Scent of a species
A reversal in sensory processing accompanies ongoing ecological divergence and speciation in Rhagoletis pomonella
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) Apple flies have fascinated scientists right from the mid-19th century, as they are a captivating example of speciation, the beginning of a new species. Correspondence between Charles Darwin and Benjamin Walsh, who observed the apple flies and hawthorn flies in North America, began the rich history of this scientific question in evolutionary biology. When settlers in North America introduced apple trees to the region, what happened within the hawthorn flies to make them shift to this new host plant in the last 300 years?
Continuing the 160-year-old inquiry into the origins of the apple fly, a team of scientists from around the world has just published their research in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B. The researchers span three continents, from the National Centre for Biological Sciences, the University of Trans-Disciplinary Health Sciences and Technology, the University of Notre Dame, Free University Berlin, and Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology. They have been probing the neurological processes which underlie important behavioural changes in the apple fly: preference toward a new host plant and mate choice. These behavioural changes contributed to a rapid shift from hawthorn flies into a derived race of apple-infesting flies.
Hawthorn flies and apple flies are specialist insects, they feed only on a particular fruit, either the hawthorn berries or ripe apples. They also mate on or near the fruit and lay their eggs within it. What is interesting about the apple and hawthorn flies is that each generation emerges with a specific preference for the odour of ripe fruit that they use to locate their host and a strong aversion to the odour of the other fruit. What makes these two races of flies distinct?
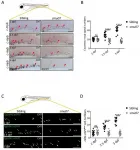
Using recordings of electrical activity and imaging the brains of the flies, the team identified that both apple and hawthorn flies use the same brain regions to process odours, but switch the locations of processing. In other words, where apple flies process the main apple odour (butyl hexanoate) is the same location in the brain where hawthorn flies process the major hawthorn odour (3-methyl-1-butanol), and vice versa. Thus, the locations for preference and aversion to fruit odours stay the same, while the odours that are processed there are inverted.
The scientists were able to locate the specific point where this difference emerges. It is at the very first synapse in the olfactory system, called the antennal lobe. "The most surprising part to me was actually seeing olfactory processing be so clearly different between the apple and hawthorn infesting host races. We knew these flies have divergent odour preference behaviours and patterns of genetic differentiation. Now, from this work we know their sensory neurophysiology differs as well,' says Cheyenne Tait, the first author of the study.
It is possible that a simple shift in the processing of important sensory information might be a major contributor to the diverse species we see. "We are seeing the stuff of speciation. The origin of new species is one of the great questions that has piqued the intellectual curiosity of humankind. Resolving the question of speciation is of great scientific importance and the ongoing evolution of apple and hawthorn host races of Rhagoletis is connected to life itself, or the origin of new life forms," says Jeffrey L. Feder, an expert in evolutionary biology and one of the scientists involved in the study.
Through the change in the neurological processing of the fruit odor, a change at a species scale can be triggered. Shannon Olsson explains her fascination with the flies, "What is most remarkable to me is the simplicity of the switch - these flies simply changed their minds along with their species. Such a subtle shift in the processing of important sensory information in the brain could be contributing to the change in behaviour that helps drive their evolution into new species."
This is not simply a question of the past, or the evolutionary history of one species, "This discovery has important implications for how animals such as insects can quickly adapt and change their behaviour to new environments, such as with invasive species, or respond to human-influenced changes in climate or land use," adds Shannon. Many subfields of biology came together for this study to understand more about these two flies. There is more to discover as scientists tackle evolution from new perspectives and with exciting advances in technology that can be used to study these questions.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-26
Hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) include hematopoietic stem cells and several lineage-biased hematopoietic progenitor cells, which can provide all blood cell types in an adult organism. Among them, hematopoietic stem cells have the ability of self-renewal and multi-lineage differentiation, and can rapidly respond under acute hematopoietic conditions. Meanwhile, the hematopoietic progenitor cells can maintain the supply of blood cells in homeostatic hematopoiesis. In a word, HSPCs are the core of the blood system, once their homeostasis is destroyed, it will lead to serious blood diseases and even death. Therefore, the researches associated with the HSPCs can provide a strong support for relevant ...
2021-03-26
Almost all wild canines in Australia are genetically more than half dingo, a new study led by UNSW Sydney shows - suggesting that lethal measures to control 'wild dog' populations are primarily targeting dingoes.
The study, published today in Australian Mammalogy, collates the results from over 5000 DNA samples of wild canines across the country, making it the largest and most comprehensive dingo data set to date.
The team found that 99 per cent of wild canines tested were pure dingoes or dingo-dominant hybrids (that is, a hybrid canine with more than 50 per cent dingo genes).
Of the remaining ...
2021-03-26
Irvine, Calif., March 25, 2021 -- A short-term intervention in daily fiber consumption can significantly alter the gut microbiome and nutrient intake, according to a study led by University of California, Irvine researchers. The research was recently published by the American Society for Microbiology.
Dietary fiber consists of resistant carbohydrates found in fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Fiber persists in our digestion system, and while not digestible by humans, our gut bacteria can metabolize fiber into short-chain fatty acids and other byproducts critical to human health.
Currently, the average person in North America consumes less than 50 percent of the recommended dietary ...
2021-03-26
Water scarcity is often understood as a problem for regions experiencing drought, but a new study led by Tufts University researchers finds that not only can localized water shortages impact the global economy, but changes in global demand can have positive and negative ripple effects in river basins across the globe.
In addition to Tufts engineers, the team included experts from the Joint Global Change Research Institute at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, and Cornell University.
"We're finding that water scarcity dynamics are more complicated than traditionally acknowledged," said Flannery Dolan, a graduate student ...
2021-03-26
International genomics research led by the University of Leicester has used artificial intelligence (AI) to study an aggressive form of cancer, which could improve patient outcomes.
Mesothelioma is caused by breathing asbestos particles and most commonly occurs in the linings of the lungs or abdomen. Currently, only seven per cent of people survive five years after diagnosis, with a prognosis averaging 12 to 18 months.
New research undertaken by the Leicester Mesothelioma Research Programme has now revealed, using AI analysis of DNA-sequenced mesotheliomas, that they evolve along similar or repeated paths between individuals. These paths predict the aggressiveness and possible therapy of this otherwise incurable cancer.
Professor ...
2021-03-26
Bottom Line: Various genetic alterations in circulating tumor cells (CTCs) were associated with clinical outcomes and resistance to hormone therapy in patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Molecular Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Andrew Armstrong, MD, MSc, a medical oncologist at the Duke Cancer Institute Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancers at Duke University
Background: While only a minority of men with mCRPC have primary resistance to the androgen receptor (AR) inhibitors enzalutamide (Xtandi) or abiraterone acetate (Yonsa or Zytiga), most men will ...
2021-03-26
A study with first-time learners of Japanese has measured how brain activity changes after just a few months of studying a new language. The results show that acquiring a new language initially boosts brain activity, which then reduces as language skills improve.
"In the first few months, you can quantitatively measure language-skill improvement by tracking brain activations," said Professor Kuniyoshi L. Sakai, a neuroscientist at the University of Tokyo and first author of the research recently published in Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience.
Researchers followed 15 volunteers as they moved to Tokyo and completed introductory Japanese classes for at least three hours each day. All volunteers ...
2021-03-26
March 23, 2021-- A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society examines if the source of physician payment for a medical opinion influences whether the physician finds that a coal miner has black lung disease. The study is the first to look at this relationship in the workers' compensation process.
In "Association Between Financial Conflicts of Interest and ILO Classifications for Black Lung Disease," Lee S. Friedman, PhD, associate professor, School of Public Health, Division of Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences, University of Illinois Chicago and colleagues looked at which party reimbursed B-readers--physicians trained and licensed by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and approved by the U.S. ...
2021-03-26
University of Illinois Chicago researchers are the first to report on the financial conflicts of interest that exist among doctors who review the chest X-rays of coal miners who file workers' compensation claims of totally disabling disease with the U.S. Department of Labor's Federal Black Lung Program.
The UIC researchers found that the determinations of these doctors - who are known as B-readers and who are certified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, or NIOSH - were strongly associated with the party that hired them.
By analyzing ...
2021-03-26
X-rays, first used clinically in the late 1890s, could be a leading-edge diagnostic tool for COVID-19 patients with the help of artificial intelligence, according to a team of researchers in Brazil who taught a computer program, through various machine learning methods, to detect COVID-19 in chest X-rays with 95.6 to 98.5% accuracy.
They published their results in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, a joint publication of the IEEE and the Chinese Association of Automation.
The researchers have previously focused on detecting and classifying ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scent of a species
A reversal in sensory processing accompanies ongoing ecological divergence and speciation in Rhagoletis pomonella