Expressing some doubts about android faces
Researchers at Osaka University study the expressiveness of android faces using motion capture cameras and identify ways in which they still lack the complexity of real human reactions, which may help guide future robot design
2021-03-22
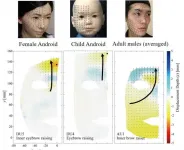
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan - Researchers from the Graduate School of Engineering and Symbiotic Intelligent Systems Research Center at Osaka University used motion capture cameras to compare the expressions of android and human faces. They found that the mechanical facial movements of the robots, especially in the upper regions, did not fully reproduce the curved flow lines seen in the faces of actual people. This research may lead to more lifelike and expressive artificial faces.
The field of robotics has advanced a great deal over the past decades. However, while current androids can appear very humanlike at first, their active facial expressions may still be unnatural and slightly unsettling to us. The exact reasons for this effect have been difficult to pinpoint. Now, a research team at Osaka University has used motion capture technology to monitor the facial expressions of five android faces and compared the results with actual human facial expressions. This was accomplished with six infrared cameras that monitored reflection markers at 120 frames per second and allowed the motions to be represented as three-dimensional displacement vectors.
"Advanced artificial systems can be difficult to design because the numerous components have complex interactions with each other. The appearance of an android face can experience surface deformations that are hard to control," study first author Hisashi Ishihara says. These deformations can be due to interactions between components such as the soft skin sheet and the skull-shaped structure, as well as the mechanical actuators.
The first difference the team found between the androids and adult males was in their flow lines, especially the eye and forehead areas. These lines tended to be almost straight for the androids but were curved for the human adult males. Another major difference was with the skin surface undulation patterns in the upper part of the face.
"Redesigning the face of androids so that the skin flow pattern resembles that of humans may reduce the discomfort induced by the androids and improve their emotional communication performance," senior author Minoru Asada says. "Future work may help give the android faces the same level of expressiveness as humans have. Each robot may even have its own individual "personality" that will help people feel more comfortable."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Comparison between the facial flow lines of androids and humans," was published in Frontiers in Robotics and AI at DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2021.540193
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Although cancers that occur in the gallbladder or bile ducts are rare, their rates are increasing. A recent study provides details on the burden of gallbladder and biliary tract cancer (GBTC) across 195 countries and territories from 1990 to 2017. The findings are published early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Determining GBTC estimates and trends in different global regions can help to guide research priorities and policies for prevention and treatment. With this in mind, a team of scientists examined publicly available information ...
2021-03-22
Patient care by a single primary care physician is associated with many health benefits, including increased treatment adherence and decreased hospital admissions and mortality risk. But can the relationship built between doctor and patient also lead to unnecessary care?
A new University of Florida study finds that male patients who have a single general physician were more likely to receive a prostate cancer screening test during a period when the test was not recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force. The study, which appears in END ...
2021-03-22
When power stations burn coal, a class of compounds called Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, or PAHs, form part of the resulting air pollution. Researchers have found that PAHs toxins degrade in sunlight into 'children' compounds and by-products.
Some 'children' compounds can be more toxic than the 'parent' PAHs. Rivers and dams affected by PAHs are likely contaminated by a much larger number of toxins than are emitted by major polluters, researchers show in Chemosphere.
A coal-fired power station and a cigarette have more in common than one might think. So do the exhaust pipes from cars and burning crop residues. The same is true for an aeroplane passing high over a wildfire ...
2021-03-22
Human actions are threatening the resilience and stability of Earth's biosphere - the wafer-thin veil around Earth where life thrives. This has profound implications for the development of civilizations, say an international group of researchers in a report published for the first Nobel Prize Summit, a digital gathering to be held in April to discuss the state of the planet in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Humanity is now the dominant force of change on planet Earth," according to the analysis published in Ambio, a journal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences.
"The risks we are taking are astounding," says co-author Johan Rockström, director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and co-author of the analysis. "We are at the dawn of what must be a transformative ...
2021-03-22
Study taken throughout the pandemic shows those who feel government should be less controlling believe COVID-19 poses less risk, which in turn was associated with the adoption of fewer protective behaviours
"A fearful population is not necessarily desirable... people may be underestimating or overestimating the actual risk at different times."
People's politics and values are exerting a bigger influence on how much of a threat they feel from COVID-19 compared to objective indicators such as the number of confirmed cases.
That's the finding of a new University of Cambridge survey which measured how attitudes to the coronavirus have varied over the course of 10 months of the pandemic for more ...
2021-03-22
Hearing loss and other auditory problems are strongly associated with Covid-19 according to a systematic review of research evidence led by University of Manchester and NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre (BRC) scientists.
Professor Kevin Munro and PhD researcher Ibrahim Almufarrij found 56 studies that identified an association between COVID-19 and auditory and vestibular problems.
They pooled data from 24 of the studies to estimate that the prevalence of hearing loss was 7.6%, tinnitus was 14.8% and vertigo was 7.2%.
They publish their findings in the International Journal of Audiology.
However, the team - who followed up their review carried out a year ago - ...
2021-03-22
Scientists from the University of Leeds's Nutritional Epidemiology Group used data from 500,000 people, discovering that consuming a 25g serving of processed meat a day, the equivalent to one rasher of bacon, is associated with a 44% increased risk of developing the disease.
But their findings also show eating some unprocessed red meat, such as beef, pork or veal, could be protective, as people who consumed 50g a day were 19% less likely to develop dementia.?
The researchers were exploring a potential link between consumption of meat and the development of dementia, a health condition that affects 5%-8% of over 60s worldwide.
Their results, titled Meat consumption and risk of incident dementia: cohort study of 493888 UK Biobank participants, are published today in the American ...
2021-03-21
WASHINGTON--One in five adults with type 1 diabetes who require in-hospital treatment of the life-threatening condition diabetic ketoacidosis has an unplanned repeat hospital visit within a month and is twice as likely to die during the second hospitalization, a new study finds. The results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, also identified several factors that increased the readmission risk for these patients.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, which can occur from insufficient insulin medicine or from an infection, is a dangerous accumulation of acid in the blood due to ...
2021-03-21
WASHINGTON--A new once-weekly basal insulin injection demonstrated similar efficacy and safety and a lower rate of low blood sugar episodes compared with a daily basal insulin, according to a phase 2 clinical trial. The study results, which will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, compared an investigational drug called basal insulin Fc (BIF) with insulin degludec, a commercially available long-lasting daily insulin, in patients with type 2 diabetes.
"These study results demonstrate that BIF has promise as a once-weekly basal insulin and could be an advancement in insulin therapy," ...
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Some patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease seem to experience inflammation of the thyroid gland that is different from thyroid inflammation caused by other viruses, according to a study presented virtually at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
One-third of the study participants still had signs of thyroid inflammation after three months, even though their thyroid function had normalized. The study is following patients to determine whether this inflammation will trigger permanent thyroid dysfunction.
In spring 2020, 15 percent of the COVID-19 patients hospitalized in acute medicine units ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Expressing some doubts about android faces
Researchers at Osaka University study the expressiveness of android faces using motion capture cameras and identify ways in which they still lack the complexity of real human reactions, which may help guide future robot design

