'Opposite action' could improve industrial gas separation
A design concept changes how materials separate gaseous mixtures
2021-03-19
(Press-News.org) A more energy-efficient method improves how an industrial gas is purified by reversing the traditional process. The concept was developed and successfully tested by scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) in Japan and colleagues. The findings were reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Acetylene is a gas used in many industries, including as a fuel in welding and a chemical building block for materials like plastics, paints, glass and resins. To produce acetylene, it first needs to be purified from carbon dioxide. Traditionally, this is done by passing the acetylene/carbon dioxide gaseous mixture through a material. Carbon dioxide weakly interacts with the material and so passes through, while acetylene reacts strongly and becomes attached to it. The problem is that the subsequent removal of acetylene from the material takes several energy-consuming steps.
Scientists have been looking for ways to reverse this process, so that acetylene becomes the gas that passes through the material and carbon dioxide is held back. But so far, this has been very challenging.
"A problem is that both gases have similar molecular size, shape and boiling points," explains iCeMS chemist Susumu Kitagawa, who led the study. "Adsorbents that favour carbon dioxide over acetylene do exist but are rare, especially those that work at room temperature."
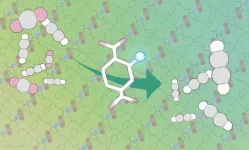
Kitagawa, iCeMS materials chemist Ken-ichi Otake and their colleagues improved carbon dioxide adsorption of a crystalline material called porous coordination polymers by modifying its pores. The team anchored amino groups into the pore channels of two porous coordination polymers. This provided additional sites for carbon dioxide to interact with and attach to the material. The additional interaction site also changed the way acetylene bound to the material, leaving less space for acetylene molecule attachment. This meant that more carbon dioxide and less acetylene was adsorbed compared to the same material that did not have the amino group anchors.
These newly designed materials adsorbed more carbon dioxide and less acetylene compared to other currently available carbon dioxide adsorbents. They also functioned well around room temperature, and performed stably through several cycles.
"This 'opposite action' strategy could be applicable to other gas systems, offering a promising design principle for porous materials with high performance for challenging recognition and separation systems," says Kitagawa.
INFORMATION:
DOI: 10.1002/anie.202016673
About Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS):
At iCeMS, our mission is to explore the secrets of life by creating compounds to control cells, and further down the road to create life-inspired materials.
https://www.icems.kyoto-u.ac.jp/
For more information, contact:
I. Mindy Takamiya/Mari Toyama
pe@mail2.adm.kyoto-u.ac.jp
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-19
Colorectal cancer survivors who maintained a stable body weight but lost muscle and developed fatty deposits in their muscles faced a 40 percent higher risk of premature death than patients who avoided both health issues.
"The conventional wisdom has been that colorectal cancer patients should avoid losing or gaining weight during treatment," said Dr. Justin C. Brown, Assistant Professor and Director of the Cancer Metabolism Program at Pennington Biomedical Research Center. "But maintaining your weight does not mean your body composition remains the same. Muscle can ...
2021-03-19
COVID-19 vaccines being rolled out in the UK are effective in preventing severe disease, but the extent to which they prevent against infection is still unclear.
First modelling study looking at relaxing control measures (eg, mask wearing, physical distancing, and lockdown measures) and planned vaccination rollout in the UK suggests that vaccination alone may not be enough to prevent the spread of infection - with the R number estimated to be 1.58 even if the vaccine prevents 85% of new infections occurring, after vaccine rollout is complete and all other control measures are removed.
Relaxing control measures is highly likely to lead to another wave of infection, ...
2021-03-19
Reporting in the Lancet Psychiatry today, psychologists at the University of Bath highlight that a widely used technique for autism screening is being misused, which may have prevented many people from receiving an autism diagnosis over the past decade.
When individuals with suspected autism are assessed by a GP, a decision to refer them to a specialist for diagnosis is informed by using the Autism Spectrum Quotient. This ten-point scale, known as the 'AQ-10', is an internationally used technique, whereby individuals agree or disagree with statements such as 'I find it difficult to work out people's intentions'. ...
2021-03-18
URBANA, Ill. - Opioid use has dramatically increased in the 21st century, especially among young adults. A new study from the University of Illinois provides insights on usage patterns among Illinois high school students to help inform prevention and treatment strategies.
"The societal and personal costs of opioid misuse are massive. There's been a lot of focus on trying to understand how to combat the current epidemic. But we also need to make sure we have good data in order to know how we should apply our efforts," says Allen Barton, assistant professor in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies at U of I and lead author on the study.
The researchers based their study ...
2021-03-18
Using molecular dating tools and epidemiological simulations, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, with colleagues at the University of Arizona and Illumina, Inc., estimate that the SARS-CoV-2 virus was likely circulating undetected for at most two months before the first human cases of COVID-19 were described in Wuhan, China in late-December 2019.
Writing in the March 18, 2021 online issue of Science, they also note that their simulations suggest that the mutating virus dies out naturally more than three-quarters of the time without causing an epidemic.
"Our study was designed to answer the question of how long could SARS-CoV-2 have circulated in China before it was discovered," said senior author Joel O. Wertheim, PhD, associate professor in the ...
2021-03-18
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- In 2018, physicists showed that something interesting happens when two sheets of the nanomaterial graphene are placed on top of each other. When one layer is rotated to a "magic angle" of around 1.1 degrees with respect to the other, the system becomes a superconductor -- meaning it conducts electricity with zero resistance. Even more exciting, there was evidence that it was an unconventional form of superconductivity -- a type that can happen at temperatures well above absolute zero, where most superconducting materials function.
Since the initial discovery, researchers have been working to understand this exotic state of matter. Now, a research ...
2021-03-18
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute at Texas Children's Hospital (NRI) have identified and characterized two regions of DNA required for the proper expression of Mecp2/MECP2 in mice and humans.
These findings, published in Genes & Development, are helping to shed light on the function of these DNA regions and how they could be potential targets for diagnostic and therapeutic interventions for intellectual disabilities such as Rett Syndrome and MECP2 Duplication Syndrome.
Both of these intellectual disabilities are examples of the importance of precise MeCP2 protein levels for proper brain function. A decrease in this protein leads to Rett Syndrome, while an increase in this protein ...
2021-03-18
A set of surveys fielded last year found that a large majority of U.S. adults support COVID-19 mitigation measures, including indoor mask wearing, social distancing, and contact tracing, with significant differences across certain groups. The surveys, which followed the same people in April, July, and November 2020, were conducted by a team of researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health with colleagues at the SNF Agora Institute at Johns Hopkins University.
Overall public support for COVID-19 mitigation measures was strongest in April 2020 with support remaining high in July and November. The November survey found that 79 percent of U.S. adults supported mask wearing, 78 percent supported social distancing, ...
2021-03-18
While the drug tamoxifen reduces the risk of developing breast cancer and prevents recurrence, the side-effects cause many women to discontinue their treatment. A study involving researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm has now found that a much lower dose than the standard produces a good effect with fewer adverse reactions in women who have yet to enter the menopause. The study, which has been published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, can play a significant role in the treatment of cancer.
The anti-hormone drug tamoxifen has been used for over 40 years to reduce the risk of relapse in women who have been treated for hormone-related ...
2021-03-18
Oncotarget published "Quantitative proteome profiling stratifies fibroepithelial lesions of the breast" which reported that the current grading system remains unreliable in differentiating these tumors due to histological heterogeneity and lack of appropriate markers to monitor the sudden and unpredictable malignant transformation of PTs.
The high- throughput quantitative proteomic analysis suggested that FAD and PTs form distinct clusters away from borderline and malignant though there exist marked differences between them.
Interestingly, over-expression of extracellular matrices related proteins and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in borderline PTs led these authors to hypothesize a model of deposition and degradation leading to ECM remodeling and EMT acquisition ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Opposite action' could improve industrial gas separation
A design concept changes how materials separate gaseous mixtures