The social support for mothers of patients with eating disorders
Association between the social support for mothers of patients with eating disorders, maternal mental health, and patient symptomatic severity: A cross-sectional study
2021-03-05
(Press-News.org) Background: Although caregivers of patients with eating disorders usually experience a heavy caregiving burden, the effects of social support on caregivers of patients with eating disorders are unknown. This study aimed to investigate how social support for mothers who are caregivers of patients with an eating disorder improves the mothers' mental status and, consequently, the symptoms and status of the patients.
Methods: Fifty-seven pairs of participants were recruited from four family self-help groups and one university hospital in Japan. Recruitment was conducted from July 2017 to August 2018. Mothers were evaluated for social support using the Japanese version of the Social Provisions Scale-10 item (SPS-10), self-efficacy using the General Self-Efficacy Scale, loneliness using the University of California, Los Angeles Loneliness Scale, listening attitude using the Active Listening Attitude Scale, family functioning using the Family Assessment Device, depression symptoms using the Beck Depression Inventory (Second Edition), and psychological distress using the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale. Patients were evaluated for self-esteem using the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale, assertion using the Youth Assertion Scale, and their symptoms using the Eating Disorder Inventory. We divided the mothers and patients into two groups based on the mean score of the SPS-10 of mothers and compared the status of mothers and patients between the high- and low-scoring groups.
Results: High social support for mothers of patients with eating disorders was significantly associated with lower scores for loneliness and depression of these mothers. We found no significant differences in any patient scores based on mothers' level of social support.
Conclusions: For patients with eating disorders, social support for a caregiver cannot be expected to improve their symptoms, but it may help prevent caregiver depression and loneliness.
INFORMATION:
Keywords: Caregiver; Depression; Eating disorders; Listening attitude; Loneliness; Psychological distress; Self-efficacy; Social support.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-05
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation process of cytosolic materials and damaged organelles. Researchers at Ubiquitin Project of TMIMS have been studying the molecular mechanism of mitophagy, the selective autophagy process to eliminate damaged mitochondria. PINK1 (a serine/threonine kinase) and Parkin (a ubiquitin ligating enzyme: E3) work together to ubiquitylate the outer membrane proteins of damaged mitochondria, then ubiquitin chains are recognized as signals for autophagy degradation. Dysfunction of mitophagy causes a decrease in mitochondrial quality with overproduction of ROS, and is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's disease.
In Autophagy machinery, cellular components targeted for degradation are engulfed by phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P)-rich ...
2021-03-05
Frequently occurring chronic skin inflammation like in atopic dermatitis (AD or neurodermatitis) and psoriasis have different causes such as genetic predisposition, stress or allergens. These frequently occurring skin diseases are mostly attributed by biomedical scientists to a disturbed immune system, although the noticeable thickening and flaking of the epidermis, which is the outermost layer of skin, also indicates a disruption of the epithelial cells. A team of researchers from the University Clinic for Dermatology and the Clinical Institute for Laboratory Medicine at MedUni Vienna has now been able to identify new molecular ...
2021-03-05
WHO: Giovanni Traverso, MB, BChir, PhD, Associate Physician, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women's Hospital; corresponding author of a new article published in JAMA Network Open.
Peter Chai, MD, MMS, Assistant Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; first author.
WHAT: In the age of COVID-19, mobile robotic telehealth systems could help clinicians and patients interact without contact. Last spring, some health care systems deployed robotic systems within a hospital to evaluate and interact with patients. In a JAMA Network Open article, Traverso and colleagues report the results of a national survey and a cohort study in an emergency department (ED), which analyzed patients' satisfaction with an initial evaluation ...
2021-03-05
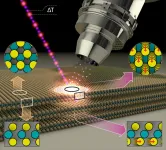
MoS2 thin films of superposed alternating layers of molybdenum and sulfur atoms form a two-dimensional semiconducting surface. However, even a surprisingly low-intensity blue light pulse is enough to alter the properties of the surface and make it metallic. This has now been demonstrated by a team at BESSY II.
The exciting thing is that the MoS2 layers in this metallic phase are also particularly active catalytically. They can then be employed, for example, as catalysts for splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen. As inexpensive catalysts, they could facilitate the production of hydrogen - an energy ...
2021-03-05
Approximately 15-to-30 percent of patients with metastatic breast cancer have brain metastasis (BM), with basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) metastasizing to the brain most frequently. The prognosis for BLBC-BM patients is poor, as the blood-brain barrier prevents most therapeutics from reaching the brain. Testing candidate therapies in clinical trials is also challenging because animal models that mimic BM are limited. In a new study, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and collaborators engineered a bimodal tumor-suppressing and killing molecule that can be delivered to the brain by stem cells. They tested ...
2021-03-05
Beijing, 26 February 2021: the journal Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (CVIA) has just published the third issue of Volume 5. This issue brings together important research from authors in the USA and China, including several important papers concerned with the various cardiological implications of COVID-19.
Papers in the issue are as follows.
RESEARCH PAPERS
Diyu Cui, Yimeng Liao, Jianlin Du and Yunqing Chen
A Meta-analysis of Major Complications between Traditional Pacemakers and Leadless Pacemakers
(http://ow.ly/CgYO30rz3eA)
Yue Wu, Guoyue Zhang, Rong Hu and Jianlin Du
Risk of Target Organ Damage in Patients with Masked Hypertension versus
Sustained Hypertension: A Meta-analysis (http://ow.ly/x63E30rzjEp)
Jing Li, Lijie Sun, Fang Wang, Bing Liu, Hui Li, Guodong ...
2021-03-05
If you stretch an elastic band, it becomes thinner - a physical behavior that applies to most "common" materials. Since the 20th century, an opposite behavior has been known in materials research: The so-called auxetic (from ancient Greek auxetos, meaning 'stretchable') materials expand in the direction orthogonal to the strain. Likewise, they shrink when they are compressed. Scientifically, they are characterized by a negative Poisson's ratio. Probably the best known and oldest application of unusual Poisson's ratios is the bottle cork, which has a Poisson's ratio of zero. This has the effect that the cork ...
2021-03-05
Biodiversity is declining at an unprecedented rate, due primarily to human activity. Illegal and unsustainable wildlife trade is one of the major drivers of these declines, while much wildlife trade is legal, and the quantity of trade provides the opportunity to launder illegally sourced and traded species and products.
Researchers from the Conservation Forensics Lab at HKU and Research Division for Ecology and Biodiversity, analyzed trends in global legal wildlife trade from 1997 to 2016, and revealed that legal wildlife trade averaged $220 billion per year over this period, approximately double the international trade in tea, coffee and spices, and eclipsing - by order of magnitude - annual trade in trafficked wildlife, estimated ...
2021-03-05
Less than one-third of COVID-19 clinical trials are led by women, which is half the proportion observed in non-COVID-19 trials, according to research led by Queen Mary University of London, University of St Andrews, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The study suggests that gender disparities during the pandemic may signify not only a lack of women's leadership in international clinical trials and new research projects, but also may expose the imbalances in women's access to research activities and funding during health emergencies.
The results of the study are being publicised to mark International Women's Day on Monday 8 March. This ...
2021-03-05
SMU Office of Research & Tech Transfer - For most of human history, populations across the world lived in low-density, rural settings. Over the past few centuries, however, this changed dramatically with the trend of urbanisation. Today, more than four billion people live in urban settings worldwide; by 2050, about two thirds of the world's population are expected to live in cities.
Despite their rapid growth, cities do not spring up fully formed, but are shaped by evolving human constructs including government policy, legal frameworks and emerging technologies. It is precisely ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The social support for mothers of patients with eating disorders
Association between the social support for mothers of patients with eating disorders, maternal mental health, and patient symptomatic severity: A cross-sectional study