(Press-News.org) During the COVID-19 pandemic, people have grown accustomed to wearing facemasks, but many coverings are fragile and not easily disinfected. Metal foams are durable, and their small pores and large surface areas suggest they could effectively filter out microbes. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have transformed copper nanowires into metal foams that could be used in facemasks and air filtration systems. The foams filter efficiently, decontaminate easily for reuse and are recyclable.
When a person with a respiratory infection, such as SARS-CoV-2, coughs or sneezes, they release small droplets and aerosolized particles into the air. Particles smaller than 0.3 μm can stay airborne for hours, so materials that can trap these tiny particles are ideal for use in facemasks and air filters. But some existing filter materials have drawbacks. For example, fiberglass, carbon nanotubes and polypropylene fibers are not durable enough to undergo repeated decontamination procedures, while some further rely on electrostatics so they can't be washed, leading to large amounts of waste. Recently, researchers have developed metallic foams with microscopic pores that are stronger and more resistant to deformation, solvents, and high temperatures and pressures. So, Kai Liu and colleagues wanted to develop and test copper foams to see if they could effectively remove submicron-sized aerosols while also being durable enough to be decontaminated and reused.
The researchers fabricated metal foams by harvesting electrodeposited copper nanowires and casting them into a free-standing 3D network, which was solidified with heat to form strong bonds. A second copper layer was added to further strengthen the material. In tests, the copper foam held its form when pressurized and at high air speeds, suggesting it's durable for reusable facemasks or air filters and could be cleaned with washing or compressed air. The team found the metal foams had excellent filtration efficiency for particles within the 0.1-1.6 μm size range, which is relevant for filtering out SARS-CoV-2. Their most effective material was a 2.5 mm-thick version, with copper taking up 15% of the volume. This foam had a large surface area and trapped 97% of 0.1-0.4 μm aerosolized salt particles, which are commonly used in facemask tests. According to the team's calculations, the breathability of their foams was generally comparable to that of commercially available polypropylene N95 facemasks. Because the new material is copper-based, the filters should be resistant to cleaning agents, allowing for many disinfection options, and its antimicrobial properties will help kill trapped bacteria and viruses, say the researchers. In addition, they are recyclable. The researchers estimate that the materials would cost around $2 per mask at present, and disinfection and reuse would extend their lifetime, making them economically competitive with current products.
The authors acknowledge funding from the END
Copper foam as a highly efficient, durable filter for reusable masks and air cleaners
2021-03-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Creating patterns spontaneously in synthetic materials
2021-03-24
Nature produces a startling array of patterned materials, from the sensitive ridges on a person's fingertip to a cheetah's camouflaging spots. Although nature's patterns arise spontaneously during development, creating patterns on synthetic materials is more laborious. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have found an easy way to make patterned materials having complex microstructures with variations in mechanical, thermal and optical properties -- without the need for masks, molds or printers.
In animals, patterns form before birth ...
Bees form scent-driven phone tree to pass along messages
2021-03-24
Honeybees play a scent-driven game of telephone to guide members of a colony back to their queen, according to a new study led by University of Colorado Boulder. The research, published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, highlights how insects with limited cognitive abilities can achieve complex feats when they work together--even creating what looks like a miniature and buzzing version of a telecommunications network.
The findings also serve as a testament to a honeybee's love for its queen. These matriarchs are the most important members of any hive: They're the only females able ...
Scientists improve a photosynthetic enzyme by adding fluorophores
2021-03-24
Given the finite nature of fossil fuel reserves and the devastating environmental impacts of relying on fossil fuels, the development of clean energy sources is among the most pressing challenges facing modern industrial civilization. Solar energy is an attractive clean energy option, but the widescale implementation of solar energy technologies will depend on the development of efficient ways of converting light energy into chemical energy.
Like many other research groups, the members of Professor Takehisa Dewa's research team at Nagoya Institute of Technology in Japan have turned to biological photosynthetic apparatuses, which ...
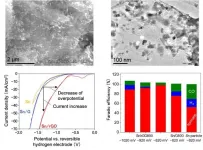
Electrochemical synthesis of formate from CO2 using a Sn/reduced graphene oxide catalyst
2021-03-24
[Background]
Decreasing the emission and efficient utilization (fixation) of carbon dioxide (CO2) are worldwide issues to prevent global warming. Promotion of the use of renewable energy is effective in reducing CO2 emissions. However, since there are large time-dependent fluctuations and large regional differences in renewable energy production, it is necessary to establish a fixation technology to allow efficient energy transportation and storage. Thus, there is increasing interest in technologies for synthesizing useful chemicals from CO2 using electricity derived from renewable energy. ...
Alzheimer's patients' cognition improves with Sargramostim (GM-CSF), new study shows
2021-03-24
A new study suggests that Sargramostim, a medication often used to boost white blood cells after cancer treatments, is also effective in treating and improving memory in people with mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. This medication comprises of a natural human protein produced by recombinant DNA technology (yeast-derived rhu GM-CSF/Leukine®).
The study, from the University of Colorado Alzheimer's and Cognition Center at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus (CU Anschutz), presents evidence from their clinical trial that shows that Sargramostim may ...
Midlife loneliness is a risk factor for Dementia and Alzheimer's disease
2021-03-24
(Boston)--Being persistently lonely during midlife (ages 45-64) appears to make people more likely to develop dementia and Alzheimer's Disease (AD) later in life. However, people who recover from loneliness, appear to be less likely to suffer from dementia, compared to people who have never felt lonely.
Loneliness is a subjective feeling resulting from a perceived discrepancy between desired and actual social relationships. Although loneliness does not itself have the status of a clinical disease, it is associated with a range of negative health outcomes, including sleep disturbances, depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, and stroke. Still, feeling lonely may happen to anyone at some point in life, ...
1º of global warming causes a ~50% increase in population displacement risk
2021-03-24
A new study shows that if the population were fixed at current levels, the risk of population displacement due to river floods would rise by ~50% for each degree of global warming. However, if population increases are taken into account, the relative global flood displacement risk is significantly higher.
The research, by an international team from Switzerland, Germany, and the Netherlands, used a global climate-, hydrology- and inundation-modelling chain, including multiple alternative climate and hydrological models, to quantify the effect of global warming on displacement ...
Once-in-a-century UK wildfire threats could happen most years by end of century
2021-03-24
Extremely hot and dry conditions that currently put parts of the UK in the most severe danger of wildfires once a century could happen every other year in a few decades' time due to climate change, new research has revealed.
A study, led by the University of Reading, predicting how the danger of wildfires will increase in future showed that parts of eastern and southern England may be at the very highest danger level on nearly four days per year on average by 2080 with high emissions, compared to once every 50-100 years currently.
Wildfires need a source of ignition which ...
Deforestation, forest conversion and palm oil plantations linked to disease outbreaks
2021-03-24
Deforestation, certain types of reforestation and commercial palm plantations correlate with increasing outbreaks of infectious disease, shows a new study in Frontiers in Veterinary Science. This study offers a first global look at how changes in forest cover potentially contribute to vector-borne diseases--such as those carried by mosquitos and ticks--as well as zoonotic diseases, like Covid-19, which jumped from an animal species into humans. The expansion of palm oil plantations in particular corresponded to significant rises in vector-borne ...
Meta-analysis shows children prefer people who speak like them
2021-03-24
Research shows that children prefer to befriend, listen to, and imitate people who speak similarly to them. While most of this research has been conducted on monolingual (speaking only one language) children from Western societies, a growing subset of research has begun examining whether this pattern holds for children from more diverse linguistic and cultural backgrounds. A new meta-analysis including studies with monolingual as well as bilingual children helps to shed light on the range of factors that contribute to the development of linguistic-based biases in early childhood. Understanding these patterns can eventually guide efforts to diminish biases based on how one speaks.
The findings were published in a Child Development article written by researchers ...