INFORMATION:
Partnership with churches increases COVID-19 vaccine delivery among Black population
New approach uses mobile vaccine clinics in church parking lots of Black communities
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Incorporating Black churches and clergy in COVID-19 vaccination education and distribution has been found to be an effective model in helping to increase vaccination delivery to historically at-risk populations in San Bernardino County, a study says.
Focused education efforts and an on-site mobile clinic in Black church parking lots resulted in the vaccinations of 417 people, 84% of whom were Black. The study also found an increase in Black attendance of mass vaccination clinics to 3.6% of total patients, up from 3%, in the week post-initiative.
Researchers at Loma Linda University School of Pharmacy published their findings on March 10 in The Lancet Global Health, highlighting their model that sought to ensure equitable distribution of vaccines among a diverse population. The study, A three-tiered approach to address barriers to COVID-19 vaccine delivery in the Black community, illustrates a method of partnership among Black faith leaders, public health officials, and Black medical professionals that has led to more COVID-19 vaccinations in the Black community.
The initiative was developed in the wake of decades of the Black community's institutional distrust, inadequate access to healthcare, and ultimately, the absence of transparency in vaccine allocation to heavily disparaged areas, which have left them at a disadvantage, researchers said.
"The U.S. is considered a highly religious nation, and prayer, as well as the promotion of medical treatment by religious leaders, has been historically important in establishing trust in healthcare among Black Americans," said Jacinda Abdul-Mutakabbir, PharmD, assistant professor at Loma Linda University School of Pharmacy and first author of the paper. "The pastors' leadership was integral to the success of this initiative, as they are well acquainted and had established direct communication with individuals in the Black community."
Various barriers to vaccination disproportionately affect Black communities, such as access to the internet and computers, and lack of transportation, Abdul-Mutakabbir said. In the United States, particularly in California, the delivery of COVID-19 vaccinations to Black individuals continues to lag significantly behind that of their non-Hispanic white counterparts, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and COVID-19 death rates among Black, Hispanic and Native Americans are three times higher than the rate of white Americans.
Public health officials joined researchers in mobilizing their efforts around Loma Linda University Health's mass vaccination clinics, which is the largest vaccination effort for residents of San Bernardino County. Three major sites deliver approximately 2,000 vaccines a day. Like other nationwide vaccination efforts, the sites in Loma Linda are located in a suburban area, appointments are made online, and vaccines are available to individuals free of charge. Public health officials lamented the low percentage of Black individuals coming through the clinics.
"A more proactive approach was clearly required," Abdul-Mutakabbir said.
Researchers developed relationships with two organizations dedicated to confronting prominent issues in the Black community: Inland Empire Concerned African American Churches (IECAAC) and Congregations Organized for Prophetic Engagement (COPE) to assist Loma Linda University in organizing a COVID-19 faith summit -- a comprehensive COVID-19 information session to gain the pastors' support of the available vaccines.
After the summit, pastors advertised and coordinated educational webinars about the COVID-19 vaccinations, distributed registration paperwork designed to ensure internet access was not a barrier, and managed appointment lists for their community members before they attended the vaccination clinic.
Recognizing the need for intended education measures to decrease COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy, Abdul-Mutakabbir a Black pharmacist with specialized infectious disease training, provided several COVID-19 vaccination webinars before the mobile vaccination clinic date.
Abdul-Mutakabbir also managed transportation of the vaccines to the clinic and ensured each vaccine was properly drawn from the vials before administration to individuals during the clinic visits. These efforts resulted in establishing a trusting environment of familiarity among Black faith leaders and community members.
"The equitable allocation of the COVID-19 vaccines is essential to confronting the racial disparities magnified by the current pandemic," Abdul-Mutakabbir said. "We hope to continue our efforts using the power of faith and science to keep these vulnerable populations healthy and protected from the virus."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study outlines testing strategies for safer air travel during the pandemic
2021-03-23
Almost 90 percent of infectious travelers could be detected with rapid SARS-CoV-2 tests at the airport, and most imported infections could be prevented with a combination of pre-travel testing and a five-day post-travel quarantine that would only lift with a negative test result, according to a computer simulation by UC San Francisco researchers.
The study offers much-needed data to airlines and states that have struggled through a year of the pandemic with little guidance on how to enable safe travel.
The issue is becoming more pressing as states ...
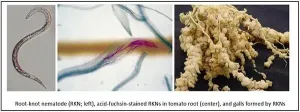
Phytol may be promising for eco-friendly agrochemicals to control root-knot nematodes
2021-03-22
Root-knot nematodes (RKNs, Meloidogyne spp.) infect a broad range of plants, including several agriculturally important species such as cotton, soybean and corn, as well as various vegetables and ornamentals. These parasites cause roots to develop galls that result in severe plant damage and, ultimately, important crop losses. Growers currently use synthetic nematicides to manage RKNs; however, these compounds are detrimental to the microbial diversity of soil and harmful for the environment. Thus, it is necessary to develop alternative sustainable control methods.
"We have been seeking natural compounds that activate plant defense ...
UMass Amherst researchers develop ultra-sensitive flow microsensors
2021-03-22
A team of scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed the thinnest and most sensitive flow sensor, which could have significant implications for medical research and applications, according to new research published recently in Nature Communications.
The research was led by Jinglei Ping, assistant professor of mechanical and industrial engineering, along with a trio of mechanical engineering Ph.D. students: Xiaoyu Zhang, who fabricated the sensor and made the measurement, Eric Chia and Xiao Fan. The findings pave the way for future research on all-electronic, in-vivo flow monitoring in investigating ...
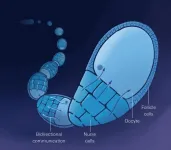
Fruit fly egg takes an active hand in its own growth, highlighting parallels to mammals
2021-03-22
A cast of so-called 'nurse cells' surrounds and supports the growing fruit fly egg during development, supplying the egg -- or 'oocyte' -- with all the nutrients and molecules it needs to thrive. Long viewed as passive in this process, the Drosophila egg actually plays an active role not only in its own growth, but also in the growth of the surrounding nurse cells, Princeton University researchers report on March 21 in Developmental Cell.
"Here we show an example of bidirectional communication -- a dialogue -- between different cells. The egg is taking an active hand in controlling its own feeding ...
A strong coffee half an hour before exercising increases fat-burning
2021-03-22
Scientists from the Department of Physiology of the University of Granada (UGR) have shown that caffeine (about 3 mg/kg, the equivalent of a strong coffee) ingested half an hour before aerobic exercise significantly increases the rate of fat-burning. They also found that if the exercise is performed in the afternoon, the effects of the caffeine are more marked than in the morning.
In their study, published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, the researchers aimed to determine whether caffeine--one of the most commonly-consumed ergogenic substances in ...
Fans prefer teams that built success over time more than with purchased super
2021-03-22
LAWRENCE -- When a franchise buys a superstar like Tom Brady or LeBron James, the team tends to win more games. But do the fans follow? How much team loyalty is purchased along with an expensive star? Maybe not as much as some owners might hope -- in the NBA Finals between the Miami Heat and San Antonio Spurs, many fans expressed their dislike of the "bought" Miami team.
In a new paper published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Applied Social Psychology, researchers at the University of Kansas asked over 1,500 Americans how much they liked teams that purchased excellence and compared that with liking teams that built excellence from the ground up.
"People reliably ...
Scientists develop AI platform to assess blood vessel anomalies and eye disease
2021-03-22
An international team of scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Brown University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has developed an artificial intelligence (AI) platform that could one day be used in a system to assess vascular diseases, which are characterised by the abnormal condition of blood vessels.
The AI-powered platform combines machine learning and a specially-designed microfluidic chip with analysis of 2D video images of blood flow and the application of physical laws, to infer how blood flows in 3D. In tests, it accurately predicted blood flow characteristics such as speed, pressure, and shear stress, ...
Energizing India
2021-03-22
The world needs more electricity. As populations grow, standards of living increase and more people gain access to modern conveniences, countries will need to expand their energy generation capacity.
India, with its rapidly developing economy and a population of more than 1.3 billion, epitomizes this trend. The country finds itself at a crossroads regarding its energy future: Small decisions today will resound in the coming years.
In their latest report, the Indian government set a target of 450 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity by 2030. For comparison, the country's total energy generation capacity today is about 380 gigawatts, out of which 90 gigawatts are of renewable energy, not including large hydropower stations. How this plan shapes up will dictate how ...
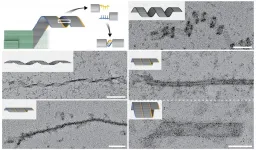
Planting the seed for DNA nanoconstructs that grow to the micron scale
2021-03-22
(BOSTON) -- A team of nanobiotechnologists at Harvard's Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) led by Wyss Founding Core Faculty member William Shih, Ph.D., has devised a programmable DNA self-assembly strategy that solves the key challenge of robust nucleation control and paves the way for applications such as ultrasensitive diagnostic biomarker detection and scalable fabrication of micrometer-sized structures with nanometer-sized features. Using the method, called "crisscross polymerization", the researchers can initiate weaving ...
What early-budding trees tell us about genetics, climate change
2021-03-22
One of the surest signs of spring is the vibrantly lime-green tinge trees develop as their buds open and tiny new leaves unfurl. Bud-break is the scientific name for this process -- a straightforward term for the grand genetic mechanism that allows trees to leaf out and do their summer work of photosynthesis to store up energy for the coming winter.
Bud-break is precluded by bud-set, which occurs in the autumn. After trees have dropped their leaves and as the days shorten and grow colder, new buds grow on branches. Like many wildflowers, trees require a period of dormancy at colder temperatures -- a process fine-tuned by evolution ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Partnership with churches increases COVID-19 vaccine delivery among Black populationNew approach uses mobile vaccine clinics in church parking lots of Black communities