(Press-News.org) ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Pharmacogenomics is a valuable tool for health care providers to help prescribe the right drug for the right patient to enhance efficacy and avoid side effects.
A new research paper funded in part by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) shows a clear advantage of genetic testing in helping health care providers choose the appropriate anti-platelet drug. Testing helps determine if a patient carries genetic variants in CYP2C19 that cause loss of its function. These variants interfere with the body's ability to metabolize and activate clopidogrel, an anti-platelet medication.
Anti-platelet drugs are given to prevent complications from blood clotting after a procedure to open clogged arteries. These patients can use one of the various anti-platelet medications, such as clopidogrel, ticagrelor or prasugrel.
Patients with coronary artery disease are typically prescribed clopidogrel to reduce the risk of ischemic events, such as blood clots, stroke, heart attack, recurrent chest pain and death following a percutaneous coronary intervention or stent placement. But people who carry the CYP2C19 genotype that prevents them from activating the drug would benefit from the other anti-platelet medications.
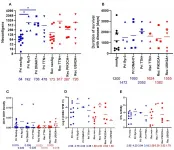
The meta-analysis published in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions sourced more than 1,000 research studies, including seven randomized clinical trials. One of the trials was TAILOR-PCI, a large study funded by the Mayo Center for Individualized Medicine and NHLBI.
Researchers from Mayo Clinic, University of Toronto and several other institutions evaluated data about the effect of the CYP2C19 gene on ischemic events in nearly 16,000 people. The meta-analysis compared patients who were treated with the newer anti-platelet agents ticagrelor or prasugrel, as opposed to clopidogrel.
"Our results suggest that clopidogrel can safely be given to approximately 70% of patients with coronary artery disease following percutaneous coronary intervention," says Naveen Pereira, M.D., a Mayo Clinic cardiologist, and first and corresponding author of the paper. "For patients who do not have the loss-of-function CYP2C19 genotype, there is no difference in using clopidogrel, as compared to ticagrelor or prasugrel. But these data show a 30% risk reduction in ischemic events for patients who are identified by genetic testing to have the loss-of-function CYP2C19 genotype. This information means that with the help of genetic testing, we could safely prescribe generic, well-tolerated, once-daily clopidogrel to most patients and reserve the use of the newer, more expensive drugs ? ticagrelor or prasugrel ? for those with the loss-of-function genetic variants."
Dr. Pereira notes that point-of-care genetic testing for CYP2C19 genetic variants is available and can be used by personnel who are not laboratory-trained. This testing has greater than 99% accuracy in identifying the genetic makeup of patients to guide such treatment. The test is inexpensive and can be administered at the bedside via an oral swab. Results are available in under an hour.
"We are pleased that our decision to fund the TAILOR-PCI study with the NHLBI several years ago will help ensure better and safer care for patients suffering from coronary artery disease, and serve to illustrate the value of genomic testing in the clinic," says Richard Weinshilboum, M.D., a pharmacologist and director of Mayo Clinic's Center for Individualized Medicine.
Knowing that most people can be safely and effectively treated with clopidogrel is useful information for health care providers, and this knowledge has practical benefits. Compared to ticagrelor and prasugrel, clopidogrel is less costly; accepted by most insurance companies; and carries fewer side effects, such as bleeding and shortness of breath.
"This meta-analysis confirms the impact of a pharmacogenomics approach to tailoring anti-platelet therapy in the treatment of coronary artery disease," says Michael Farkouh, M.D., a cardiologist and multinational clinical trials chair at the University Health Network's Peter Munk Cardiac Centre. "We believe this work should inform the next guidelines in the field and warrant further study with other databases." Dr. Farkouh is senior author of the paper.
INFORMATION:
About Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a nonprofit organization committed to innovation in clinical practice, education and research, and providing compassion, expertise and answers to everyone who needs healing. Visit the Mayo Clinic News Network for additional Mayo Clinic news.
Media contact:
Terri Malloy,
Mayo Clinic Public Affairs,
newsbureau@mayo.edu
While scientists have known that creatures may adjust the timing of their daily routines based on starvation and predation, these shifts have only previously been measured based on data from a population at a single point in time. Now, using data collected as 71 elephant seals undertook their foraging migrations across the North Pacific Ocean, researchers report a view of how these animals divide their time between light and darkness to optimize tradeoffs between risks and rewards based on 7 months of data per seal, collected between 2004 and 2012. Their findings refute a hypothesis about how seals prioritize feeding. To better understand how seals divide their time between light ...
The giraffe is a truly puzzling animal. With its exceptional anatomy and suite of evolutionary adaptations, the giraffe is an outstanding case of animal evolution and physiology. Now, an international team of researchers from the University of Copenhagen and Northwestern Polytechnical University in China have produced a high-quality genome from the giraffe and investigated which genes are likely to be responsible for its unique biological features.
The extraordinary stature of the giraffe has led to a long list of physiological co-adaptations. The blood pressure of the giraffe, for instance, is twice as high as in humans and ...
Washington, DC-- Algae colonizing dead coral are upending scientists' ability to accurately assess the health of a coral reef community, according to new work from a team of marine science experts led by Carnegie's Manoela Romanó de Orte and Ken Caldeira. Their findings are published in Limnology and Oceanography.
Corals are marine invertebrates that build tiny exoskeletons, which accumulate to form giant coral reefs. Widely appreciated for their beauty, these reefs are havens for biodiversity and crucial for the economies of many coastal communities. But they are endangered by ocean warming, seawater ...
Information on individuals' mobility--where they go as measured by their smartphones--has been used widely in devising and evaluating ways to respond to COVID-19, including how to target public health resources. Yet little attention has been paid to how reliable these data are and what sorts of demographic bias they possess. A new study tested the reliability and bias of widely used mobility data, finding that older and non-White voters are less likely to be captured by these data. Allocating public health resources based on such information could cause disproportionate harms to high-risk elderly and minority groups.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and Stanford University, appears in the Proceedings of the ...
Oncotarget published "Genomic and neoantigen evolution from primary tumor to first metastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma" which reported that prior work has characterized changes in the mutation burden between primary and recurrent tumors; however, little work has characterized the changes in neoantigen evolution.
These authors characterized genomic and neoantigen changes between 23 paired primary and recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tumors.
Within these tumors, they identified 6 genes which have predicted neoantigens in 4 or more patients.
Within HNSCC tumors examined in this Oncotarget ...
A sustainable, powerful micro-supercapacitor may be on the horizon, thanks to an international collaboration of researchers from Penn State and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. Until now, the high-capacity, fast-charging energy storage devices have been limited by the composition of their electrodes -- the connections responsible for managing the flow of electrons during charging and dispensing energy. Now, researchers have developed a better material to improve connectivity while maintaining recyclability and low cost. ...
(BOSTON) ¬-- Human cells typically transcribe half of their roughly 20,000 genes into RNA molecules at any given time. Just like with proteins, the function of those RNA species not only relies on their abundance but also their precise localization within the 3D space of each cell. Many RNA molecules convey gene information from the cell's nucleus to the protein-synthesizing machinery distributed throughout the cytoplasm (messenger RNAs or mRNAs), others are components of that machinery itself, while still different ones regulate genes and their expression, or have functions that remain to be discovered. Importantly, many diseases including cancer and neurological diseases have signatures that appear as changes in the abundance and distribution of RNAs.
To enable the analysis ...
DALLAS - March 17, 2021 - UT Southwestern researchers have identified the structure of a key member of a family of proteins called nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in three different shapes. The work, published online today in Cell, could eventually lead to new pharmaceutical treatments for a large range of diseases or infections including schizophrenia, lung cancer, and even COVID-19.
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are members of a broader super-family of proteins called Cys-loop receptors that function as ion channels on cell surfaces and are found in the membranes of many cell types. When the right molecule settles ...
From climate change and carbon emissions to biodiversity and global hunger, humanity faces so many challenges that tackling them quickly is a daunting task. One solution that potentially addresses multiple issues could provide the impetus society needs to make significant progress.
An international team of 26 authors, including six at UC Santa Barbara, has just published a study in the prestigious journal Nature offering a combined solution to several of humanity's most pressing challenges. It is the most comprehensive assessment to date of where strict ocean protection can contribute ...
BOSTON - There are several effective interventions to reduce the risk of suicide, the tenth-leading cause of death in the United States, but difficulties in identifying people at risk for suicide and concerns about the potentially high costs of suicide-prevention strategies have hampered their wider use.
But as researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) demonstrate, statistical suicide risk prevention models could be implemented cost-effectively in U.S. health care systems and might help save many lives each year.
By evaluating data on the incidence of suicide and suicide attempts, the costs to society and the health care system of suicide, and the cost and effectiveness of suicide risk-reduction interventions, Eric ...