Real-world data at UT Southwestern shows benefit of early vaccination on health care workforce
2021-03-23
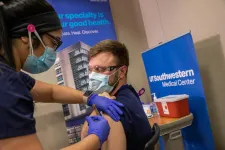
(Press-News.org) DALLAS - March 23, 2021 - Vaccinating health care workers resulted in an immediate and notable reduction of positive COVID-19 cases among employees, reducing the number of required isolations and quarantines by more than 90 percent, according to data at UT Southwestern Medical Center published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Health care workers were among the first groups to be eligible for vaccination.
"Real-world experience with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination at UT Southwestern demonstrated a marked reduction in the incidence of infections among our employees, preserving the workforce when it was most needed," notes Daniel K. Podolsky, M.D., president of UT Southwestern and senior author.
During the first 31 days of vaccinations becoming available, UT Southwestern provided a first dose to 59 percent of roughly 23,000 employees, while 30 percent were able to be fully vaccinated in that time frame. Among the findings:
1.5 percent became infected.
Infection rates were highest - 2.6 percent - among nonvaccinated employees.
Infection rates were lowest - .05 percent - among those fully vaccinated.
"Our ability to quickly vaccinate a majority of our workforce in the midst of what became the largest surge to date in the region made a critical difference in ensuring we were able to continue providing top-flight care while health systems were strained," says John Warner, M.D., executive vice president for health system affairs at UT Southwestern.
Researchers also saw advantages among partially vaccinated individuals, and from Jan. 9, the actual number of positive tests among all UT Southwestern employees was consistently lower than the number projected.
The data also show continued need to address vaccine hesitancy, with UT Southwestern now approaching 70 percent immunization among its workforce.
"In light of this real-world experience clearly demonstrating the effectiveness of immunization, further understanding of the reticence of some individuals to take advantage of vaccination bears even greater importance," says first author William Daniel, M.D., vice president and chief quality officer at UT Southwestern.
UT Southwestern has provided educational outreach to community groups and businesses, developed extensive online resources including Q&As and blogs, and is preparing to launch a multilingual public service announcement campaign to help educate diverse communities about vaccination and address issues of hesitancy.
"It is important to reach out across multiple platforms to effectively address people's questions so that we can continue to make progress on vaccine hesitancy," says Marc Nivet, Ed.D., executive vice president for institutional advancement at UT Southwestern.
INFORMATION:
Dr. Daniel, professor of internal medicine, holds the William T. Solomon Professorship in Clinical Quality Improvement at UT Southwestern Medical Center. Dr. Nivet is associate professor of family and community medicine. Dr. Podolsky, professor of internal medicine, holds the Philip O'Bryan Montgomery, Jr., M.D. Distinguished Presidential Chair in Academic Administration and the Doris and Bryan Wildenthal Distinguished Chair in Medical Science. Dr. Warner, professor of internal medicine, holds the Nancy and Jeremy Halbreich, Susan and Theodore Strauss Professorship in Cardiology and the Jim and Norma Smith Distinguished Chair for Interventional Cardiology.
About UT Southwestern Medical Center
UT Southwestern, one of the premier academic medical centers in the nation, integrates pioneering biomedical research with exceptional clinical care and education. The institution's faculty has received six Nobel Prizes, and includes 23 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 17 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and 13 Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigators. The full-time faculty of more than 2,500 is responsible for groundbreaking medical advances and is committed to translating science-driven research quickly to new clinical treatments. UT Southwestern physicians provide care in about 80 specialties to more than 105,000 hospitalized patients, nearly 370,000 emergency room cases, and oversee approximately 3 million outpatient visits a year.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
ITHACA, N.Y. - New research from Mildred Warner, professor of city and regional planning at Cornell University, shows that state laws designed to hinder union activity and indulge corporate entities do not enhance economic productivity.
"We find that where state policy is captured by corporate interests, this undermines inclusive growth," Warner said. "These interests see union and city power as a threat, which is why there are groups like the American Legislative Exchange Council, for example, focused on crafting state laws that erode labor protections and enhance corporate interests."
The ...
2021-03-23
California's restrictions on vehicle emissions have been so effective that in at least one urban area, Los Angeles, the most concerning source of dangerous aerosol pollution may well be trees and other green plants, according to a new study by University of California, Berkeley, chemists.
Aerosols -- particles of hydrocarbons referred to as PM2.5 because they are smaller than 2.5 microns in diameter and easily lodge in the lungs -- are proven to cause cardiovascular and respiratory problems.
As a result of strict vehicle emissions laws, organic aerosol levels have been significantly reduced throughout the United States, but the drop has been particularly dramatic ...
2021-03-23
Understanding the evolution of the polar sea ice is not enough to study the effects of the climate change on marine ecosystems in Antarctic seafloors. It is also necessary to determine the intensity of phytoplankton local production during the Antarctic summer, as stated in a new study by a research team of the Faculty of Biology and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the University of Barcelona, published in the journal Marine Environmental Research.
When the sea freezes in Antarctica
Extremely low temperatures, strong ocean currents and the broad seasonal coverage of marine ice are factors that determine the features of the Antarctic marine ecosystems. IN particular, the seasonality ...
2021-03-23
The rate of sea-level rise in the 20th century along much of the U.S. Atlantic coast was the fastest in 2,000 years, and southern New Jersey had the fastest rates, according to a Rutgers-led study.
The global rise in sea-level from melting ice and warming oceans from 1900 to 2000 led to a rate that's more than twice the average for the years 0 to 1800 - the most significant change, according to the study in the journal Nature Communications.
The study for the first time looked at the phenomena that contributed to sea-level change over 2,000 years at six sites along the coast (in Connecticut, New York City, New Jersey and North Carolina), using a sea-level budget. A budget enhances ...
2021-03-23
Researchers at North Carolina State University have designed and demonstrated a new system that allows them to remotely monitor the behavior of freshwater mussels. The system could be used to alert researchers to the presence of toxic substances in aquatic ecosystems.
"When mussels feed, they open their shells; but if there's something noxious in the water, they may immediately close their shells, all at once," says Jay Levine, co-author of a paper on the work and a professor of epidemiology at NC State. "Folks have been trying to find ways to measure how widely mussels or oysters open their shells off and on since the 1950s, but there have been a wide variety ...
2021-03-23
All viruses mutate as they make copies of themselves to spread and thrive. SARS-CoV-2, the virus the causes COVID-19, is proving to be no different. There are currently more than 4,000 variants of COVID-19, which has already killed more than 2.7 million people worldwide during the pandemic.
The UK variant, also known as B.1.1.7, was first detected in September 2020, and is now causing 98 percent of all COVID-19 cases in the United Kingdom. And it appears to be gaining a firm grip in about 100 other countries it has spread to in the past several months, including France, Denmark, and the United States.
The World Health Organization says B.1.1.7 is one of several variants of concern along with others that have emerged in South Africa and Brazil.
"The UK, ...
2021-03-23
Many organisms use sunlight to fuel cellular functions. But exactly how does this conversion of solar energy into chemical energy unfold?
In a recent experiment, an international team of scientists, including two researchers from UWM, sought answers using an advanced imaging technique called time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography to watch a pigment found in some marine bacteria as it was exposed to sunlight outside the cell.
For this experiment, the researchers documented, for the first time, the dynamics of the "chloride ion-pumping rhodopsin," an atomic "pump," which is jump-started by sunlight and moves chloride ions unidirectionally into the ...
2021-03-23
DALLAS - March 23, 2021 - It's not just your legs and heart that get a workout when you walk briskly; exercise affects your brain as well. A new study by researchers at UT Southwestern shows that when older adults with mild memory loss followed an exercise program for a year, the blood flow to their brains increased. The results were published online today in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
"This is part of a growing body of evidence linking exercise with brain health," says study leader Rong Zhang, Ph.D., professor of neurology at UTSW. "We've shown for the first time in a randomized ...
2021-03-23
A study of ancient bones shows that Early Neolithic sheep-breeders were faced with high levels of mortality among young animals in their herds. A statistical model, partly developed at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich, allowed the age distribution of the bones to be precisely determined.
In the 8th millennium BCE, early sheep-herders were already aware that the conditions under which their animals were housed had an impact on mortality rates among the lambs. This one result of a study researchers led by Nadja Pöllath (a curator at the State Collection for Anthropology and Palaeoanatomy in Munich), LMU zooarchaeologist Joris Peters (who is also the Director of the state collection) ...
2021-03-23
The BioRescue consortium develops and applies new technological approaches as a last straw for saving critically endangered species such as the northern white rhinoceros. Advanced Assisted Reproductive Technologies (aART) push the boundaries of what can be done to create new offspring. Consequently, new ethical questions regarding the application of these tools arise and need to be answered, and relevant animal welfare issues to be addressed. In order to ensure that the ethical risk assessment matches the technological breakthrough with aART, the BioRescue ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Real-world data at UT Southwestern shows benefit of early vaccination on health care workforce