A project by Russian scientists will help create capsules for targeted drug delivery
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) Scientists from MIPT and ITMO University and their colleagues have studied the formation and growth of crystals from simple organic molecules into large associations. These experiments will help create capsules for targeted drug delivery to specific tissues in the human body. The scientific paper was published in the journal Crystal Growth & Design.
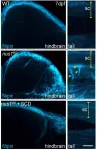
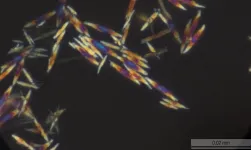
Melamine cyanurate consists of melamine, colourless crystals, and cyanuric acid, whose molecules associate in a similar way to DNA formation. The various studies associated with it could be useful in developing techniques for introducing drugs into crystals with a similar structure. This will enable scientists to conduct experiments on targeted drug delivery, a technology which in the future will allow drugs to go directly to "targets", i.e. specific organ tissues, rather than be distributed throughout the body.
However, there are still many questions about the mechanism of molecular organisation at different stages of crystal growth.
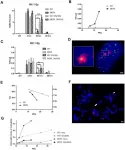
"Our joint work is about an interesting effect: by varying the ratios of the initial components, it is possible to regulate the formation process and the appearance of the melamine cyanurate crystal," says Aleksandra Timralieva, co-author of the study and curator of educational programmes at the Infochemistry Scientific Centre of ITMO University, "We looked at the formation of a supramolecular complex of melamine cyanurate. Its formation directly depends on the local concentration of the components. It turned out that it is the control of proportions that allows us to control the growth of crystals and introduce other substances into them".
The main calculations were done by MIPT scientists.
"One of the main activities of our laboratory at MIPT is molecular dynamics simulation, an approach that allows us to numerically describe and predict the behaviour of each individual atom in some, usually very small, volume of matter. From the computational point of view, such methods are extremely resource-intensive and require high-performance machines that can simultaneously use hundreds and sometimes thousands of individual processors to solve a single problem," explains Nikita Orekhov, deputy head of the Laboratory of Supercomputing Methods in Condensed Matter Physics at MIPT, - "In this work, armed with one of these supercomputers, we have tried to find out which types of intermolecular interactions are responsible for the formation of the primary melamine cyanurate nucleus in aqueous solution, the nanoscale group of molecules from which the crystal will later grow. In our future studies, these data will be useful for a more detailed understanding of the processes that occur during the formation of melamine cyanurate shells or closely related supramolecular complexes around the bioorganic molecules of interest."
The experimental part took place in the laboratories of the Infochemistry Scientific Centre at ITMO University. The researchers studied how a change in concentration of one of the two components affects the formation of melamine cyanurate.
"We plan to conduct model tests with many organic molecules, for instance with antibiotics like tetracycline," explains Alexandra Timralieva. - Several supramolecular structures, especially melamine cyanurate, are very similar in their formation to the way DNA is formed. If we can understand the control of the formation of these structures, then we can move into the realm of the chemistry of the origin of life. The first steps have already been taken".
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio - As psychedelics gain ground as a potential therapy for mental health disorders, there remains a pressing concern that patients in clinical trials may have adverse effects to the drugs.
New research identifies personality traits that have been associated with positive and negative experiences on psychedelics in previous studies, information that could help predict how future clinical trial participants will respond to the drugs.
The findings suggest that people more open to new experiences and willing to surrender to the unknown may be best positioned to have a positive experience on psychedelics, and individuals who tend to be preoccupied or apprehensive could be more likely to have a ...
2021-03-22
ITHACA, N.Y. - As the COVID-19 pandemic took hold in 2020, the list of things people could not do grew increasingly long.
But while going to the office, attending live events and gathering with large groups of friends became difficult or impossible, other activities grew in popularity - including online learning.
Drawing on records from DataCamp, an online platform tailored toward programming skills, a research team at Cornell University and Arizona State University used U.S. states' staggered adoption of nonessential business closures (NBC) to estimate their effects on the demand for online learning. The gradual closure of businesses across the U.S. gave the researchers a way to make a case for the cause and effect of NBC on increased engagement with the DataCamp ...
2021-03-22
Aging-US published "Impact of adiposity on muscle function and clinical events among elders with dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia: a community-based cross-sectional study" which reported that low muscle function determined unfavorable clinical outcome than low muscle mass; nevertheless, comparison of detrimental parameters among dynapenia, presarcopenia and sarcopenia was sparse.
The authors hypothesized that adiposity is implicated in low muscle function related adverse events.
Associations of different obesity parameters, metabolic syndrome and fall among the groups were analyzed.
Among 765 participants, ...
2021-03-22
The COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) published new findings in the Annals of Oncology, showing heightened mortality and racial disparities for patients with cancer diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
After reviewing detailed information from almost 5,000 patients with active or past cancer and laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis, CCC19 study authors found associations among laboratory measures, clinical factors -- including older age, hematological malignancy and recent chemotherapy - and poor clinical outcomes. Of the patients in the study with COVID-19 ...
2021-03-22
Aging-US published "Functional analysis of POLD1 p.ser605del variant: the aging phenotype of MDPL syndrome is associated with an impaired DNA repair capacity" which reported that Mandibular hypoplasia, Deafness and Progeroid features with concomitant Lipodystrophy define a rare systemic disorder, named MDPL Syndrome, due to almost always a de novo variant in POLD1 gene, encoding the DNA polymerase δ.
A decline of cell growth, cellular senescence and a blockage of proliferation in G0/G1 phase complete the aged cellular picture.
Moreover, the rate of telomere shortening was greater in pathological ...
2021-03-22
Researchers at the DZNE (Germany), at Massachusetts General Hospital (USA) and at the genomic medicine company Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. tested a novel gene regulation approach to treat brain diseases such as Alzheimer's in laboratory studies. It leverages zinc finger proteins, which specifically bind to the DNA that codes for the protein Tau without altering it, thereby reducing Tau production in the brain and preventing nerve damage. The preclinical results, published in the journal Science Advances, could lay the foundation for new therapies.
The Tau ...
2021-03-22
The efficacy of biosensors used in clinical tests depends critically on the surface of the device on which the biorecognition molecules are immobilized. This surface can be adjusted and sometimes controlled using self-assembled molecular monolayers as matrices. The monolayers are films made up of organic molecules that under the right conditions assemble spontaneously on metal surfaces via chemical bonds between the sulfur atoms and the metal.
A study conducted at the University of São Paulo's São Carlos Physics Institute (IFSC-USP) in Brazil compared the performances of two types of self-assembled ...
2021-03-22
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a disease of the stem cells in the bone marrow, which disturbs the maturing and differentiation of blood cells. Annually, some 200 Finns are diagnosed with MDS, which can develop into acute leukaemia. Globally, the incidence of MDS is 4 cases per 100,000 person years.
To diagnose MDS, a bone marrow sample is needed to also investigate genetic changes in bone marrow cells. The syndrome is classified into groups to determine the nature of the disorder in more detail.
In the study conducted at the University of Helsinki, microscopic images of MDS patients' bone marrow samples were examined utilising an image analysis technique based ...
2021-03-22
Greenwood, SC (March 22, 2021) - A research team at the Greenwood Genetic Center (GGC) has identified the mechanism that causes movement disorders in patients with mutations in the NUS1 gene. Using both cellular and model organism studies, cholesterol accumulation was found to contribute to the symptoms of seizures, ataxia, and movement abnormalities. This breakthrough study on NUS1, a gene that has also been potentially linked to Parkinson's Disease, is reported in the current issue of Genetics in Medicine, the Journal of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.
Chloe Murphy, 15, of Bluffton, SC began experiencing tremors at age three. Through the years she has also experienced seizures, atypical eye movements, learning delays, ...
2021-03-22
Reston, VA--A new treatment for late-stage neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) has been found to be more effective and have fewer side effects than the current standard of care, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The novel peptide receptor radionuclide therapy holds promise to reduce mortality among NET patients and decrease the financial burden of their continual treatment.
NETs are a diverse group of tumors that originate from the neuroendocrine system, which is responsible for regulating hormones throughout the body. The number of people who are diagnosed with NETs is growing; the incidence of NETs increased 6.4-fold from 1973 to 2012. However, because they are rare, varied, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A project by Russian scientists will help create capsules for targeted drug delivery