Fermented wool is the answer
FAU researchers reveal the secret of the famous Pazyryk carpet
2021-03-04
(Press-News.org) The Pazyryk carpet is the world's oldest example of a knotted-pile carpet and is kept at the State Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg, Russia. The carpet, which was made out of new wool at around 400 BC, is one of the most exciting examples of central Asian craftsmanship from the Iron Age. Ever since the carpet was discovered in 1947 by Russian archaeologists in a kurgan tomb in the Altai mountains, experts in traditional dyeing techniques have been puzzled by the vivid red, yellow and blue colours of the carpet, which lay buried in extreme conditions for almost two thousand five hundred years.
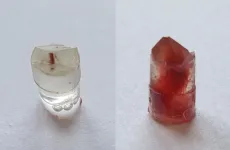
Red fibres under the microscope
Prof. Dr. Karl Meßlinger from the Institute of Physiology and Pathophysiology at FAU, and x-ray microscopy experts Dr. Andreas Späth and Prof. Dr. Rainer Fink from the Chair of Physical Chemistry II at FAU have now shed some light on this secret. Together, they came up with the idea of imaging the distribution of pigments across the cross section of individual fibres of wool using high-resolution x-ray fluorescence microscopy (μ-XRF). Dr. Späth and Prof. Fink conducted the experiments using the PHOENIX x-ray microscope at the Paul Scherrer Institute in Villigen, Switzerland. With three to five micrometres, the microscope provides sufficient spatial resolution combined with high sensitivity for characteristic chemical elements.
The study focused mainly on red wool fibres, as the pigment Turkey red has been in use almost exclusively for centuries in Central Asia and in the Far East to create a characteristic shade of red. Turkey red is a metal organic complex made of alizarin, which is derived from the roots of the rose madder, and aluminium. 'μ-XRF imaging shows the characteristic distribution of the aluminium along the cross section of fermented wool fibres,' explains Dr. Andreas Späth. 'We found the same pattern in fibres from the Pazyryk carpet.' This is by far the earliest example of the fermentation technique and provides an insight into the already highly-developed techniques used by textile craftsmen and women in the Iron Age. The results also show the high potential of x-ray microscopy for analysing samples of textiles from archaeological sites. Up to now, research in this field has used scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Fermented wool does not fade
Prof. Dr. Karl Meßlinger received a sample of some knots from the Pazyryk carpet 30 years ago in 1991 for analysis with a scanning electron microscope. Together with Dr. Manfred Bieber, an expert in oriental textile dyeing techniques, he previously discovered that SEM imaging can identify wool fibres that have been treated with a special dyeing technique based on previous fermentation of the wool. The fermentation process increases the diffusion of the pigments towards the centre of the wool fibres resulting in significantly more brilliant and permanent colours. Fermented wool can be identified by SEM imaging by means of the characteristic raised position of the outermost layers of the cuticle. 'Traditional Anatolian textile craftspeople are familiar with a less costly yet reliable technique,' says Meßlinger. 'They spread the dyed wool out on a field for several weeks in direct sunlight, then put it in a barn as bedding for their animals before rinsing it out in a stream or river. Only fermented wool retains its colour without any significant bleaching.'
Prof. Meßlinger and Dr. Bieber were able to trace the origins of this traditional dyeing technique back to the 17th century. However, the more the treated textile is used or the more it is exposed to the elements, the less remains of the cuticle layers. Most of the cuticle layers of the world-famous Pazyryk carpet were also missing. The researchers succeeded in proving the effect of fermentation by comparing the fluorescent images with those of samples of wool they fermented and dyed themselves.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-04
You didn't need a Ph.D. to contribute to research into wildlife abundance and behavior in North Carolina, thanks to a large-scale citizen science project led by North Carolina State University researchers.
Through the project, called North Carolina Candid Critters, researchers trained 580 volunteers to take candid animal photos with heat sensitive cameras, and then share their photos through a website called eMammal. In an article on the project in the journal Citizen Science: Theory and Practice, researchers reported on the successes and challenges of the effort, which gathered more than 2.2 million wildlife photos across three years, and increased the number of verified mammal records that were available in the state by a factor of five.
"The power of this is that you can get ...
2021-03-04
What The Article Says: This Viewpoint proposes ways to maximize vaccine efficacy and allocation given the rise of coronavirus variants and authorization of a Johnson & Johnson vaccine, including reserving the latter for younger healthier populations, boosting it with a single-dose messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccination and single mRNA immunization of people with prior documented SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Authors: John P. Moore, Ph.D., of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2021.3465)
Editor's Note: The article includes an Editor's Note. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
2021-03-04
Many cognitive neurodevelopmental disorders are a result of too many or too few copies of certain genes or chromosomes. To date, no treatment options exist for this class of disorders. MECP2 duplication syndrome (MDS) is one such disorder that primarily affects boys and results from a duplication spanning the methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2) locus located on the X chromosome.
A preclinical study published from the laboratory of Dr. Huda Zoghbi, professor at Baylor College of Medicine and director of the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital, provides experimental evidence that supports the use of antisense oligonucleotides as ...
2021-03-04
BOSTON - New treatments for Alzheimer's disease are desperately needed, but numerous clinical trials of investigational drugs have failed to generate promising options. Now a team at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School (HMS) has developed an artificial intelligence-based method to screen currently available medications as possible treatments for Alzheimer's disease. The method could represent a rapid and inexpensive way to repurpose existing therapies into new treatments for this progressive, debilitating neurodegenerative condition. ...
2021-03-04
Hearing the words "new species discovered" may conjure images of deep caves, uncharted rainforests, or hidden oases in the desert.
But the reality is that thousands of new species are discovered each year by enterprising scientists all over the world. Many of these new species do come from exotic locations, but more surprisingly, many come from just down the road, including the newest member of the Hokie Nation, the millipede Nannaria hokie.
The newest Hokie -- which has about 60 more legs than the HokieBird -- was discovered living under rocks by the Duck Pond behind the Grove on Virginia Tech's Blacksburg campus. Since then, the critter has been found at the area commonly referred to as stadium ...
2021-03-04
New research at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that three new, fast-spreading variants of the virus that cause COVID-19 can evade antibodies that work against the original form of the virus that sparked the pandemic. With few exceptions, whether such antibodies were produced in response to vaccination or natural infection, or were purified antibodies intended for use as drugs, the researchers found more antibody is needed to neutralize the new variants.
The findings, from laboratory-based experiments and published March 4 in Nature Medicine, suggest that COVID-19 drugs and vaccines developed thus far may become less effective ...
2021-03-04
Texas A&M University College of Medicine ressearchers have recently discovered that cytisine -- a smoking cessation drug commonly used in Europe -- reduces the loss of dopamine neurons in females. These findings provide potential evidence for the use of the drug to treat Parkinson's disease or stop its progression in women.
Sara Zarate and Gauri Pandey, graduate students from the lab of Rahul Srinivasan, assistant professor in the Department of Neuroscience & Experimental Therapeutics, are co-first authors of the research. Their findings are published in the Journal of Neurochemistry.
There ...
2021-03-04
Plants, fungi, and bacteria produce natural products that function, among other things, as defenses that are deployed against predators and competitors. In medicine, these compounds are used for antibiotics, cancer drugs, and cholesterol reducers. The team working with associate professor Dr. Robin Teufel and Dr. Britta Frensch of the Institute of Biology II of the Faculty of Biology of the University of Freiburg was able, together with researchers from the ETH Zürich in Switzerland, to shed light on the key role of three enzymes that are involved in synthesizing a class of natural products. The researchers are publishing their findings in the latest edition of "Nature Communications."
Actinobacteria produce many natural products, such as those that are ...
2021-03-04
Many species might be left vulnerable in the face of climate change, unable to adapt their physiologies to respond to rapid global warming. According to a team of international researchers, species evolve heat tolerance more slowly than cold tolerance, and the level of heat they can adapt to has limits.
In a study published in the Nature Communications, McGill professor Jennifer Sunday and her co-authors wanted to understand how species' thermal limits have evolved. To examine variation across the tree of life, the researchers developed the largest available database compiling thermal tolerances for all types of organisms (GlobTherm database).
The ...
2021-03-04
SAN ANTONIO, March 4, 2021 -- People who have had major sinus surgery should consult their ENT doctor before undergoing COVID-19 swab testing, new research indicates.
Likewise, those performing swab testing should ask whether the patient has had extensive sinus or skull base surgery, said END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fermented wool is the answer
FAU researchers reveal the secret of the famous Pazyryk carpet


