Recreational blue crab harvest in Maryland higher than current estimates
First statewide tagging study to estimate Maryland's recreational take finds it amounts to 11% of the male commercial take
2021-03-18
(Press-News.org) When it comes to recreational crabbing--one of the most iconic pastimes along Maryland's shores--the current estimate of 8% of "total male commercial harvest" runs just a little too low. Biologists, with local community support, found stronger evidence for the underestimate in the END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
University of Maryland co-publishes the first full reference genome for rye
2021-03-18
As one of the founding members of the International Rye Genome Sequencing Group (IRGSG), the University of Maryland (UMD) co-published the first full reference genome sequence for rye in Nature Genetics. UMD and international collaborators saw the need for a reference genome of this robust small grain to allow for the tracking of its useful genes and fulfill its potential for crop improvement across all major varieties of small grains, including wheat, barley, triticale (a cross between wheat and rye that is gaining popularity), and rye. Following the model of international collaboration used ...
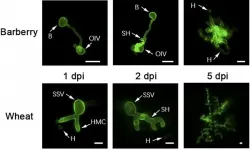
Scientists study co-evolutionary relationship between rust fungi and wheat and barberry
2021-03-18
Wheat stripe rust is one of the most important wheat diseases and is caused by the plant-pathogenic fungi Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst). Though Pst is known to be highly host-specific, it is interestingly able to infect two unrelated host plants, wheat and barberry, at different spore stages. Pst infects wheat through its urediniospores and infects barberry with its basidiospores.
"This complex life cycle poses interesting questions on the co-evolution between the pathogen and the hosts, as well the different mechanisms of pathogenesis underlying the infection of ...
New studies in indigenous languages
2021-03-18
The Journal of Anthropological Research has just published a new article on the development of linguistic documentation among heritage language speakers: "Articulating Lingual Life Histories and Language Ideological Assemblages: Indigenous Activists within the North Fork Mono and Village of Tewa Communities."
Specifically, it focuses on the biographical information of individual speakers, and the significance they place on the language in question. Author Paul V. Kroskrity focused his research on two specific communities - the North Fork Rancheria of Mono Indians in California and the Village of Tewa, First Mesa, Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona ...
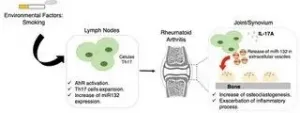
Study finds inflammatory mechanism responsible for bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis
2021-03-18
In a study aimed at investigating the mechanism responsible for exacerbating rheumatoid arthritis in smokers, researchers at the Center for Research on Inflammatory Diseases (CRID), linked to the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil, discovered a novel path in the inflammatory process associated with the bone damage caused by rheumatoid arthritis. The discovery opens up opportunities for new therapeutic interventions to mitigate the effects of the disease, for which there is no specific treatment at this time.
An article on the study is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences ...
Identifying rare genetic variants that increase risk for lung cancer
2021-03-18
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the U.S. for both men and women. While risk for this disease can be influenced by environmental and lifestyle factors like smoking, studies estimate that 18% of lung cancer cases are due to inherited genetic variants. New research led by Baylor College of Medicine investigates how genetic variants contribute to increased risk of lung cancer.
The researchers performed whole exome sequencing on germline (inherited) DNA from eight large-scale datasets, including 1,045 patients with a family history of lung cancer or early-onset cancer. Those groups are more likely to harbor genetic risk variants. The analysis ...
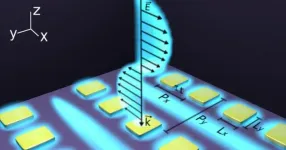
Light it up: uOttawa researchers demonstrate practical metal nanostructures
2021-03-18
Researchers at the University of Ottawa have debunked the decade-old myth of metals being useless in photonics - the science and technology of light - with their findings, recently published in Nature Communications, expected to lead to many applications in the field of nanophotonics.
"We broke the record for the resonance quality factor (Q-factor) of a periodic array of metal nanoparticles by one order of magnitude compared to previous reports," said senior author Dr. Ksenia Dolgaleva, Canada Research Chair in Integrated Photonics (Tier 2) and ...
Medical cannabis can reduce essential tremor: turns on overlooked cells in central nervous system
2021-03-18
Medical cannabis is a subject of much debate. There is still a lot we do not know about cannabis, but researchers from the Department of Neuroscience at the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences have made a new discovery that may prove vital to future research into and treatment with medical cannabis.
Cannabinoids are compounds found in cannabis and in the central nervous system. Using a mouse model, the researchers have demonstrated that a specific synthetic cannabinoid (cannabinoid WIN55,212-2) reduces essential tremor by activating the support cells of the spinal cord and brain, known as astrocytes. Previous research into medical cannabis has focussed on the ...
Study: Progesterone therapy may improve COVID-19 outcomes for men
2021-03-18
LOS ANGELES (March 18, 2021) -- COVID-19 disproportionately affects men compared with women, raising the possibility that a hormone like progesterone may improve clinical outcomes for certain hospitalized men with the disease. New research from Cedars-Sinai published online in the journal Chest supports this hypothesis.
The pilot clinical trial, involving 40 men, is believed to be the first published study to use progesterone to treat male COVID-19 patients whose lung functions have been compromised by the coronavirus. While the findings are promising, larger clinical trials are needed to establish the potential of this experimental therapy, the investigators said.
The study was prompted ...
Stanford study finds that wind energy output increases when people need heat the most
2021-03-18
In response to the recent freeze-inspired power outages in Texas, some politicians blamed the historic blackouts on wind turbines. The dubious, and largely dismissed, claims nevertheless spotlighted an intriguing fact: Texas, the land made famous by oil derricks and wildcatters, now gets a significant portion of its electricity from clean, renewable sources, most notably wind, but also from water and solar - a troika of sustainability known collectively as WWS.
"Texas gets about 20 percent of its electricity from wind alone," says Mark Z. Jacobson, a professor of civil and environmental engineering at Stanford University and senior fellow at the Stanford Woods Institute ...
Enigmatic circling behavior captured in whales, sharks, penguins, and sea turtles
2021-03-18
Technological advances have made it possible for researchers to track the movements of large ocean-dwelling animals in three dimensions with remarkable precision in both time and space. Researchers reporting in the journal iScience on March 18 have now used this biologging technology to find that, for reasons the researchers don't yet understand, green sea turtles, sharks, penguins, and marine mammals all do something rather unusual: swimming in circles.
"We've found that a wide variety of marine megafauna showed similar circling behavior, in which animals circled consecutively at a relatively ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Recreational blue crab harvest in Maryland higher than current estimatesFirst statewide tagging study to estimate Maryland's recreational take finds it amounts to 11% of the male commercial take