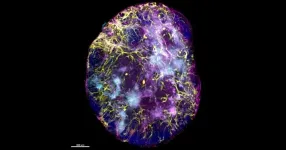
(Press-News.org) A new imaging technique is shining a light on immune responses and setting the scene for enhancing immune memory to optimise vaccine strategies.
By imaging intact lymphoid organs in three dimensions, researchers have been able to identify specialised niches, which can determine how immune T cells function.
The research, published in Nature Immunology, is a step forward in understanding the differentiation of T cells - critical cells for developing strong immune responses - and how we can use these crucial findings to inform and optimise vaccine strategies.
At a glance
Three-dimensional imaging has enabled researchers to identify the factors that play a role in determining where immune memory cells locate to in the lymph node, in response to infection or cancer.
The research identified avenues to therapeutically target effector and memory cells for a host of applications, including vaccine development.
The findings will help inform and optimise future vaccination strategies.
Keeping memory cells at the ready
WEHI researchers Ms Brigette Duckworth and Dr Joanna Groom said the imaging technique could be applied to many different settings.
"By using this type of three-dimensional imaging, we have the power to visualise how and where immune cells decide their fate. There is real interest in understanding these mechanisms, as that gives us clues about how we can therapeutically target them and harness them for a host of applications, including vaccine development," Ms Duckworth said.
The team studied two types of immune cell: effector cells, which fight infections, and memory cells, which 'remember' how to fight specific infections, like viruses, so they can be rapidly cleared if they return in the future.
"These memory cells are particularly important because they keep chronic infections and cancers in check and act rapidly if we see the virus a second time," Ms Duckworth said.
"This work opens the door to harnessing extrinsic factors like vaccines to alter immune cell positioning in the lymph node and potentially direct the exact type of immune response we would like to generate."
Understanding vaccine strategies
Dr Groom said COVID-19 had put vaccines and vaccination strategies in the spotlight and had highlighted the importance of having a better understanding of our immune response to vaccination.
"These memory cells are what we want to generate when we vaccinate. Previously, we have focussed on the overall immune response, but our data suggests that may not be the best strategy," she said.
"A more efficient response might be to specifically direct vaccines towards memory formation because we want those cells to remain long after vaccination and to react when we come in contact with a virus."
Using T cell differentiation to improve the immune response
Dr Groom said the research team had identified factors that played a role in determining where the memory cells locate to in the lymph node.
"We have identified several ways we can modify the direction of the T cell differentiation," she said.
"These modifiers can be used as a lever to control whether we want more effector cells, which is good to overcome an immediate threat, such as cancer; or whether we want to switch to memory cells for longer lasting immunity benefits."
"We are now looking at these targets to identify the therapeutic window of opportunity and pinpointing which cells will be most effective and have the most impact in future vaccination strategies."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported with funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council, a WEHI Centenary Fellowship sponsored by CSL, the Australian Research Council, the Norman, Ann and Graeme Atkins Charitable Trust and the Victorian Government.
Professor Chunghun Lim and his research team in the Department of Biological Sciences unveiled a neuroprotective pathway that suppresses Lou Gehrig's Disease (ALS).
Nucleocytoplasmic transport (NCT) defects have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, such as C9ORF72-associated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (C9-ALS/FTD). In this study, the research team has identified a neuroprotective pathway of like-Sm protein 12 (LSM12) and exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP 1 (EPAC1) that sustains the nucleocytoplasmic ...
A new coating for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), developed by scientists at UNIST promises extended driving for future electric vehicles (EVs). The coating, described in a paper published in the journal Nature Energy, when applied to LIBs is shown to have improved cycling stability even after being charged and discharged more than 500 times. As a result, the development of EV batteries that can drive longer distances with a single battery charge has gained considerable momentum.
Distinguished Professor Jaephil Cho and his research team in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST unveiled ...
Binge drinking in adolescence is associated with changes in the volume of the cerebellum in young adulthood, a new study from the University of Eastern Finland and Kuopio University Hospital shows. Earlier studies have shown that excessive, long-term alcohol consumption causes damage to the cerebellum in adults, but there is very little data on the effects of adolescent drinking on the cerebellum. The findings were published in Alcohol.
The study included 58 young adults aged 21 to 28 years, whose alcohol consumption had been monitored for the previous ten years. Of the participants, 33 had been heavy drinkers since adolescence, while 25 were light drinkers, consuming little or no alcohol at all. All of them were highly functional and had normal ...
An international research collaboration has used an omnidirectional camera attached to humpback whale to reveal how these creatures rest underwater. These findings demonstrate how wide-angle lens cameras can be useful tools for illuminating the ecology of difficult-to-observe animals in detail.
The research group consisted of Assistant Professor Takashi Iwata of Kobe University's Graduate School of Maritime Sciences, Researcher Martin Biuw of the Norwegian Institute of Marine Research, Assistant Professor Kagari Aoki and Professor Katsufumi Sato of the Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo, and Professor Patrick Miller of the University of St. Andrews.
These research results ...
A growing number of studies show that the environmental factors and lifestyle habits of pregnant women play an important role in the health of their child. But how about the semen quality of young men? Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, showed two years ago that only 38% of Swiss men had semne parameters above the thresholds set by the World Health Organisation (WHO) for fertile men. Epidemiologists from the Institut de recherche en santé, environnement et travail (IRSET, Rennes, France), in collaboration with the UNIGE team analyzed the potential impact of endocrine disruptors on semen quality of men whose mothers were working at the early ...
For the first time researchers from Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Radboudumc, Maastricht UMC+ and international colleagues have gained insight into the "hidden genetic defects" of the general European population. This is important because these defects, if inherited from both father and mother, can lead to all kinds of illnesses in their children. Research in the Dutch and Estonian population shows that every person has two to four such hidden genetic defects. In 1 in 100 couples, this leads to a situation with an increased risk of a genetic disease for future children. In the case of consanguinity, even 20 percent of the couples appear to be at high risk. This research is published in The American Journal of Human Genetics and Genetics in Medicine.
The genes of a every ...
Aspergillus fumigatus kills as many people as malaria and tuberculosis, but is less known. It is found "everywhere", for example in the soil or in our compost, but is not normally dangerous to healthy people.
Those who die from it often have a poor immune system or are hospitalized for lung infections, such as covid-19.
Aspergillus also constitutes an increasing problem in agriculture, because the fungus causes deadly infections in both plants and animals. In the same way that many bacteria are resistant to antibiotics, also this fungus is now becoming more and more resistant to the limited repertoire of treatments. It is therefore important to find new ways to fight fungal ...
March 19, 2021, Bristol, UK - A new peer-reviewed study published in the journal Toxicological Research & Application shows acute exposure of a 3D human bronchial tissue model to e-cigarette aerosol has minimal impact on gene expression compared to smoke from combustible cigarettes.
The research involved sub-cytotoxic exposure to cells in a 3D human bronchial model (MucilAirTM) to nicotine-containing vape aerosol, combustible cigarette smoke and fresh air control under strict laboratory conditions.
The highly sensitive Toxicity Testing in the Twenty-First Century (TT21C)-based technique allows researchers to gain a ...
Approximately 8 out of every 10 health professionals in Spain are willing to be vaccinated against COVID-19, according to a study led by researchers from the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC). Published in the open-access journal Vaccines, the study assessed for the first time this population segment's willingness to be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 and concluded that the level of acceptance is higher among physicians than among nursing staff. Among the reasons given by health personnel for not wanting to be immunized, fears about the vaccines' safety and the potential side effects stood out.
Although vaccination is considered to the most effective method for preventing and eradicating viral infections and stopping ...
The risk of being bullied at work is twice as high if you were born abroad. And if you come from a culture that is culturally dissimilar to Sweden's, the risk is even higher. These are the results of a Swedish study from Linköping University that was recently published in The International Journal of Human Resource Management.
Employers in Sweden have a duty to ensure that the workplace is safe, with a healthy atmosphere. Despite this, some employees are treated poorly, excluded and ignored. When such treatment has continued for a longer period, it is defined as bullying.
Researchers at Linköping University wanted to see if people born abroad run a greater risk of being bullied at work.
"Our results show an increased risk of bullying ...