Correcting altered brain circuit could tackle coinciding obesity and depression
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) Research has found that obesity and mental disorders such as depression and anxiety seem to often go hand in hand. Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are providing new insights into this association by identifying and characterizing a novel neural circuit that mediates the reciprocal control of feeding and psychological states in mouse models.
Similar to human patients, mice that consumed a high-fat diet not only became obese, but also anxious and depressed, a condition mediated by a defective brain circuit. When the researchers genetically or pharmacologically corrected specific disruptions they had observed within this circuit, the mice became less anxious and depressed and later lost excess body weight.
Interestingly, weight loss was not the result of lack of appetite, but of the animals' change of food preference. Before the treatment, the mice naturally preferred to eat a high-fat diet, but after the treatment they turned their preference toward a healthier diet with reduced fat and abundant protein and carbohydrates. The findings, published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, for the first time, not only reveal a key regulatory mechanism for coinciding obesity and mental disorders, but also suggest the possibility of a pharmacological treatment.
"Reports indicate that 43% of adults with depression are obese and that adults with mental illness are more likely to develop obesity than those who are mentally healthy," said corresponding author Dr. Qi Wu, a Pew Scholar for Biomedical Sciences, Kavli Scholar and assistant professor in pediatrics-nutrition at Baylor's Children's Nutrition Research Center. "Factors such as hormonal dysregulation, genetic deficiency and inflammation have been proposed to be involved in the connection between obesity and mental disorders. Here we provide evidence that supports the involvement of a neural component."
To investigate the neuronal circuits that could be involved in reciprocally regulating weight gain and depression or anxiety, the researchers provided mice with a high-fat diet. As expected, the animals became obese. They also developed anxiety and depression. In these mice, the team studied the function of neuronal circuits.
"We discovered in normal mice that two groups of brain cells, dBNST and AgRP neurons located in separate brain areas, form a circuit or connection to each other by extending cellular projections," said co-first author Dr. Guobin Xia, postdoctoral associate in the Wu lab. "This newly discovered circuit was malfunctioning in mice that were both obese and depressed."
"Using genetic approaches, we identified specific genes and other mediators that were altered and mediated the circuit's malfunction in the obese and depressed mice," said co-first author Dr. Yong Han, postdoctoral associate in the Wu lab.
"Importantly, genetically restoring the neural defects to normal eliminated the high fat diet-induced anxiety and depression and also reduced body weight," Xia said. "We were surprised to see that the animals lost weight, not because they lost their appetite, but because genetically-aided readjustment of the mental states changed their feeding preference from high-fat to low-fat food."
"Keeping in mind translational applications of our findings to the clinic, we investigated the possibility of restoring the novel circuit pharmacologically," Wu said. "We discovered that the combination of two clinically-approved drugs, zonisamide and granisetron, profoundly reduced anxiety and depression in mice and promoted weight loss by synergistically acting upon two different molecular targets within our newly identified brain circuit. We consider that our results provide convincing support for further studies and future clinical trials testing the value of a cocktail therapy combining zonisamide and granisetron (or a selection of their derivatives) to treat metabolic-psychiatric diseases."
INFORMATION:
Other contributors to this work include Fantao Meng, Yanlin He, Dollada Srisai, Monica Farias, Minghao Dang, Richard D. Palmiter and Yong Xu. The authors are affiliated with one of the following institutions: Baylor College of Medicine, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and University of Washington, Seattle.
This work was supported by NIH grants (1R01DK109194, 1R56DK109194, R01DK093587, R01DK101379, R01DK117281, and R01-DA24908), Pew Charitable Trust awards, American Diabetes Association awards (7-694 13-JF-61, 1-17-700 PDF-138), American Heart Association awards (17GRNT32960003), USDA/CRIS grants (3092-5-001-059), Baylor Collaborative Faculty Research Investment Program grants and Faculty Start-up grants from USDA/ARS. Further support was provided in part by NIH Centers of Biomedical Research Excellence, COBRE grant (P20 GM135002), IDDRC Grant Number U54HD083092 from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development, the Clinical and Translational Proteomics Service Center at the University of Texas Health Science and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-26
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) cause oxidative stress at the cellular level. Research shows that this way, amongst others, they inhibit the germination capacity of plants, produce cytotoxins or exert toxic effects on aquatic invertebrates. Environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFR) are potential precursors of ROS because they can react with water to form these radical species. "Therefore, EPFR are associated with harmful effects on the ecosystem and human health," explains Gabriel Sigmund, the lead investigator of the study.
"Our study shows that these environmentally persistent free radicals ...
2021-03-26
Colorectal cancer risk does not rise after bariatric surgery, a study from the University of Gothenburg shows. This finding is important for patients with obesity, and their healthcare professionals, when deciding upon such an operation.
Obesity is a known risk factor for several types of cancer, including colorectal cancer (affecting the colon or rectum). It is already established that bariatric surgery leads to a decrease in overall cancer risk in patients with obesity.
However, some studies on colorectal cancer have shown an elevated cancer risk after bariatric surgery, while others have reported a risk reduction. ...
2021-03-26
The immune systems of all vertebrates contain specialized cells, called T cells, that play a fundamental role in protecting against fungal, bacterial, parasitic and viral infections. T cells use 'molecular sensors' called T cell receptors (TCRs) on their surface that can detect and eliminate the invading pathogens. For most of the past four decades, it was considered that there were only two T cell lineages, αβ and γδ T cells, characterized by their cell surface expressed αβ and γδ TCRs, respectively.
In a paper published today in Science, an international team of scientists at the University of New Mexico (US), Monash University (Australia), and the US National Institutes of Health, has defined a novel T cell lineage, called γμ ...
2021-03-26
Renewable energy demand and consumption is at an all-time high in the United States.
Shrub willow - a quick-growing woody crop - can be an excellent source of renewable bioenergy. The crop is harvested and turned into wood chips, which can be used for heat, mulch, animal bedding, biochar, and biofuel.
In a new study, researchers grew shrub willow on a semi-commercial scale to better understand the nuances of this bioenergy crop. The research was published in Agronomy Journal, a publication of the American Society of Agronomy.
"We learned and developed key know-hows that we can transfer to industry partners interested in this crop," says Armen Kemanian. Kemanian is a member of the American Society of Agronomy and is the ...
2021-03-26
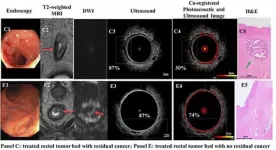
Rectal cancer, along with colon cancer, is the third-most common type of cancer in the United States, and treatment and surgery greatly affect the quality of life of patients. A multi-disciplinary team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed and tested an innovative imaging technique that is able to differentiate between rectal tissues with residual cancers and those without tumors after chemotherapy and radiation, which could one day help to avoid unnecessary surgeries in some patients who have achieved complete tumor destruction after chemoradiation.
Quing Zhu, PhD, professor of biomedical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering, and members of her lab developed ...
2021-03-26
The Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) revised its methods paper and published the German original version "Allgemeine Methoden 6.0" (General Methods 6.0) on http://www.iqwig.de in November 2020. This document is the basis for the scientific work of the Institute and its external experts as well as for the collaboration with its contracting agencies, the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) and Federal Ministry of Health (BMG). The English translation is now available on http://www.iqwig.de/en/about-us/methods/methods-paper/.
New features include statements on the investigation of the relationship between volume of services and quality, a section on different treatment periods in studies, and a more concrete approach to the assessment of clinical relevance.
In ...
2021-03-26
Scientists have developed a method to use lasers to control the movement of nanodiamonds with fluorescent centers.
Scientists have long been working on improving their ability to use lasers to move small objects without actually touching them. This method of 'optical trapping and manipulation' is already utilized in optics, biological sciences and chemistry. But objects become much more difficult to control once they grow to nanoscale size.
Now, a team of scientists including Hokkaido University's Keiji Sasaki and Osaka Prefecture University ...
2021-03-26
Leesburg, VA, March 26, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), updated United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lung cancer screening (LCS) guidelines based solely on age, pack-years, and quit-years perpetuate eligibility disparities among racial and ethnic minorities, although incorporating certain risk prediction models may help reduce such inequalities.
By pulling data from the 2015 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), Journal of the National Cancer Institute researchers (Landy et al.) were able to "estimate the effects of USPSTF-2020 guidelines on disparities in LCS eligibility for the non-institutionalized civilian US population," wrote Massachusetts ...
2021-03-26
The Basques are a unique population in Western Europe; their language is not related to any Indo-European language. Furthermore, genetically speaking, they have been considered to have distinct features. However, until now there was no conclusive study to explain the origin of their singularity.
Now, an international research team led by UPF has confirmed that the Basques' genetic uniqueness is the result of genetic continuity since the Iron Age, characterized by periods of isolation and scarce gene flow, and not its external origin in respect of other Iberian populations.
The study, led by David Comas, principal investigator at UPF and at the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE: CSIC-UPF), has involved ...
2021-03-26
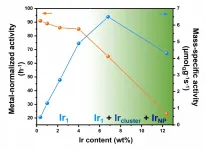
Atomically dispersed catalysts have received extensive research attention, because they exhibit excellent activity and unique selectivity for many important catalytic reactions. The atomically dispersed nature of these metal catalysts confers their unique electronic structures as well as designated coordination-unsaturated environments for the optimized adsorption/activation of the reactants. One grand challenge faced by these atomically dispersed catalysts is that the supported isolated metal \atoms are usually thermally unstable and tend to aggregate into large clusters/particles at evaluated reaction temperatures. As a result, most reported atomically dispersed catalysts have an extremely low metal loading below ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Correcting altered brain circuit could tackle coinciding obesity and depression