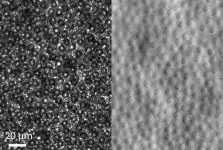
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a noninvasive technique that can capture images of rod and cone photoreceptors with unprecedented detail. The advance could lead to new treatments and earlier detection for retinal diseases such as macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss.
"We are hopeful that this technique will better reveal subtle changes in the size, shape and distribution of rod and cone photoreceptors in diseases that affect the retina," said research team leader Johnny Tam from the National Eye Institute. "Figuring out what happens to these cells before they are lost is an important step toward developing earlier interventions to treat and prevent blindness."
In Optica, The Optical Society's (OSA) journal for high impact research, the researchers show that their new imaging method overcomes resolution limitations imposed by the diffraction barrier of light. The researchers accomplish this feat while using light that is safe for imaging the living human eye.
"The diffraction limit of light can now be routinely surpassed in microscopy, which has revolutionized biological research," said Tam. "Our work represents a first step toward routine sub-diffraction imaging of cells in the human body."
Using less light to see more
Achieving high-resolution images of photoreceptors in the back of the eye is challenging because the eye's optical elements (such as lens and cornea) distort light in a way that can substantially reduce image resolution. The diffraction barrier of light also limits the ability of optical instruments to distinguish between two objects that are too close together. Although there are various methods for imaging beyond the diffraction limit, most of these approaches use too much light to safely image living human eyes.
To overcome these challenges, the researchers improved upon a retinal imaging technique known as adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscopy, which uses deformable mirrors and computational methods to correct for optical imperfections of the eye in real time.
"One might think that more light is needed to get a better image, but we demonstrate that we can improve resolution by strategically blocking light in various locations within our instrument," said Tam. "This approach reduces the overall power of light delivered to the eye, making it ideal for live imaging applications."
For the new approach, the researchers generated a ring-shaped, or hollow, beam of light. Using this type of beam improved the resolution across the photoreceptors but at the expense of depth resolution. To regain the lost depth resolution, the researchers used a small pinhole called a sub-Airy disk to block light coming back from the eye. They showed that this imaging approach could be used to enhance a microscopy technique called non-confocal split-detection, which is used to acquire complementary views of the photoreceptors.
Testing in the clinic
After demonstrating that imaging resolution was improved in theoretical simulations, the researchers confirmed their simulations using various test targets. They then used the new method to image rod and cone photoreceptors in five healthy volunteers at the National Institutes of Health's Clinical Center.
The new approach yielded about a 33 percent increase in transverse resolution and 13 percent improvement in axial resolution compared to traditional adaptive optics scanning light ophthalmoscopy. Using their optimized approach, the researchers were able to see a circularly shaped subcellular structure in the center of cone photoreceptors that could not be clearly visualized previously.
"The ability to noninvasively image photoreceptors with subcellular resolution can be used to track how individual cells change over time," said Tam. "For example, watching a cell begin to degenerate, and then possibly recover, will be an important advance for testing new treatments to prevent blindness."
The researchers plan to image the eyes of more patients with the new technique and use the images to begin to answer fundamental questions linked to rod and cone health. For example, they are interested in visualizing rod and cone health in people who have rare genetic diseases. They say that their imaging approach could be applied to other point scanning-based microscopy and imaging approaches in which it is important to image with low levels of light.
INFORMATION:
The research was supported in part by NEI grants U01 EY025477 and R01 EY025231, and by the Intramural Research Program at the NEI, part of the National Institutes of Health.
Paper: R. Lu, N. Aguilera, T. Liu, J. Liu, J. P. Giannini, J. Li, A. J. Bower, A. Dubra, J. Tam, "In vivo sub-diffraction adaptive optics imaging of photoreceptors in the human eye with annular pupil illumination and sub-Airy detection," Optica 8(3), 333-343 (2021).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1364/OPTICA.414206.
About Optica
Optica is an open-access, journal dedicated to the rapid dissemination of high-impact peer-reviewed research across the entire spectrum of optics and photonics. Published monthly by The Optical Society (OSA), Optica provides a forum for pioneering research to be swiftly accessed by the international community, whether that research is theoretical or experimental, fundamental or applied. Optica maintains a distinguished editorial board of more than 60 associate editors from around the world and is overseen by Editor-in-Chief Prem Kumar, Northwestern University, USA. For more information, visit Optica.
About The Optical Society
Founded in 1916, The Optical Society (OSA) is the leading professional organization for scientists, engineers, students and business leaders who fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate achievements in the science of light. Through world-renowned publications, meetings and membership initiatives, OSA provides quality research, inspired interactions and dedicated resources for its extensive global network of optics and photonics experts. For more information, visit osa.org.
Media Contacts:
Aaron Cohen
(301) 633-6773
aaroncohenpr@gmail.com
mediarelations@osa.org
A team led by scientists at the National Eye Institute (NEI) has noninvasively visualized the light-sensing cells in the back of the eye, known as photoreceptors, in greater detail than ever before. Published in Optica, the researchers report how they improved imaging resolution by a third by selectively blocking the light used to image the eye. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
The achievement is the latest in an evolving strategy to monitor cell changes in retinal tissue that, in turn, will help identify new ways to treat and prevent vision loss from diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in people age ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- Non-O blood type may increase the risk of stroke among women who smoke and take oral contraceptives, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
According to the most recent comprehensive data (January 2020) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States and a major contributor to long-term disability. Some risk factors ...
Rainbows are some of the most spectacular optical phenomena in the natural world and Hawai'i has an amazing abundance of them. In a new publication, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa makes an impassioned case for Hawaii being the best place on Earth to experience the wonder of rainbows. He begins by highlighting the Hawaiian cultural significance of rainbows, he reviews the science of rainbows and the special combination of circumstances that makes Hawai'i a haven for rainbows.
"The cultural importance of rainbows is reflected in the Hawaiian language, which has many words and phrases to describe the variety of manifestations in Hawai'i," said author Steven Businger, professor in the UH ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- Stroke patients were nearly 50% more likely than heart attack patients to develop depression, and female stroke patients had a higher risk of depression than their male counterparts, according to two preliminary studies by the same research group to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
In what researchers described as one of the largest ...
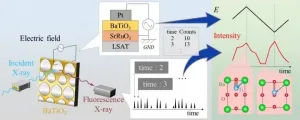
Researchers in Japan have used a novel, ultra-fast technique to explore the fine structure of a potential alternative material to lead titanate, a ferroelectric material widely used for sensors in many everyday devices. Understanding this structure takes us a step closer to eliminating these remaining sources of lead pollution.
The study appeared in the materials science journal Acta Materialia on 21 January.
Ferroelectric materials are used in a wide range of practical applications, from capacitors to memory cells, medical ultrasound to data storage and displays. These materials have a spontaneous polarization, or direction, of their electrons that can be switched back and forth via the application of an electric field, called ferroelectricity.
Worldwide, society is increasingly ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- When NA1, a neuroprotectant, was delivered to the brain in nanoparticles, it reduced stroke severity and improved survival in a mouse model of stroke, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
In an earlier human trial (the ESCAPE-NA1 trial), NA1, a small peptide designed to save brain cells from death after stroke, showed mixed results when NA1 was administered to patients undergoing clot removal for severe ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021-- Stroke survivors may be more likely to attempt or die by suicide than people who have not had a stroke, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health. This study will be simultaneously published in the American Heart Association's journal Stroke.
Rates of depression among stroke survivors range from 28% to 35%, and stroke is considered an independent risk factor for depression. Since depression after a stroke has been associated with increased suicidal ...
Contains updated information not available in the abstract.
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- Having an ischemic stroke increases dementia risk, and that risk escalates with the number and severity of strokes, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
Ischemic stroke is the most common stroke type, accounting for 87% of all strokes. It occurs when a vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed. Stroke is the leading preventable cause ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 — For every 10-minute delay between arrival at the emergency room (ER) and starting stroke treatment, patients with severe strokes may lose eight weeks of healthy life, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
Delays between the onset of stroke symptoms and arrival at the hospital have long been known to cost lives and brain cells.
“Our study showed that delays in treatment at the hospital ...
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 — Pictures of the retina may someday provide early warning signs that a person is at an increased risk of stroke and dementia, making it possible to take preventive measures, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
Studies have shown that people with severe retinopathy, damage to the light-sensing ...