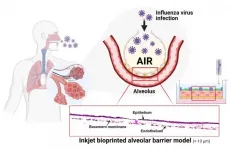
3D-printed artificial lung model
2021-03-26
(Press-News.org) The warmer temperature and blooming flowers signal the arrival of spring. However, worries about respiratory diseases are also on the rise due to fine dust and viruses. The lung, which is vital to breathing, is rather challenging to create artificially for experimental use due to its complex structure and thinness. Recently, a POSTECH research team has succeeded in producing an artificial lung model using 3D printing.
Professor Sungjune Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Professor Joo-Yeon Yoo and Ph.D. candidate Dayoon Kang of the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH have together succeeded in creating a three-dimensional lung model containing a variety of human alveolar cell lines using inkjet bioprinting. Inkjet bioprinting is attracting attention for enabling the production of standardized and patient-customized tissues, and is anticipated to replace conventional test models as it can be mass-produced. The findings of this study were recently published in Advanced Science.
Human lungs constantly breathe to take in oxygen necessary for vital activity and expel carbon dioxide generated as a by-product. Oxygen entering the body arrives at the alveoli through the airways and is replaced with carbon dioxide carried by blood through the capillaries of the alveoli.
Here, the alveoli are made of a thin layer of epithelial cells and are surrounded by thin capillaries that mimic hollow grapes. The alveolar membrane, through which oxygen and carbon dioxide travel, is a three-layered structure of epithelial/basement membrane/endothelial capillary layer and is very thin for ease of gas exchange process. Until now, there have been limitations in accurately replicating alveoli with such thin and complex structure.
To this, the research team fabricated a three-layer alveolar barrier model with thickness of about 10 micrometers (μm) through high-resolution deposition of alveolar cells using drop-on-demand1 inkjet printing. This newly produced model showed higher degree of simulation compared to a two-dimensional cell culture model as well as a three-dimensional non-structured model cultured from mixing alveolar cells and collagen.
The research team also confirmed that the newly developed alveolar barrier model similarly reproduced the physiological response at the actual tissue level in regards to viral infectivity and antiviral response. When this model was used as an influenza virus infection model, the researchers were able to observe the self-proliferation and antiviral response of the virus.
"We have been printing cells and fabricating tissues using the bioprinting method, but this is the first time in the world to simulate an alveolar barrier with a three-layer structure of about 10 μm thickness," explained Professor Sungjune Jung of POSTECH. "It is also the first time an artificial alveolar barrier was infected with a virus and a physiological antiviral response was observed."
Professor Jung added, "The artificial tissue produced this time can be used as an early platform for evaluating efficacy of therapeutic drugs and vaccines countering infectious respiratory viruses - including the COVID-19 virus - as it enables mass production and quality control as well as fabrication of patient-customized disease models."
INFORMATION:
This study was conducted with the support from the Mid-career Researcher Program, Leading Research Center Program, and the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-26
Key takeaways
Surgery is an underused treatment for certain pancreatic cancer patients.
Patients with pancreatic cancer who underwent surgery after chemotherapy lived nearly twice as long as those treated with only chemotherapy.
Findings confirms current recommendations for stage II pancreatic cancer: survival improves when patients receive multimodality therapy, chemotherapy before and/or after surgery.
All analyses of the data delivered the same findings.
CHICAGO (March 26, 2021, 9:00 am CDT): Patients with stage II pancreatic cancer who are treated with chemotherapy followed by resection (an operation that removes the cancerous part of the organ, structure or tissue) live nearly twice as long as patients who receive only chemotherapy, according ...
2021-03-26
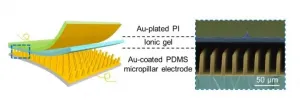
In recent years, with the rapid development of flexible electronic skins, high-performance flexible tactile sensors have received more attention and have been used in many fields such as artificial intelligence, health monitoring, human-computer interaction, and wearable devices. Among various sensors, flexible capacitive tactile sensors have the advantages of high sensitivity, low energy consumption, fast response, and simple structure. Sensitivity is an important parameter of the sensor. A common way to improve sensitivity is to introduce microstructures and use ionic dielectric materials at the interface ...
2021-03-26
A new catalyst for the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into chemicals or fuels has been developed by researchers at Ruhr-Universität Bochum and the University of Duisburg-Essen. They optimized already available copper catalysts to improve their selectivity and long-term stability. The results are described by the team led by Dr. Yanfang Song and Professor Wolfgang Schuhmann of the Bochum Center for Electrochemistry with the team led by Professor Corina Andronescu of the Duisburg-Essen Technical Chemistry III group in the journal Angewandte Chemie, published online on 9 February 2021.
Boron makes copper catalyst stable
The ...
2021-03-26
Current approaches to a common and debilitating knee injury that occurs more frequently for women than men have focused for too long on biology at the expense of understanding social factors, say the authors of a new paper in the British Journal of Sports Medicine (BJSM).
Girls and women are said to be between three to six times more likely to suffer an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, where one of the key ligaments that helps to stabilise the knee joint is damaged. The devastating injury, which in extreme cases can be career ending for professional sportspeople, commonly occurs during sports that involve sudden changes in direction (e.g. basketball, football ...
2021-03-26
When the brain suffers injury or infection, glial cells surrounding the affected site act to preserve the brain's sensitive nerve cells and prevent excessive damage. A team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin have been able to demonstrate the important role played by the reorganization of the structural and membrane elements of glial cells. The researchers' findings, which have been published in Nature Communications*, shed light on a new neuroprotective mechanism which the brain could use to actively control damage following neurological injury or disease.
The nervous system lacks the ability to regenerate nerve cells and is therefore particularly vulnerable to injury. Following brain injury or infection, various cells ...
2021-03-26
An elusive whale species in the Southern Ocean could be resilient to near-future ecosystem changes, according to a new study by the universities of Exeter and Copenhagen.
Gray's beaked whales living in the deep oceans of the Southern Hemisphere are rarely seen alive and their ecology has remained a mystery to scientists until now.
The study used genome sequencing of 22 whales washed up on beaches in South Africa, Australia and New Zealand to investigate the history of the population over the past 1.1 million years.
Author of the study Dr Kirsten Thompson, of the University of Exeter, said: "The population approximately doubled about 250 thousand years ago, coinciding with a period of increased Southern Ocean productivity, sea surface temperature and a potential ...
2021-03-26
Nanowires are vital components for future nanoelectronics, sensors, and nanomedicine. To achieve the required complexity, it is necessary to control the position and growth of the metal chains on an atomic level. In the journal Angewandte Chemie, a research team has introduced a novel approach that generates precisely controlled, helical, palladium-DNA systems that mimic the organization of natural base pairs in a double-stranded DNA molecule.
A team from Europe and the USA led by Miguel A. Galindo has now developed an elegant method for producing individual, continuous chains of palladium ions. The process is based on self-organized assembly of a special palladium complex ...
2021-03-26
A new study analyzes the larval dispersal of nine fish species in the western Mediterranean and identifies three large areas in which there is barely fish exchange, so fish would remain in the same area all their life.
The study, published in the journal Progress in Oceanography, is led by experts of the Faculty of Biology of the University of Barcelona and the Biodiversity Research Institute (IRBio) of the UB, the Blanes Center for Advanced Studies (CEAB-CSIC), the Balearic Islands Coastal Observing and Forecasting System (ICTS - SOCIB), and the Mediterranean Institute for Advanced Studies (IMEDEA, CSIC-UIB).
The three identified areas are the Balearic Sea, the West Algerian Basin, and ...
2021-03-26
A new method makes it much easier to follow the progression of multiple myeloma, a form of blood cancer. With a single drop of blood, it is possible to very accurately show whether the number of cancerous cells in the bone marrow is increasing in a patient. In time, this blood test could potentially replace the current bone marrow puncture.
Researchers at Radboud university medical center, in collaboration with Erasmus MC, have taken an important step towards implementing this new diagnostic, with a study published in Clinical Chemistry. Multiple myeloma is a severe form ...
2021-03-26
Perovskites, a class of materials first reported in the early 19th century, were "re-discovered" in 2009 as a possible candidate for power generation via their use in solar cells. Since then, they have taken the photovoltaic (PV) research community by storm, reaching new record efficiencies at an unprecedented pace. This improvement has been so rapid that by 2021, barely more than a decade of research later, they are already achieving performance similar to conventional silicon devices. What makes perovskites especially promising is the manner in which they can be created. Where silicon-based devices are heavy and require high temperatures for fabrication, perovskite devices can be lightweight and formed with minimal energy investiture. It is this combination - high performance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 3D-printed artificial lung model