(Press-News.org) Researchers Mario Guarracino the HSE Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Networks Analysis in Nizhny Novgorod and Julius ?ilinskas and Algirdas Lančinskas from Vilnius University, have proposed a new method of testing for COVID-19. This group method allows results to be obtained 13 times faster as compared to individual testing of each sample. The research paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The COVID-19 pandemic has already affected millions of people from over 200 countries. The rapid virus expansion demonstrated how fast such infections can spread in today's globalized world. At the beginning of the pandemic, when little was known about the virus and vaccines had not yet been developed, it was possible to slow its spread only by means of limiting the population's mobility. Almost everyone around the world went through various lockdowns and periods of isolation. If large groups of people can be tested quickly, the restrictions can be less strict and more effective at the same time, believe the authors of the paper 'Pooled testing with replication as a mass testing strategy for the COVID-19 pandemics.'
Present COVID-19 testing solutions are based on the extraction of RNA from patients using oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs, and then testing with real?time PCR for the presence of specific RNA filaments identifying the virus. The speed of this approach is limited by the availability of reactants, trained technicians and laboratories.
One way to speed up the testing procedures is group testing, where the swabs of multiple patients are grouped together and tested. The swabs from groups that return a positive result are then tested individually in order to detect specific COVID-19 positive patients. This approach helps decrease the number of tests twofold or more (depending on the spread of the disease) as compared to individual testing of each swab.
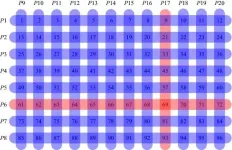
For example, suppose 96 samples should be tested and pools of up to 12 samples are possible. In individual testing, 96 tests are necessary. In pool testing, 8 pools of 12 samples are taken and testing is performed. If the result of one pool is positive, then additional 12 individual tests are needed. If two or three groups return a positive result, 24 or 36 additional tests are required, which, together with the first eight tests, will mean a decrease in the number of tests from two to five times as compared to individual testing.
The researchers believe that the number of tests can be decreased by optimizing the size of groups that takes into account the total number of swabs and the forecasted number of infected individuals. As the number of infected individuals increases, the possibility of saving swabs decreases but is still about 40% in the event of an incidence of 100 positive samples per 1,000, and 18% for an incidence of 200 per 1,000.
There are ways to optimize group testing, such as choosing the optimal group size based on the total number of swabs and the projected level of disease spreading. Another is the binary splitting method, in which a positive group is split into halves and is tested again, until individual positive swabs are detected. The second method, however, is very time-consuming, which decreases its attractiveness during a pandemic.
In addition, to optimize group testing, transposition-based replication is used: after grouping the swabs, researchers form additional control groups from the same swabs and test them together with the main groups. This helps further cut the number of tests, and if the disease levels are low, it also helps to detect positive swabs in one step, which speeds up the testing considerably.
However, this method does not allow for experimenting with group sizes to detect the optimal group size under specific conditions. Researchers from HSE University and Vilnius University suggested OptReplica technology, which uses a more complicated algorithm of swab grouping in key and control groups and helps decrease the number of control groups. In addition, the algorithm helps calculate the optimal group size for the present number of swabs and the forecasted level of disease spreading.
The authors conducted experimental research on samples of 96 and 384 swabs, carrying out 100 randomized tests for each sample size, and compared the effectiveness of transposition-based replication and OptReplica method for different levels of disease incidence. The studies have shown that if the optimal size of groups is chosen, OptReplica is more effective than transposition-based replication. In cases with low incidence, the use of OptReplica, a 13x average reduction of tests can be achieved compared to individual testing without time delay.
'Our simulations are actually proving that using this optimization replication strategy is always advantageous and, even in case of high spread of the disease (10% or 20% of positives in the population), we are still competitive with individual testing strategy', explained Mario Guarracino, Chief Research Fellow of the Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Networks Analysis.
The authors of the new technology suggest using it for asymptomatic populations with seemingly low incidence of coronavirus cases, where it will help detect the infected individuals at a maximum speed with a minimum number of tests, and timely apply the quarantine measures in order to prevent spreading of the disease. In regions with disease incidents over 50 cases per 1,000 tests, the authors suggest using other methods of group replication, or testing without replication.
INFORMATION:
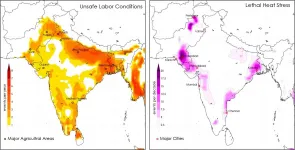
WASHINGTON--Residents of South Asia already periodically experience heat waves at the current level of warming. But a new study projecting the amount of heat stress residents of the region will experience in the future finds with 2 degrees Celsius of warming, the population's exposure to heat stress will nearly triple.
Limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius will likely reduce that impact by half, but deadly heat stress will become commonplace across South Asia, according to the new study in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU's journal publishing high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
With ...
An old technique flexes its muscles
Sarcomeres are small repeating subunits of myofibrils, the long cylinders that bundle together to make the muscle fibres. Inside the sarcomeres, filaments of the proteins myosin and actin interact to generate muscle contraction and relaxation. So far, traditional experimental approaches to investigate the structure and function of muscle tissue were performed on reconstructed protein complexes or suffered from low resolution. "Electron cryo-tomography, instead, allows us to obtain detailed and artefact-free 3D images of the frozen muscle", says Raunser.
Cryo-ET was for a long time an established yet niche methodology. But recent technical advances in electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) as well as the new development of ...
In the heart of black cherry's native range, including a part of the Allegheny Hardwoods that bills itself as the "Black Cherry Capital of the World," the tree's regeneration, growth and survival have all been declining for more than a decade. In a new analysis, a team of USDA Forest Service and University of Missouri scientists identify likely factors behind the tree's decline and, more significantly, conclude that black cherry may be the tip of the iceberg in terms of change in eastern deciduous forests.
Scientists used a combination of synthesis of existing research and new analyses to examine the leading hypotheses for black cherry's regeneration failure. They conclude that the two factors that are ...
Family-centered prevention programs that foster protective caregiving can buffer the negative effects of racial discrimination on young Black people, according to a study published by University of Georgia researchers.
Research shows that Black youth exposed to various levels of racial discrimination--including slurs, threats and false accusations--are at a high risk for poor mental health outcomes such as hopelessness, conduct problems, drug use and depression. After participating in family-oriented programs, high school-age adolescents who encountered high levels of racial discrimination and received supportive caregiving evinced fewer increases in conduct problems and depression/anxiety symptoms two years later.
"This research shows that ...
The high temperatures and pressures of the Earth's mantle forge carbon-rich minerals known as carbonates into diamond. But less is known about the fate of carbonates that travel even deeper underground -- depths from which no sample has ever been recovered.
Now, Michigan State University's Susannah Dorfman and her team are unearthing an answer with lab tools that mimic these extreme conditions.
"What we were interested in is, when is carbon not diamond?" added Dorfman.
In a paper recently published in Nature Communications, scientists in Dorfman's Experimental ...
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have studied for the first time how chemical reactions in clouds can influence the global climate. They found that isoprene, the dominant non-methane organic compound emitted into the atmosphere, can strongly contribute to the formation of organic aerosols in clouds. They published their results today in the journal Science Advances.
Aerosols, a mixture of solid or liquid particles suspended in the air, play an important role in Earth's climate. Aerosols originate either from natural or human sources. They influence Earth's radiation balance by interacting with sunlight and forming clouds. However, their effect remains the single most significant uncertainty ...
CHICAGO -- Immunotherapy, which recruits the body's own immune system to attack cancer, has given many cancer patients a new avenue to treat the disease.
But many cancer immunotherapy treatments can be expensive, have devastating side effects, and only work in a fraction of patients.
Researchers at the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago have developed a new therapeutic vaccine that uses a patient's own tumor cells to train their immune system to find and kill cancer.
The vaccine, which is injected into the skin just like a traditional vaccine, stopped ...
Addressing uncertainties about where large earthquakes are most likely to occur along the southern San Andreas fault, which splits into multiple strands east of Los Angeles, a new study identifies a strand that has largely flown under the radar of public concern as the region's greatest earthquake threat. The study determines that the Mission Creek strand, which passes through major water and power infrastructure for the greater Los Angeles region, may account for almost the entire slip rate of this portion of the fault, suggesting it may actually be the primary Pacific-North American plate boundary fault at this latitude. The San Andreas fault threatens large future earthquakes, since its southernmost section has not ruptured in almost 300 years ...
A 12-centimetre-thick sample of a deposit from a cave in the northeast of Greenland offers unique insights into the High Arctic's climate more than 500,000 years ago. The geologist and cave scientist Prof. Gina Moseley collected it during an exploratory expedition in 2015 for her palaeoclimatic research in one of the most sensitive areas of the world to climate change. The cave is located at 80° North 35 km from the coast and 60 km from the Greenland Ice Sheet margin. It was part of the Greenland Caves Project, funded by 59 different sponsors including the National Geographic Society. Moseley and her team are interested in the climate and environmental history captured by the unique cave deposit. "Mineral deposits formed ...
A study of 49 patients reveals that toxins from the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus can destroy the body's blood-clotting platelets, raising the risk of death during bacterial blood infections. Further experiments in mice also showed that the approved drugs ticagrelor and oseltamivir protected platelets and helped treat infections, suggesting these compounds could be repurposed into badly needed therapies for blood infections. Bacterial blood infections have mortality rates as high as 20% to 30% even with supportive care, and these rates have remained high for decades. Blood infections can also cause complications such as sepsis and endocarditis, and the rise of multidrug resistance has only compounded what was already a serious ...