(Press-News.org) Green tea supplements modulate facial development of children with Down syndrome
A new study led by Belgian and Spanish researchers published in Scientific Reports adds evidence about the potential benefits of green tea extracts in Down syndrome. The researchers observed that the intake of green tea extracts can reduce facial dysmorphology in children with Down syndrome when taken during the first three years of life. Additional experimental research in mice confirmed the positive effects at low doses. However, they also found that high doses of the extract can disrupt facial and bone development. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of green tea extracts and therefore they should always be taken under medical supervision.
Down syndrome is caused by the presence of a third copy of chromosome 21, leading to an overexpression of the genes in this region and resulting in a number of physical and intellectual disabilities. One of the genes, DYRK1A, contributes to altering brain and bone development in people with Down syndrome. The green tea compound EGCG (epigallocatechin-3-gallate) is known to inhibit DYRK1A activity, although it also has other mechanisms of action. Previous research has shown the potential of EGCG to improve cognition in young adults with Down syndrome.
In a new study, researchers analysed the effect of green tea supplements on facial development in Down syndrome. In the experimental part of the study, the EGCG supplements were tested in mice at different dosages. In a second part of the research, they did an observational study on children with and without Down syndrome. This work, led by the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and University of Barcelona in Spain and KU Leuven in Belgium, is an international effort involving researchers from University of Central Florida, La Salle - University Ramon Llull, and IMIM - Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute.
For the mouse study, carried out at KU Leuven, the researchers started the treatment before birth, while the pups were developing in the wombs of their mothers, by adding either a low or a high dose of green tea extracts to their drinking water. "The low dose treatment had a positive effect on mice that are a model of Down syndrome," Professor Greetje Vande Velde (KU Leuven) comments, co-lead author of the study. "Sixty percent of them showed a facial shape similar to the control group."
"The high dose treatment, however, generated very mixed results, and even disrupted normal facial development in some cases, causing additional dysmorphology. This occurred in all mice, in the model of Down syndrome as well as in the control group."
Age-dependent effects
The observational study was set up in Spain and also included participants from North America. 287 children between 0 and 18 years participated, including children with Down syndrome who did (n = 13) or didn't (n = 63) receive EGCG supplementation. The treated group were all self-medicated and didn't follow a prescribed protocol.
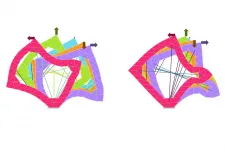
"All participants were photographed from various angles to create a 3D model of their faces," explains Neus Martínez-Abadías, professor at the University of Barcelona and co-lead author of the study. "We use 21 facial landmarks, and the distances between them, to compare the faces of the participants. In the youngest group between 0 and 3 years, we observed that 57 percent of the linear distances are significantly different when you compare the faces of children with Down syndrome that never received the treatment to those of children that do not have Down syndrome. For babies and toddlers who did receive EGCG treatment, this difference was much smaller, only 25 percent. After green tea supplementation, the facial dysmorphology decreases and the children with or without Down syndrome look more alike."
"We didn't identify a similar effect in the adolescent group. Even when treated with green tea extracts, children with Down syndrome still show a difference of more than 50 percent compared to the control group. These findings suggest that the green tea supplements only affect facial development when they are administered in the early stages of life when the face and skull are rapidly growing."
Further research required
"Despite the potential benefits we observed, we must handle these findings with caution considering they are preliminary and based on an observational study," Professor Vande Velde warns. "Much more research is necessary to evaluate the effects of EGCG-containing supplements, the appropriate dose and their therapeutic potential in general. We also need to take into the account possible effects on other organs and systems, not just on the development of the face. This requires first more basic research in the lab with mice, and then clinical studies with more participants and controlled use of these supplements."
"Our findings suggest that effects of EGCG strongly depend on the dose." Professor Martínez-Abadías concludes. "EGCG products are commercially available and they are used regularly as a general health-promoting compounds. However, it's important to follow the European Food Safety Authority recommendations regarding the maximal intake and to always consult a physician before taking the supplements. Our research shows potential beneficial effects of facial development at low doses, but at very high doses they can produce unpredictable effects in mice. More research is needed in humans to determine the optimal dose at each age that maximizes the potential benefits."
INFORMATION:
Funding information
We acknowledge support from private foundations BBVA, Marguerite-Marie Delacroix and Jerome Lejeune Foundation; institutional support from CRG Centro de Excelencia Severo Ochoa, University of Central Florida and KU Leuven; as well as public funding resources from American Association of Physical Anthropologists, Flemish Research Foundation and previous Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness.
Imagine a robot.
Perhaps you've just conjured a machine with a rigid, metallic exterior. While robots armored with hard exoskeletons are common, they're not always ideal. Soft-bodied robots, inspired by fish or other squishy creatures, might better adapt to changing environments and work more safely with people.
Roboticists generally have to decide whether to design a hard- or soft-bodied robot for a particular task. But that tradeoff may no longer be necessary.
Working with computer simulations, MIT researchers have developed a concept for a soft-bodied robot that can turn rigid on demand. The approach could enable a new generation of robots that combine the strength and precision of rigid robots with the fluidity and safety of ...
The models used to produce global climate scenarios may overestimate the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency, warns new research led by academics at the University of Sussex Business School and the University of Leeds.
In a review of 33 studies, the researchers find that economy wide rebound effects may erode around half of the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency.
These rebound effects result from individuals and businesses responding to the benefits of improved energy efficiency - such as cheaper heating, lighting and travel. These responses improve quality-of-life, raise productivity and boost industrial competitiveness, ...
Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper (attached PDF) was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. ...
Recently, research team led by academician GUO Guangcan from CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of CAS, has made an important progress in quantum information theory. Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. XIANG Guoyong from the team, cooperated with Dr. Strelstov from University of Warsaw, investigated the imaginary part of quantum theory as a resource, and several important results have been obtained. Relevant results are now jointly published as Editors' Suggestion in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A.
Complex number is a mathematical ...
It is millions of trillions of times brighter than the sunlight and a whopping 1,000 trillionth of a second, appropriately called the instantaneous light. It is the X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL) light that opens a new scientific paradigm. Combining it with AI, an international research team has succeeded in filming and restoring the 3D structure of nanoparticles that share structural similarities with viruses. With the fear of a new pandemic growing around the world due to COVID-19, this discovery is attracting the attention among academic circles for imaging the structure of the virus with both high accuracy and speed.
An international team of researchers from POSTECH, National University of ...
Targeted, efficient and with few side effects: A new method for combating periodontitis could render the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics superfluous. It was developed and tested for the first time by a team from Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the Fraunhofer Institute for Cell Therapy and Immunology IZI and Periotrap Pharmaceuticals GmbH. The aim is to neutralise only bacteria that cause periodontitis while sparing harmless bacteria. The study appeared in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Periodontitis is a common bacterial inflammation of the gums. According to the World Health Organization WHO Oral ...
Ask Eric Weaver about pandemics, and he's quick to remind you of a fact that illustrates the fleeting nature of human memory and the proximal nature of human attention: The first pandemic of the 21st century struck not in 2019, but 2009.
That's when the H1N1/09 swine flu emerged, eventually infecting upwards of 1.4 billion people -- nearly one of every five on the planet at the time. True to the name, swine flus jump to humans from pigs. It's a phenomenon that has been documented more than 400 times since the mid-2000s in the United States alone.
"They're considered the great mixing vessel," said Weaver, associate professor of biological sciences at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. "They're susceptible to their own circulating ...
Parents who reported more hassles using a child car seat or booster seat - such as the child is uncomfortable or having to make multiple trips in a day - were less likely to follow recommendations from the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) on child passenger safety, according to a study published in the journal Academic Pediatrics.
Researchers obtained information about transportation safety behaviors and 20 hassles when using child car seats among 238 socioeconomically and racially diverse parents of children 1 to 10 years of age. Eighty percent of parents reported at least a little bit of a problem with one ...
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease are in the firing line after researchers identified an attractive therapeutic drug target.
An international collaboration, co-led by University of Queensland researchers, has isolated and analysed the structure and function of a protein found in the brain's nerve fibres called SARM1.
Dr Jeff Nanson said the protein was activated when nerve fibres were damaged by injury, disease, or as a side effect of certain drugs.
"After a damaging incident occurs, this protein often induces ...
Fireworks are used in celebrations around the world, including Independence Day in the U.S., the Lantern Festival in China and the Diwali Festival in India. However, the popular pyrotechnic displays emit large amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, sometimes causing severe air pollution. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have estimated that, although so-called environmentally friendly fireworks emit 15-65% less particulate matter than traditional fireworks, they still significantly deteriorate air quality.
Fireworks displays can cause health problems, such as respiratory ailments, because they ...