rice harbours the risk of possible contamination with arsenic that can reach the grains following uptake by the roots. In their investigation of over 4,000 variants of rice, a Chinese-German research team under the direction of Prof. Dr Rüdiger Hell from the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS) of Heidelberg University and Prof. Dr Fang-Jie Zhao of Nanjing Agricultural University (China) discovered a plant variant that resists the toxin. Although the plants thrive in arsenic-contaminated fields, the grains contain far less arsenic than other ...
WASHINGTON -- About 17 years ago, J. Martin Laming, an astrophysicist at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory, theorized why the chemical composition of the Sun's tenuous outermost layer differs from that lower down. His theory has recently been validated by combined observations of the Sun's magnetic waves from the Earth and from space.
His most recent scientific journal article describes how these magnetic waves modify chemical composition in a process completely new to solar physics or astrophysics, but already known in optical sciences, having been the subject of Nobel Prizes awarded to Steven Chu in 1997 and Arthur Ashkin in 2018.
Laming ...
Travellers looking to book a hotel should trust their gut instinct when it comes to online reviews rather than relying on computer algorithms to weed out the fake ones, a new study suggests.
Research, led by the University of York in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, shows the challenges of online 'fake' reviews for both users and computer algorithms. It suggests that a greater awareness of the linguistic characteristics of 'fake' reviews can allow online users to spot the 'real' from the 'fake' for themselves.
Dr Snehasish Banerjee, Lecturer in Marketing from the University of York's Management School, said: "Reading and writing online reviews ...
A UK wide survey of 2252 adults, carried out five weeks into the first lockdown revealed 95% of those who took part were following lockdown restrictions. Of that 95% more than 80% reported finding it challenging. Adjusting to changes in daily routines, and mental and physical health struggles were the most common challenges faced by participants. Women and adults under the age of 55 were most likely to report experiencing challenges.
The research, 'What challenges do UK adults face when adhering to COVID-19-related instructions? Cross-sectional survey in a representative sample'*, was published in the journal, Preventive ...
TAMPA, Fla. - Advanced melanoma is one of the deadliest types of cancer, with a 5-year survival rate of only 27% for patients with distant metastases. Recent advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have greatly improved patient prognosis; however, many patients eventually develop resistance and disease recurrence. Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center are investigating how to combine and sequence new therapies to improve survival. In a new article published in Cancer Immunology Research, the Moffitt team shows that sequential administration of immunotherapy followed by targeted therapy prolongs anti-tumor responses in preclinical models and may be a potential ...
A foundational study conducted by scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) shows for the first time that white-rot fungi are able to use carbon captured from lignin as a carbon source.
The research confirms a hypothesis from Davinia Salvachúa Rodriguez, the senior author of a newly published paper. Until now, scientists were unsure whether white-rot fungi--the most efficient lignin-degrading organisms in nature--actually consume the products generated from breaking down lignin.
"What we have demonstrated here is that white-rot fungi can actually utilize lignin-derived aromatic compounds as a carbon source, which means they can eat them and utilize them to grow," Salvachúa said. "That is another strategy for carbon sequestration in ...