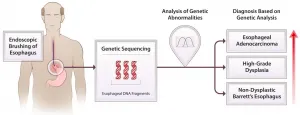
(Press-News.org) A combination of esophageal brushing and extensive genetic sequencing of the sample collected can detect chromosome alterations in people with Barrett's Esophagus, identifying patients at risk for progressing to esophageal cancer, according to a new study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and Case Western Reserve University.
In Barrett's Esophagus (BE), chronic acid reflux from the stomach damages the cells lining the lower esophagus, causing them to become more like cells of the lower digestive system. Cells in the lower esophagus progress through several precancerous stages before sometimes developing into esophageal adenocarcinoma, a cancer with a five-year survival rate below 20 percent. BE is the only known precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Clinicians can detect these progressive states in BE by looking for chromosomal alterations known as aneuploidy--a common feature in most cancer cells--but until now the process has involved multiple biopsies.
A single esophageal brushing paired with the sequencing technique called RealSeqS is sensitive and specific enough to identify aneuploidy at several stages of BE progression, and can even match specific types of aneuploidy with specific stages of the disease, the researchers say.
"Aneuploidy has long been implicated in the development, initiation or progression of esophageal cancer but the assays or experimental methods to detect this have not been as easily achieved or as high throughput as we would have wanted to allow for clinical implementation," says senior study author END
Procedures identify Barrett's esophagus patients at risk for cancer progression
2021-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mapping policy for how the EU can reduce its impact on tropical deforestation
2021-03-29
EU imports of products including palm oil, soybeans, and beef contribute significantly to deforestation in other parts of the world. In a new study, researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Louvain, Belgium, evaluated over a thousand policy proposals for how the EU could reduce this impact, to assess which would have the largest potential to reduce deforestation - while also being politically feasible.
"Unsurprisingly, there is weaker support for tougher regulations, such as import restrictions on certain goods. But our study shows that there is broad support in general, ...
Genetic sleuthing reveals endangered river dolphins in Asia as different species
2021-03-29
New genetic analysis and years of painstaking research has revealed that one of the world's most endangered marine mammals is actually two species rather than one, as scientists had long assumed.
Scientists spent about two decades crossing Asia and Europe in pursuit of river dolphins skulls and reexamining tissue samples with modern genetic techniques. Their findings revealed that Indus and Ganges river dolphins are separate species, according to a new study published in Marine Mammal Science.
The two dolphins that live in the muddy waters ...
Getting on top of rural Asia's blood pressure
2021-03-29
SINGAPORE, 29 March 2021 - A low-cost intervention to improve hypertension--or high blood pressure (BP)--prevention and management can be cost-effectively scaled up for rural communities in low- and middle-income countries, according to findings from a multi-country trial published in The Lancet Global Health.
Led by Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore, the Control of Blood Pressure and Risk Attenuation--Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka (COBRA-BPS) trial, conducted in partnership with the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Diseases Research, Bangladesh (ICDDR,B), Aga Khan University in Pakistan, the University of Kelaniya in Sri Lanka, analysed the budget impact and cost-effectiveness ...
Detecting for carpal tunnel syndrome with a smartphone game
2021-03-29
A Japanese research group combined motion analysis that uses smartphone application and machine learning that uses an anomaly detection method, thereby developing a technique to easily screen for carpal tunnel syndrome. Carpal tunnel syndrome is common amongst middle-aged women. The disease causes compressed nerves in the wrist, causing numbness and difficulty with finger movements. While an accurate diagnosis can be reached with nerve conduction study, this is not widely used because it requires expensive devices and specialized skills. Thus, a simple screen tool that does ...
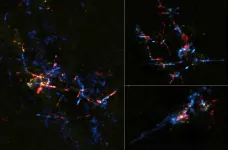
Stellar eggs near galactic center hatching into baby stars
2021-03-29
Astronomers found a number of stellar eggs containing baby stars around the center of the Milky Way using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). Previous studies had suggested that the environment there is too harsh to form stars. These findings indicate that star formation is more resilient than researchers thought.
Stars form in stellar eggs, cosmic clouds of gas and dust which collapse due to gravity. If something interferes with the gravity driven contraction, star formation will be suppressed. There are many potential sources of interference near the Galactic Center. Strong turbulence can stir up the clouds ...
New drug to regenerate lost teeth
2021-03-29
Japan -- The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the pillow, but the child can be assured of a new tooth in a few months. The same cannot be said of adults who have lost their teeth.
A new study by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui, however, may offer some hope. The team reports that an antibody for one gene -- uterine sensitization associated gene-1 or USAG-1 -- can stimulate tooth growth in mice suffering from tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The paper was published in Science Advances.
Although the normal adult mouth has 32 teeth, about ...
Natural resources decrease income inequality in resource-rich countries
2021-03-29
A group of researchers from Russia, Germany, the Czech Republic, and Switzerland contest the common belief that resource-based economies have higher levels of within-country inequality than resource-scarce economies. The researchers document a direct causal link between natural resources and within-country inequality and conclude that the extraction of oil and gas can reduce inequality or has no significant effect on it. The results were published in the journal Empirical Economics.
"When we compare the natural resource rents to GDP 10 years after the discovery of natural ...
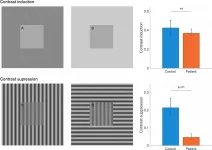
Depression affects visual perception
2021-03-29
Researchers specialised in psychiatry and psychology at the University of Helsinki investigated the effects of depression on visual perception. The study confirmed that the processing of visual information is altered in depressed people, a phenomenon most likely linked with the processing of information in the cerebral cortex.
The study was published in the Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience.
In the study, the processing of visual information by patients with depression was compared to that of a control group by utilising two visual tests. In the perception tests, the study subjects compared the brightness and contrast of simple patterns.
"What ...
Getting the inside track on street design
2021-03-29
Pedestrian movements are tricky to track, but now the first large-scale statistical analysis of pedestrian flow using anonymous phone data collected in three European capital cities, London, Amsterdam and Stockholm, has been conducted by researchers from KAUST with Swedish colleagues from Gothenburg.
Analyzing the flow of pedestrians through city streets provides insights into how city design influences walking behavior. Studies of pedestrian flow inform new urban developments, enable designers to define quieter areas and "urban buzz" zones and reveal how spaces are used at different times.
"In a previous study, we found strong links between the total ...
Artificial intelligence as a co-driver
2021-03-29
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming more common in many branches of industry and online retailing. Traditional lines of work, such as transport logistics and driving, are developing in a similar direction although mainly out of public view. Scientists at the University of Göttingen have now investigated how efficient the use of AI can be in the commercial management of trucks. Their answer: the best option is an intelligent combination of human decision-making and AI applications. The study was published in the International Journal of Logistics Management.
"As has happened in the private sector, digital applications - as well as machine learning, a kind of AI - are increasingly permeating operations ...