(Press-News.org) The software tool presents data visually and this allows those without specialist training – both professionals and older people – to better understand and contribute to discussions about the mechanics of movement, known as biomechanics, when carrying out everyday activities.
The software takes motion capture data and muscle strength measurements from older people undertaking everyday activities. The software then generates a 3D animated human stick figure on which the biomechanical demands of the activities are represented visually at the joints. These demands, or stresses, are shown as a percentage of maximum capability through a colour gradient: green is 0 per cent, amber is 50 per cent and red is 100 per cent or maximum stress.
The research shows the new software tool has the potential to improve diagnostic, therapeutic, communication and education procedures by increasing the use and integration of biomechanical expertise in both design and healthcare practices.
The visualisation software could be used to improve the designer's understanding of the different needs when developing products for older people, including enhancing the ergonomic and as well as the functional attributes of products, and improving the design of landscapes and buildings.
In a healthcare setting the tool could be used as part of a range of assessment techniques. It could improve the understanding by different healthcare profession of older people's mobility challenges and improve communication across these professions to provide a more joined-up approach to clinical assessment, diagnosis and rehabilitation.
Commenting on the research, Professor Alastair Macdonald of the Glasgow School of Art, said: "The visualisation software is a simple yet highly effective tool to help older people and professionals explain, discuss and address mobility problems. Better understanding of older people's mobility can help healthcare professionals improve diagnosis or treatment of problems, and design professionals to adapt the way they design for older people."
INFORMATION:
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION, CONTACT
Professor Alastair Macdonald, (Tel: 0141 353 4715, email: a.macdonald@gsa.ac.uk)
ESRC Press Office:
Danielle Moore (Tel: 01793 413122, email: danielle.moore@esrc.ac.uk)
Jeanine Woolley (Tel: 01793 413119, email: jeanine.woolley@esrc.ac.uk)
NOTES FOR EDITORS
1. The project, Innovation in envisioning dynamic biomechanical data to inform healthcare and design guidelines and strategy was led by Professor Alastair Macdonald, School of Design, The Glasgow School of Art. This work was carried out in conjunction with the Bioengineering Unit at the University of Strathclyde, with Journey Associates providing substantial research support.
2. Due to the positive findings from the New Dynamics of Ageing research, The Glasgow School of Art is continuing its collaboration with the University of Strathclyde's Bioengineering Unit through the evaluation of the use of the visualisation method as interventions in a series of Phase II Random Controlled Trials. This new project is funded by the Medical Research Council's Lifelong Health and Wellbeing programme and is being led by Professor Phil Rowe at the University of Strathclyde with Professor Macdonald as a co-investigator.
3. This project is part of the New Dynamics of Ageing Programme which is a seven year multidisciplinary research initiative with the ultimate aim of improving quality of life of older people. The programme is a collaboration between five UK Research Councils, led by the ESRC, and includes EPSRC, BBSRC, MRC, ESRC and AHRC.
4. The visualisation tool was evaluated through a qualitative methodology. For the purposes of evaluating the prototype, two main groups were recruited: 1) older people (N=18); and 2) healthcare and design professionals (N=15). Older participants in the 60+, 70+ and 80+ year old age groups were recruited through the University of Strathclyde's Centre for Lifelong Learning and Age Concern Scotland. The older people were selected to match as closely as possible the cohort of individuals (and their associated age- and health-related conditions) from whom the original biomechanical data for the visualisations were obtained. The range of professions selected comprised clinical medicine, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, bioengineering, disability consultancy, engineering design, and interior design.
5. Research Councils UK (RCUK) is the strategic partnership of the UK's seven Research Councils. We invest annually around £3 billion in research. Our focus is on excellence with impact. We nurture the highest quality research, as judged by international peer review, providing the UK with a competitive advantage. Global research requires we sustain a diversity of funding approaches, fostering international collaborations, and providing access to the best facilities and infrastructure, and locating skilled researchers in stimulating environments. Our research achieves impact – the demonstrable contribution to society and the economy made by knowledge and skilled people. To deliver impact, researchers and businesses need to engage and collaborate with the public, business, government and charitable organisations. www.rcuk.ac.uk
Software improves understanding of mobility problems
2010-12-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Insight offers new angle of attack on variety of brain tumors
2010-12-16
A newly published insight into the biology of many kinds of less-aggressive but still lethal brain tumors, or gliomas, opens up a wide array of possibilities for new therapies, according to scientists at Brown University and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). In paper published online Dec. 15 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, they describe how a genetic mutation leads to an abnormal metabolic process in the tumors that could be targeted by drug makers.
"What this tells you is that there are some forms of tumors with a fundamentally altered ...
Novel therapy for metastatic kidney cancer developed at VCU Massey Cancer Center
2010-12-16
Richmond, Va. (Dec. 15, 2010) – Researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University Massey Cancer Center and the VCU Institute of Molecular Medicine (VIMM) have developed a novel virus-based gene therapy for renal cell carcinoma that has been shown to kill cancer cells not only at the primary tumor site but also in distant tumors not directly infected by the virus. Renal cell carcinoma is the most common form of kidney cancer in adults and currently there is no effective treatment for the disease once it has spread outside of the kidney.
The study, published in the journal ...
Close proximity leads to better science
2010-12-16
Absence makes your heart grow fonder, but close-quarters may boost your career.
According to new research by scientists at Harvard Medical School, the physical proximity of researchers, especially between the first and last author on published papers, strongly correlates with the impact of their work.
"Despite all of the profound advances in information technology, such as video conferencing, we found that physical proximity still matters for research productivity and impact," says Isaac Kohane, the Lawrence J. Henderson Professor of Pediatrics at Children's Hospital ...
Study links increased BPA exposure to reduced egg quality in women
2010-12-16
A small-scale University of California, San Francisco-led study has identified the first evidence in humans that exposure to bisphenol A (BPA) may compromise the quality of a woman's eggs retrieved for in vitro fertilization (IVF). As blood levels of BPA in the women studied doubled, the percentage of eggs that fertilized normally declined by 50 percent, according to the research team.
The chemical BPA, which makes plastic hard and clear, has been used in many consumer products such as reusable water bottles. It also is found in epoxy resins, which form a protective ...
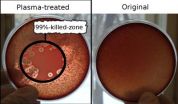
Plasma therapy: An alternative to antibiotics?
2010-12-16
Cold plasma jets could be a safe, effective alternative to antibiotics to treat multi-drug resistant infections, says a study published this week in the January issue of the Journal of Medical Microbiology.
The team of Russian and German researchers showed that a ten-minute treatment with low-temperature plasma was not only able to kill drug-resistant bacteria causing wound infections in rats but also increased the rate of wound healing. The findings suggest that cold plasmas might be a promising method to treat chronic wound infections where other approaches fail.
The ...
MDMA: Empathogen or love potion?
2010-12-16
15 December 2010, MDMA or 'ecstasy' increases feelings of empathy and social connection. These 'empathogenic' effects suggest that MDMA might be useful to enhance the psychotherapy of people who struggle to feel connected to others, as may occur in association with autism, schizophrenia, or antisocial personality disorder.
However, these effects have been difficult to measure objectively, and there has been limited research in humans. Now, University of Chicago researchers, funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, are reporting their new findings in healthy volunteers ...
Sticking to dietary recommendations would save 33,000 lives a year in the UK
2010-12-16
If everyone in the UK ate their "five a day," and cut their dietary salt and unhealthy fat intake to recommended levels, 33,000 deaths could be prevented or delayed every year, reveals research published online in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
Eating five portions of fruit and vegetables a day accounts for almost half of these saved lives, the study shows. Recommended salt and fat intakes would need to be drastically reduced to achieve similar health benefits, say the authors.
The researchers base their findings on national data for the years 2005 ...
Doctors on Facebook risk compromising doctor-patient relationship
2010-12-16
Doctors with a profile on the social networking site Facebook may be compromising the doctor-patient relationship, because they don't deploy sufficient privacy settings, indicates research published online in the Journal of Medical Ethics.
The authors base their findings on a survey of the Facebook activities of 405 postgraduate trainee doctors (residents and fellows) at Rouen University Hospital in France. Half those sent the questionnaire returned it.
Almost three out of four respondents (73%) said they had a Facebook profile, with eight out of 10 saying they had ...
Study classifies and uses artificial proteins to analyze protein-protein interfaces
2010-12-16
Interactions between proteins are at the heart of cellular processes, and those interactions depend on the interfaces where the direct physical contact occurs. A new study published this week suggests that there may be roughly a thousand structurally-distinct protein-protein interfaces – and that their structures depend largely on the simple physics of the proteins.
Believed to be the first systematic study of the nature of the protein-protein interfaces, the research could help explain the phenomena of "promiscuous" proteins that bind to many other proteins. The results ...
p53 determines organ size
2010-12-16
In studies conducted on the fruit fly, researchers at IRB Barcelona headed by ICREA Professor Marco Milán have revealed that organs have the molecular mechanisms to control their proportions. In this process the protein p53 plays a crucial role. The study is published today in the prestigious journal PLoS Biology.
The correct establishment of organ proportions, which occurs during embryonic development, is vital for the proper function of all organisms. Alterations in the mechanisms responsible for these processes cause fatal errors in embryos and even cause their death. ...