(Press-News.org) CHAPEL HILL, NC -- Calling the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force's newly released recommendation statement to expand eligibility for annual lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography a step forward, UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers say future changes should address equity and implementation issues.
In an editorial published in JAMA, Louise M. Henderson, PhD, professor of radiology at UNC School of Medicine, M. Patricia Rivera, MD, professor of medicine at UNC School of Medicine, and Ethan Basch, MD, MSc, the Richard M. Goldberg Distinguished Professor in Medical Oncology and chief of oncology at the UNC School of Medicine, outlined their concerns and offered potential approaches to make the screening recommendation more inclusive of populations that have been historically underserved.
"The revised U.S. Preventive Services Task Force's recommendations are sound and based on well-conceived evidence and modeling studies, but they alone are not enough, as we have seen limited uptake of the prior recommendations," Basch said. "Implementation will require broader efforts by payers, health systems and professional societies, and, in the future, a more tailored, individual risk prediction approach may be preferable."
The task force has made two significant changes to the screening recommendation it issued in 2013: Annual screening will begin at age 50, instead of 55, and smoking intensity has been reduced from 30 to 20 pack-year history. These more inclusive criteria could more than double the number of adults eligible for lung cancer screening, from 6.4 million to 14.5 million, according to some estimates. This represents an 81% increase.
Henderson, Rivera and Basch are encouraged that lung cancer screening will be available to more people, and they point out that expanding access alone won't reduce racial inequities, especially as measured by lung cancer deaths prevented and life-years gained.
It may be possible to counter this shortcoming, they said, by adding risk-prediction models that identify high-benefit individuals who do not meet USPSTF criteria. This could reduce or eliminate some, though not all, racial disparities, according to one study. Also, future research should explore risks such as family history of lung cancer and genetic susceptibility to develop risk assessment strategies that may identify individuals who never smoked and still have a high risk for lung cancer but currently are not eligible to be screened.
Financial-based barriers are also an issue. Expanding screening access to include people as young as 50 may lead to greater inequities for those who are enrolled in Medicaid, the state-based public health insurance program.
"Medicaid is not required to cover the USPSTF recommended screenings and even when screening is covered, Medicaid programs may use different eligibility criteria," Henderson said. She adds this is problematic because people who receive Medicaid are twice as likely to be current smokers than those with private insurance (26.3% compared to 11.1%), and they are disproportionately affected by lung cancer. "This is a significant issue, particularly in the nine states where Medicaid does not cover lung cancer screening."
Putting the screening recommendation into practice will be a substantial challenge, Rivera said. Primary care providers are critical to implementing the screening process because they initiate the conversation with their patients about the potential benefits and risk of lung cancer screening and make the screening referral. However, Rivera said many already have an overburdened workload, and it may be unrealistic to expect them to be able to spend the necessary time to have these complex conversations.
"A significant barrier to implementation of lung cancer screening is provider time. Many primary care providers do not have adequate time to have a shared decision-making conversation and to conduct a risk assessment," Rivera said. "Although a lung cancer screening risk model that incorporates co-morbidities and clinical risk variables may be the best tool for selecting high risk individuals who are most likely to benefit from screening, such a model requires input of additional clinical information, thereby increasing the time a provider will spend; the use of such a model in clinical practice has not been established."
Despite these limitations and challenges, the new recommendation can expand access to lung cancer screening, the researchers said in the editorial. "Beyond implementation challenges, the future of screening strategies lies in individualized risk assessment including genetic risk. The 2021 USPSTF recommendation statement represents a leap forward in evidence and offers promise to prevent more cancer deaths and address screening disparities. But the greatest work lies ahead to ensure this promise is actualized."
INFORMATION:
Disclosures
Henderson reported receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute. Rivera reported receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute for research in lung cancer screening, serving on the advisory panel for Biodesix and bioAffinity, and serving as a research consultant to Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work. Basch reported receiving fees from Astra Zeneca, CareVive Systems, Navigating Cancer, and Sivan Healthcare for serving as a scientific advisor/consultant, outside the submitted work.
Researchers have come up with a better way to test which fabrics work best for masks that are meant to slow the spread of COVID-19. By testing those fabrics under conditions that mimic the humidity of a person's breath, the researchers have obtained measurements that more accurately reflect how the fabrics perform when worn by a living, breathing person.
The new measurements show that under humid conditions, the filtration efficiency -- a measure of how well a material captures particles -- increased by an average of 33% in cotton fabrics. Synthetic fabrics performed poorly relative to cotton, and their performance did not improve with humidity. The material from medical-procedure masks also did not improve with humidity, though it performed ...
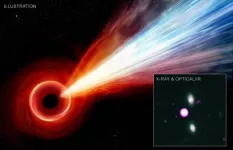
Astronomers have discovered evidence for an extraordinarily long jet of particles coming from a supermassive black hole in the early universe, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
If confirmed, it would be the most distant supermassive black hole with a jet detected in X-rays. Coming from a galaxy about 12.7 billion light-years from Earth, the jet may help explain how the biggest black holes formed at a very early time in the universe's history.
The source of the jet is a quasar - a rapidly growing supermassive black hole - named PSO J352.4034-15.3373 (PJ352-15 for short), which sits ...
Most teenagers don't remember life before the internet. They have grown up in a connected world, and being online has become one of their main sources of learning, entertaining and socializing.
As many previous studies have pointed out, and as many parents worry, this reality does not come risk-free. Whereas time on the internet can be informative, instructive and even pleasant, there is already significant literature on the potential harm caused by young children's problematic internet use (PIU).
However, a new study led by END ...
"It was clear that the greater an individual's sensitivity to motion parallax cues, the more severe the motion sickness symptoms," says lead NYU Abu Dhabi researcher
Fast facts:
The visual system is often studied in relative isolation, but it has clear connections to other components of the nervous system.
A notable example of this is motion sickness, which affects certain people much more severely than others.
Motion sickness is typically associated with traveling in cars, boats, and airplanes, however discomfort or "cybersickness" also arises with technological use such as in virtual reality (VR).
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 9, 2021: A new study led by Head of the Rokers Vision Laboratory and NYUAD Associate Professor of Psychology Bas Rokers explored why ...
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent form of lung cancer, accounting for more than 80 percent of all lung cancer cases. Despite the aggressive nature of NSCLC, circulating tumor cells that lead to metastases often go undetected in the blood compared to breast, prostate, colorectal, and other cancers.
Now, scientists have developed a novel method to better detect the circulating tumor cells (CTCs) that are a telltale sign of metastases. The research was published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
ISB and a collaborative team of researchers looked at hexokinase-2, or HK2, a ...
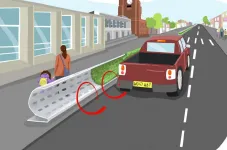
A unique curved barrier has been designed by researchers at Imperial College London, who publish new findings in the peer-reviewed journal END ...
Researchers from the HealthPartners Institute and University of Minnesota in Minneapolis conducted an observational analysis of interviews and characteristics of primary care clinics, comparing the strategies, facilitators and barriers to high performance in treating patients with diabetes. The purpose of the study was to learn what strategies and factors seem most important to leaders of primary care clinics to ensure high performance. The percentage of Minnesota diabetes patients who achieved optimal diabetes care measures increased from 12 to 45 percent between 2004 and 2017, while national measures of diabetes care outcomes did not improve significantly around the same time ...
Smoke from local wildfires can affect the health of Colorado residents, in addition to smoke from fires in forests as far away as California and the Pacific Northwest.
Researchers at Colorado State University, curious about the health effects from smoke from large wildfires across the Western United States, analyzed six years of hospitalization data and death records for the cities along the Front Range, which reaches deep into central Colorado from southern Wyoming.
They found that wildfire smoke was associated with increased hospitalizations for asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and some cardiovascular health outcomes. They also discovered that wildfire smoke was associated with deaths from asthma and cardiovascular disease, but that ...
Researchers at Skoltech and their colleagues proposed a photonic device from two optical resonators with liquid crystals inside them to study optical properties of this system that can be useful for future generations of optoelectronic and spinoptronic devices. The paper was published in the journal Physical Review B.
The simplest kind of optical resonator consists of two mirrors directly opposite each other, "squeezing" light between them. When you stand inside a mirror resonator, you see infinite copies of yourself in the mirrors; when a liquid crystal - the kind in your computer and smartphone screen - is placed into a much smaller and a bit more complex resonator, ...
Cancer patients often experience fragmented care, particularly as they undergo cancer treatments. Although family physicians seek to provide continuous and comprehensive care, they often lose touch with their cancer patients during the treatment phase. Researchers conducted a randomized intervention that aimed to improve continuity of care and interprofessional collaboration as perceived by lung cancer patients and their family physicians.
The components of the intervention included the bidirectional exchange of patient information and care summaries between oncology teams and family physicians. Oncology ...