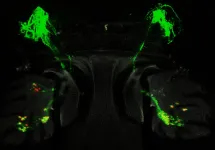
USC Stem Cell scientists start a buzz around fruit flies in hearing research
2021-03-16
(Press-News.org) Even though a fruit fly doesn't have ears, it can hear with its antennae. In a END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Patient wait times reduced thanks to new study by Dartmouth engineers
2021-03-16
The first known study to explore optimal outpatient exam scheduling given the flexibility of inpatient exams has resulted in shorter wait times for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) patients at END ...
In women, higher body fat may protect against heart disease death, study shows
2021-03-16
FINDINGS
A new UCLA study shows that while men and women who have high muscle mass are less likely to die from heart disease, it also appears that women who have higher levels of body fat -- regardless of their muscle mass -- have a greater degree of protection than women with less fat.
The researchers analyzed national health survey data collected over a 15-year period and found that heart disease-related death in women with high muscle mass and high body fat was 42% lower than in a comparison group of women with low muscle mass and low body fat. However, women who had high muscle mass and low ...
While drowning numbers soar, beach safety programs are largely unevaluated
2021-03-16
A global review of coastal drowning science has found there is only one study worldwide that has evaluated beach safety education programs in schools.
Researchers from UNSW's Beach Safety Research Group have conducted the first in-depth review specific to coastal drowning.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, reviewed 146 coastal drowning studies from around the world.
"We found that evaluation of coastal drowning prevention strategies is rare," said William Koon, the lead author of the study and a PhD candidate in the School of Biological, Earth ...
NYU Tandon professor wins NSF CAREER award for promising young researchers
2021-03-16
The National Science Foundation (NSF) selected an NYU Tandon School of Engineering professor who is developing new approaches to training deep learning (DL) artificial intelligence frameworks, to receive its most prestigious award for promising young academics.
Anna Choromanska, an assistant professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering (ECE), received a 2021 NSF Faculty Early Career Development Award, more widely known as a CAREER Award, which supports early-career faculty who have the potential to serve as academic role models in research and education.
A five-year, $532,892 grant will support a project that focuses on new, more efficient ways of training ...
Three-dimensional disadvantage
2021-03-16
The continuous improvement of imaging technology holds great promise in areas where visual detection is necessary, such as with cancer screening. Three-dimensional imaging in particular has become popular because it provides a more complete picture of the target object and its context.
"More doctors and radiologists are looking at these 3D volumes, which are new technologies that allow you to look not just at one image, but a set of images," said UC Santa Barbara psychology professor Miguel Eckstein(link is external), whose expertise lies in the field of visual search. "In some imaging modalities this gives doctors information about volume and it allows them to segment what they're interested in."
Common wisdom is that with all ...
Picking up a book for fun positively affects verbal abilities: Concordia study
2021-03-16
Bring on Twilight. Lee Child's Jack Reacher? Yes, please. More of James Patterson's Alex Cross while we're at it. And let's finish off with revisiting the million-plus words of the Harry Potter saga.
No one will confuse the above book series with high literature. But a new study published in the journal Reading and Writing shows that the more people read any kind of fiction -- even mass market stuff sniffily derided as pulp -- the better their language skills are likely to be.
The piece was written by Sandra Martin-Chang, professor of education in the Faculty of Arts and Science, and PhD student Stephanie Kozak. They found that people who enjoyed reading fiction for leisure and who identified as a reader scored higher on language tests, whereas ...
Meandering rivers create "counter-point bars" no matter underlying geology
2021-03-16
It's not uncommon for crescent-shaped swaths of sand to dot the shorelines of meandering rivers. These swaths usually appear along the inner side of a river bend, where the bank wraps around the sandy patch, forming deposits known as a "point bars."
When they appear along an outer bank, which curves the opposite way, they form "counter-point" bars, which are usually interpreted by geoscientists as an anomaly: a sign that something - such as a patch of erosion-resistant rocks - is interfering with the river's usual manner of sediment deposition.
But according to research led by The University of Texas at Austin, counter-point bars are not the oddities they're often ...
Return to work and the path to recovery after serious injury in Black men
2021-03-16
PHILADELPHIA (March 16, 20201) - After a traumatic injury, returning to work (RTW) can be a strong indication of healing and rehabilitation and may play a pivotal role in promoting physical and functional recovery. But how does RTW after a traumatic injury affect mental health recovery, particularly in individuals who experience social and economic marginalization?
In a new study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing (Penn Nursing), researchers investigated the ways that RTW after an injury predict mental health outcomes in Black men living and recovering in Philadelphia. The study found that men ...
New AI model learns from thousands of possibilities to suggest medical diagnoses & tests
2021-03-16
AI has, for some time, been applied to diagnose medical conditions in specific fields. It can build on knowledge of particular disciplines to hone in on details such as the shape of a tumor that suggests breast cancer or abnormal cells that indicate cervical cancer. While AI is very good when trained on years of human data in specific domains, it has not been able to deal with the huge number of diagnostic tests (about 5000) and disorders (about 14,000) of modern clinical practice. Now, a new algorithm developed by engineers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering can think and learn just like a doctor but with essentially infinite experience.
The work comes out of the lab of Gerald Loeb, a professor ...
Heart-healthy lifestyles linked to lower risk of future cancers
2021-03-16
BOSTON - In addition to lowering risk of heart disease, maintaining a heart-healthy lifestyle may pay off in lower risk for developing cancer, researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and other centers in the United States and the Netherlands have found.
Looking at the potential link between cardiovascular disease (CVD) and cancer among participants in two large population-based health studies, Emily S. Lau, MD, and Jennifer E. Ho, MD, from the division of Cardiology at MGH and their co-authors found that traditional risk factors for CVD, including older age, male ...