E. Coli calculus: Bacteria find the derivative optimally
2021-03-24
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Scientists from the Graduate School of Information Science and Technology at The University of Tokyo calculated the efficiency of the sensory network that bacteria use to move towards food and found it to be optimal from an information theory standpoint. This work may lead to a better understanding of bacterial behavior and their sensory networks.
Despite being single-celled organisms, bacteria such as E. Coli can perform some impressive feats of sensing and adaptation in constantly changing environmental conditions. For example, these bacteria can sense the presence of a chemical gradient indicating the direction of food and move towards it. This process is called chemotaxis, and has been shown to be remarkably efficient, both for its high sensitivity to tiny changes in concentration and for its ability to adapt to background levels. However, the question of whether this is the best possible sensing system that can exist in noisy environments, or a suboptimal evolutionary compromise, has not been determined.
Now, researchers from The University of Tokyo have shown that the standard model biologists use to describe bacterial chemotaxis is, in fact, mathematically equivalent to the optimal dynamics. In this framework, receptors on the surface of the bacterium can be modulated by the presence of the target molecules, but this signaling network can be affected by random noise. Once the bacteria determine if they are swimming towards or away from the food, they can adjust their swimming behavior accordingly.
"E. coli can either move in a straight line or randomly reorient via tumbling. By reducing the frequency of tumbling when it senses a positive attractant concentration gradient, the bacterium can preferentially move toward the food," first author Kento Nakamura says.
Using nonlinear filtering theory, which is a branch of information theory that deals with updating information based on a stream of real-time information, the scientists showed that the system used by bacteria is indeed optimal.
"We find that the best possible noise-filtering system coincides with the biochemical model of the E. coli sensory system," explains senior author Tetsuya J. Kobayashi.
The findings of this research may also be applied to sensory systems in other organisms, such as G protein-coupled receptors used for vision. Since all living systems need to be able to sense and react to their environments, this project can help evaluate the efficiency of information filtering more generally.
INFORMATION:
The work is published in Physical Review Letters as "Connection between the bacterial chemotactic network and optimal filtering." (DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.128102).
About Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo
Institute of Industrial Science (IIS), the University of Tokyo is one of the largest university-attached research institutes in Japan.
More than 120 research laboratories, each headed by a faculty member, comprise IIS, with more than 1,000 members including approximately 300 staff and 700 students actively engaged in education and research. Our activities cover almost all the areas of engineering disciplines. Since its foundation in 1949, IIS has worked to bridge the huge gaps that exist between academic disciplines and realworld applications.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-24
Imbued with special electric, mechanical and other physical properties due to their tiny size, nanofibers are considered leading-edge technology in biomedical engineering, clean energy and water quality control, among others. Now, researchers in Italy and UK have developed an automatic process to assess nanofiber fabrication quality, producing 30% more accurate results than currently used techniques.
Details were published on January 2021 in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
"In recent years, nanostructured materials have gained continuously growing interest both in scientific and industrial contexts, because of their research appeal and versatile applications," ...
2021-03-24
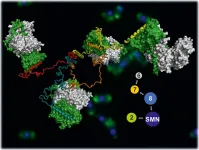
SMN or in full Survival Motor Neuron: Professor Utz Fischer has been analyzing this protein and the large molecular complex of the same name, of which SMN is one of the building blocks, for many years. He holds the Chair of the Department of Biochemistry at the Julius-Maximilian's University of Würzburg (JMU), and he first discovered the molecule during his search for the root cause of spinal muscular atrophy. As scientists found out a few years ago, this disease is caused by a lack of the SNM complex.
The work group around Prof. Fischer has now succeeded in presenting a first three-dimensional model of the ...
2021-03-24
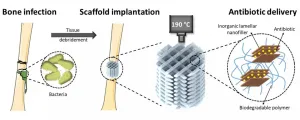
In a ground-breaking first, researchers have fabricated 3D scaffold implants containing antibiotics at high temperatures. These scaffolds not only support bone regeneration but manage the bone infections that can arise as a result of injury or surgery.
Each year, around 4 million people worldwide develop bone infection following an open fracture or surgery. The gold standard treatment consists of a lengthy antibiotic therapy, usually delivered orally or Intravenously, and the removal of infected bone tissue, which often leaves behind a hole too large for the body to fill via normal bone regeneration. In a study published in the KeAi journal Bioactive Materials, a group of researchers from the Netherlands, Italy and Spain, outline a new treatment ...
2021-03-24
A genetic variation that regulates iron metabolism may enhance athletes' endurance performance, researchers at the University of Toronto have shown.
The findings could help explain studies that show an association between the genetic variation and elite athletes across many sports, and may help competitive athletes fine-tune their iron intake to boost performance.
The variation, found in the homeostatic iron regulator (HFE) gene, is a known cause of iron overload, a condition called hemochromatosis in which the body absorbs too much iron leading to organ and joint damage.
Athletes at risk for hemochromatosis but with iron stores below potentially toxic levels could have ...
2021-03-24
Bacteria plucked from a desert plant could help crops survive heatwaves and protect the future of food.
Global warming has increased the number of severe heatwaves that wreak havoc on agriculture, reduce crop yields and threaten food supplies. However, not all plants perish in extreme heat. Some have natural heat tolerance, while others acquire heat tolerance after previous exposure to higher temperatures than normal, similar to how vaccines trigger the immune system with a tiny dose of virus.
But breeding heat tolerant crops is laborious and expensive, and slightly warming entire fields is even trickier.
There is growing interest in harnessing microbes to protect plants, and biologists have shown that root-dwelling bacteria can help their herbaceous ...
2021-03-24
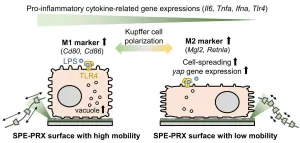
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify biomaterials that can be used to modulate liver immune cell behavior
Tokyo, Japan - Biomaterials are substances, natural or manmade, that are used in medicine to interact with the human body for various purposes, such as wound healing and tissue regeneration. Previous work on biomaterials has shown that they can affect cells in many ways, including how they grow, move, and the type of cell they develop into. Scientists have recently begun investigating biomaterials with properties that can be fine-tuned to optimize their use in regenerative ...
2021-03-24
Usually scaled, the skin of fish can also be naked or made up of bony plates that form an armour, sometimes even covered with teeth. But how has this skin evolved over the ages? To answer this question, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, have reconstructed the evolution of the protective skin structures in fish, going back to the common ancestor of ray-finned fish, more than 420 million years ago. They found that only fish that had lost their scales were able to develop a bony armour, and that the protective state of their skin influenced their choice of open water or sea floor habitats. This study, published in the journal Evolution Letters, provides a new explanation for the incredible ...
2021-03-24
In spring 2020, when the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic hit Finland, older adults drastically reduced their out-of-home activities. During the period of government restrictions, physical exercise was the most common reason to leave home, a recent study at the University of Jyväskylä Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences finds.
"In spring 2020, it was feared that the closure of many activity destinations and the recommendations to avoid close contact with persons from other households put in place by the government would decrease physical activity levels, and thus, negatively affect older adults' physical functional capacity," Senior ...
2021-03-24
The tiger shark is one of the largest predatory sharks known today. This shark is a cosmopolitan species occurring in all oceans worldwide. It is characterized by a striped pattern on its back, which is well marked in juveniles but usually fades in adults.
The fossil history of modern sharks reaches back to the Permian, about 295 million years ago. Complete fossil shark skeletons are very rare - the skeleton, which consists almost entirely of cartilage, is only preserved under very special circumstances during the fossilization processes. Due to the lifelong continuous tooth replacement, most extinct sharks are therefore only known by their well-mineralized teeth, which, nonetheless, can provide deep insights into their evolutionary history.
The ...
2021-03-24
Heavy elements known as the actinides are important materials for medicine, energy, and national defense. But even though the first actinides were discovered by scientists at Berkeley Lab more than 50 years ago, we still don't know much about their chemical properties because only small amounts of these highly radioactive elements (or isotopes) are produced every year; they're expensive; and their radioactivity makes them challenging to handle and store safely.
But those massive hurdles to actinide research may one day be a thing of the past. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley have demonstrated how a world-leading ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] E. Coli calculus: Bacteria find the derivative optimally