study: Precautions used to prevent COVID-19 decreased common respiratory illness rates
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) Boston - Wearing masks and physical distancing - two key infection prevention strategies implemented to stop the spread of COVID-19 - may have led to the dramatic decrease in rates of common respiratory viral infections, such as influenza. A study led by researchers at Boston Medical Center (BMC) showed an approximately 80 percent reduction in cases of influenza and other common viral respiratory infections when compared to similar time periods in previous years, before wearing masks, physical distancing, and school closures were implemented to help stop the spread of COVID-19. Published online in Open Forum Infectious Diseases, these results suggest that public health measures used to prevent COVID-19 transmission could be useful in helping prevent other respiratory viral infections.
"We know viruses that cause the common cold and pneumonia are spread through close contact, aerosols and/or droplets, which is why we decided to look into how the measures implemented to prevent the spread of COVID-19 may have impacted the incidence of other common viral respiratory illnesses," said Manish Sagar, MD, an infectious diseases physician and researcher at BMC and the study's corresponding author.
In this retrospective cohort analysis, the researchers analyzed all (inpatient and outpatient) documented respiratory viral infections at BMC for certain time periods between January 1, 2015 and November 25, 2020. These infections were diagnosed using a comprehensive respiratory panel polymerase chain-reaction test, which screens for 20 common respiratory pathogens, and positive results were recorded. Positive and negative results for SARS-CoV-2 tests were excluded from the study given the focus on other common respiratory illnesses prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The year 2020 was divided into two specific periods. The first, referred to as Period 1, represents the time before the implementation of mask wearing, physical distancing and school closures (Weeks 1-10 from Jan. 1 - March 10, 2020). The second, referred to as Period 2, represents the time after the implementation of these practices to stop the transmission of COVID-19 (Weeks 11-46, March 11 - Nov. 25, 2020). The researchers analyzed the number of viral infections during periods 1 and 2 for 2015 - 2019 and compared to the 2020 results.
In 2020 period 2, after the implementation of measures to stop COVID-19, newly detected respiratory viruses were approximately 80 percent lower compared to the same time period from 2015 to 2019. In contrast, in 2020 period 1, before COVID-19 prevention measures, there were more respiratory virus infections compared to 2015 to 2019. Additionally, the phased re-opening in Boston, which occurred around July 20, 2020, was associated with an increase in the detection of rhinovirus infections.
"Our study results may be particularly helpful for developing prevention strategies in settings where respiratory infections are very harmful, such as congregate settings and for the elderly and immunosuppressed," added Sagar, an associate professor of medicine and microbiology at Boston University School of Medicine.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded in part by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
About Boston Medical Center
Boston Medical Center (BMC) is a private, not-for-profit, 514-bed, academic medical center that is the primary teaching affiliate of Boston University School of Medicine. It is the largest and busiest provider of trauma and emergency services in New England. BMC offers specialized care for complex health problems and is a leading research institution, receiving more than $166 million in sponsored research funding in fiscal year 2019. It is the 13th largest funding recipient in the U.S. from the National Institutes of Health among independent hospitals. In 1997, BMC founded Boston Medical Center Health Plan, Inc., now one of the top ranked Medicaid MCOs in the country, as a non-profit managed care organization. Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Medicine are partners in Boston HealthNet - 12 community health centers focused on providing exceptional health care to residents of Boston. For more information, please visit http://www.bmc.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
SAN ANTONIO (March 23, 2021) -- More than half of all health care workers worldwide are experiencing burnout that, if not addressed, could cause many to leave their fields in favor of less-stressful occupations or choose early retirement. And the COVID-19 pandemic has only made it worse.
That's the warning of a surgeon from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio in a letter and a call for global action published March 22 in the Lancet journal EClinicalMedicine.
"A recent survey done in Medscape of nearly 7,500 physicians globally showed that burnout has reached a very high rate," said END ...
2021-03-23
By targeting an enzyme that plays a key role in head and neck cancer cells, researchers from the UCLA School of Dentistry were able to significantly slow the growth and spread of tumors in mice and enhance the effectiveness of an immunotherapy to which these types of cancers often become resistant.
Their findings, END ...
2021-03-23
Researchers have succeeded in revealing the arsenal used by protozoans of the genus Leishmania in human cells to make leishmaniasis more severe, especially in cases of the mucocutaneous variety of the disease, which can cause deformations in patients. The discovery points the way to a search for novel treatments for the disease as well as casting light on a key mechanism involved in other diseases.
The mechanism involves Leishmania, macrophages and a virus that lives endosymbiotically in the parasite and is known as the Leishmania RNA virus (LRV). According to a study published in the journal iScience, the parasite inhibits activation of caspase-11 via LRV-induced autophagy. Caspases are a family of enzymes that ...
2021-03-23
A pilot study from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found evidence of Bartonella infection in the blood of people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
"Researchers have been looking at the connection between bacterial infection and neuropsychiatric disease for some time," says Dr. Erin Lashnits, a former veterinary internist at NC State, current faculty member at the University of Wisconsin and first author of the study.
"Specifically, there has been research suggesting that cat ownership is associated with schizophrenia ...
2021-03-23
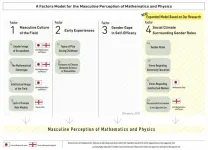
Concern over attractiveness to the opposite sex affects the masculine image of physics and mathematics only in England, while having a negative view of intellectual women is correlated with a masculine image of mathematics as a field only in Japan, according to a survey conducted in the two countries by a Japanese research group. This comparative study shows that programs to increase women's representation in these fields must take into account each country's social context surrounding gender roles.
Why do so few women choose to study and work in STEM (science, technology, ...
2021-03-23
Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) among those who have recently given birth is more common than previously thought, and much of this can be attributed to thoughts of harm related to the baby, new UBC research has found.
The researchers also learned that OCD can go undetected when new parents aren't asked specifically about infant-related harm.
OCD is an anxiety-related condition characterized by the recurrence of unwanted, intrusive and distressing thoughts. If left untreated, it can interfere with parenting, relationships and daily living.
The study estimates that eight per cent of postpartum women report symptoms ...
2021-03-23
ANN ARBOR, Mich., (March 23, 2021) Researchers are urging consumers to avoid using weight loss or sports supplements that list deterenol as an ingredient. Scientists at NSF International (NSF), Harvard Medical School and Cambridge Health Alliance recently tested 17 brands of supplements listing deterenol as an ingredient and found nine potentially harmful, experimental stimulants in the products.
Researchers at the Netherlands' National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM) and Belgium's Sciensano also participated in the study.
Supplements containing deterenol have not been approved for use in humans in the United States and have been linked to reports of adverse events, including nausea, vomiting, sweating, agitation, ...
2021-03-23
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) President and CEO Bruce Stillman has been dissecting DNA replication, a critical step in cell division, since the 1980s. His lab studies how Origin Recognition Complexes--ORCs--coordinate DNA duplication. They discovered how our cells assemble and disassemble ORCs during the cell division cycle. One ORC protein is sequestered into small liquid droplets, keeping it apart until the right time to recruit other proteins and initiate DNA replication.
The ORC recognizes where to initiate replication at numerous locations along the long, linear stretches of DNA ...
2021-03-23
Philadelphia, March 23, 2021 - During the COVID-19 pandemic, Joseph S. Alpert, MD, Editor-in-Chief of The American Journal of Medicine, published by Elsevier, has observed that although non-COVID inpatients suffered from the usual mix of conditions such as heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations, the Internal Medicine inpatient population was distinctly different from what he had seen over the past decades. They were considerably sicker and closer to dying than in the past.
Dr. Alpert has been working on the Internal Medicine, Cardiac Care Unit, and Cardiology consult services. "At ...
2021-03-23
Have you ever wondered why you are able to hear a sentence and understand its meaning - given that the same words in a different order would have an entirely different meaning? New research involving neuroimaging and A.I., describes the complex network within the brain that comprehends the meaning of a spoken sentence.
"It has been unclear whether the integration of this meaning is represented in a particular site in the brain, such as the anterior temporal lobes, or reflects a more network level operation that engages multiple brain regions," ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] study: Precautions used to prevent COVID-19 decreased common respiratory illness rates