(Press-News.org) A team of scientists has been using DESY's X-ray source PETRA III to analyse the structural changes that take place in an egg when you cook it. The work reveals how the proteins in the white of a chicken egg unfold and cross-link with each other to form a solid structure when heated. Their innovative method can be of interest to the food industry as well as to the broad field of research surrounding protein analysis. The cooperation of two groups, headed by Frank Schreiber from the University of Tübingen and Christian Gutt from the University of Siegen, with scientists at DESY and European XFEL reports the research in two articles in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Eggs are among the most versatile food ingredients. They can take the form of a gel or a foam, they can be comparatively solid and also serve as the basis for emulsions. At about 80 degrees Celsius, egg white becomes solid and opaque. This is because the proteins in the egg white form a network structure. Studying the exact molecular structure of egg white calls for energetic radiation, such as X-rays, which is able to penetrate the opaque egg white and has a wavelength that is no longer than the structures being examined.
"To understand the structural evolution in detail, you have to study the phenomenon on the micrometre scale," explains Nafisa Begam, the lead author of the first study, who is an Alexander von Humboldt fellow in Schreiber's group. The scientists used so-called X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy (XPCS) with a specific geometry allowing them to determine the structure and the dynamics of the proteins in the egg white.
For their experiments on the P10 beamline at PETRA III the scientists used a chicken egg from a supermarket and filled the egg white into a quartz tube with a diameter of 1.5 millimetres. "Inside, the egg white was heated in a controlled manner while we analysed it with the help of the X-rays," explains DESY co-author Fabian Westermeier. "The X-ray beam was expanded to 0.1 by 0.1 millimetres, to keep the radiation dose below the damage threshold of the protein structures."
The measurements reveal the protein dynamics in the egg white over a period of about a quarter of an hour. During the first three minutes, the protein network grew exponentially, reaching a plateau after about five minutes, at which virtually no more protein links were formed. At this time, the average mesh size of the protein network was about 0.4 micrometres (thousandths of a millimetre).
In the second study, the team used the XPCS technique to investigate the self-organisation of protein solutions into domains with, respectively, high and low protein concentration, as an example of structure formation in cell biology. In the process, they were able to follow the temperature-dependent dynamics over time. "At high protein densities, mobility decreases, which slows down the phase separation. This is important for the special dynamics of the system," reports lead author Anita Girelli from Schreiber's group.
The studies, which were funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), not only reveal new details about the structural changes occurring in egg whites, but also prove the experimental concept, which can be used for other samples too, as demonstrated by the second study. "Successfully applying X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy opens up a new way to study the dynamics of biomolecules, which is essential if we are to understand them properly," Schreiber comments.
DESY is one of the world's leading particle accelerator centres and investigates the structure and function of matter - from the interaction of tiny elementary particles and the behaviour of novel nanomaterials and vital biomolecules to the great mysteries of the universe. The particle accelerators and detectors that DESY develops and builds at its locations in Hamburg and Zeuthen are unique research tools. They generate the most intense X-ray radiation in the world, accelerate particles to record energies and open up new windows onto the universe. DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association, Germany's largest scientific association, and receives its funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (90 per cent) and the German federal states of Hamburg and Brandenburg (10 per cent).
INFORMATION:
References:
Kinetics of Network Formation and Heterogeneous Dynamics of an Egg White Gel Revealed by Coherent X-Ray Scattering; Nafisa Begam, Anastasia Ragulskaya, Anita Girelli, Hendrik Rahmann, Sivasurender Chandran, Fabian Westermeier, Mario Reiser, Michael Sprung, Fajun Zhang, Christian Gutt, and Frank Schreiber; Physical Review Letters, 2021; DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.098001
Microscopic dynamics of liquid-liquid phase separation and domain coarsening in a protein solution revealed by XPCS; Anita Girelli, Hendrik Rahmann, Nafisa Begam, Anastasia Ragulskaya, Mario Reiser, Sivasurender Chandran, Fabian Westermeier, Michael Sprung, Fajun Zhang, Christian Gutt, and Frank Schreiber; Physical Review Letters, 2021 (accepted; in print)
Adding the nutrient selenium to diets protects against obesity and provides metabolic benefits to mice, according to a study published today in eLife.
The results could lead to interventions that reproduce many of the anti-aging effects associated with dietary restriction while also allowing people to eat as normal.
Several types of diet have been shown to increase healthspan - that is, the period of healthy lifespan. One of the proven methods of increasing healthspan in many organisms, including non-human mammals, is to restrict dietary intake of an amino acid ...
Humans are creating or exacerbating the environmental conditions that could lead to further pandemics, new University of Sydney research finds.
Modelling from the Sydney School of Veterinary Science suggests pressure on ecosystems, climate change and economic development are key factors associated with the diversification of pathogens (disease-causing agents, like viruses and bacteria). This has potential to lead to disease outbreaks.
The research, by Dr Balbir B Singh, Professor Michael Ward, and Associate Professor Navneet Dhand, is published in the international journal, Transboundary and Emerging Diseases.
They found a greater diversity ...
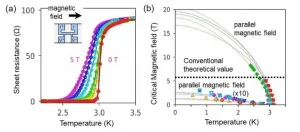
Superconductivity is known to be easily destroyed by strong magnetic fields. NIMS, Osaka University and Hokkaido University have jointly discovered that a superconductor with atomic-scale thickness can retain its superconductivity even when a strong magnetic field is applied to it. The team has also identified a new mechanism behind this phenomenon. These results may facilitate the development of superconducting materials resistant to magnetic fields and topological superconductors composed of superconducting and magnetic materials.
Superconductivity has been used in various technologies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ...
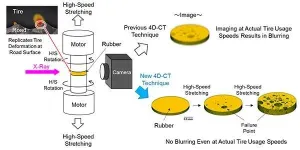
Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd (SRI) and Tohoku University teamed up to increase the speed of 4-Dimensional Computed Tomography (4D-CT) a thousand-fold, making it possible to observe rubber failure in tires in real-time.
This breakthrough will accelerate the development of new tire materials to provide super wear resistance, greater environmental friendliness, and longer service life. It will also aid significantly in the advancement of smart tires.
SRI initially developed 4D-CT as part of the ADVANCED 4D NANO DESIGN, a new materials development technology unveiled in 2015 that enables highly accurate analysis and simulation of the rubber's internal structure from the micro to nanoscale. This analysis ultimately ...
An evolutionary mystery that had eluded molecular biologists for decades may never have been solved if it weren't for the COVID-19 pandemic.
"Being stuck at home was a blessing in disguise, as there were no experiments that could be done. We just had our computers and lots of time," says Professor Paul Curmi, a structural biologist and molecular biophysicist with UNSW Sydney.
Prof. Curmi is referring to research published this month in Nature Communications that details the painstaking unravelling and reconstruction of a key protein in a single-celled, photosynthetic organism called a cryptophyte, a type of algae that evolved over a billion years ago.
Up until now, how cryptophytes acquired the proteins ...
About 61% of Americans have had at least one Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE), experts' formal term for a traumatic childhood event.
ACEs--which may include abuse, neglect and severe household dysfunction--often lead to psychological and social struggles that reach into adulthood, making ACEs a major public health challenge. But the long-term consequences of ACEs are just beginning to be understood in detail. To fill in the picture, two recent BYU studies analyzed how ACEs shape adolescents' delinquent behaviors as well as fathers' parenting approaches.
ACEs ...
An international survey that included 600 smokers in the UK has found that cessation messaging focused on easing the burden on our health system is most effective in encouraging people to quit.
The research, which was conducted in April-May 2020, randomly assigned participants to view one of four quit smoking messages, two of which explicitly referenced health implications and COVID-19, one referred more vaguely to risk of chest infection, and one highlighted financial motivations for quitting.
"We wanted to explore the effectiveness of smoking cessation messaging at a time when health systems the world over are beleaguered, and all our ...
Replacing regular common salt consumed by hypertensive patients in rural areas with a salt substitute can have a significant impact in terms of lowering their blood pressure, a new study by The George Institute for Global Health has revealed.
Researchers found that substituting a small part of the sodium in salt with potassium without altering the taste led to a substantial reduction in systolic blood pressure in these patients, supporting salt substitution as an effective, low-cost intervention for lowering blood pressure in rural India.
The study entitled "Effects of reduced-sodium added-potassium salt substitute on blood pressure in rural Indian hypertensive patients: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial" provides the first-of-its-kind evidence from ...
In a new study published in the Cell Research, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing University reports "In vivo self-assembled small RNA is the new generation of RNAi therapeutics".
The development of RNAi therapy has undergone two major stages, direct injection of synthetic siRNAs and delivery with artificial vehicles; both have not realized the full therapeutic potential of RNAi in clinic. In this study, Chen-Yu Zhang's group reprogram host liver with genetic circuits to direct the synthesis and self-assembly of siRNAs into secretory exosomes. In vivo assembled siRNAs are systematically distributed to multiple tissues or targeted to specific tissues (e.g., brain), inducing potent target gene silencing in these tissues. The therapeutic value of this strategy is demonstrated ...
A team of researchers from Graz University of Technology, Know-Center GmbH, Johannes Kepler University Linz, University of Innsbruck, Austria and University of Utrecht, the Netherlands, compared how accurate algorithm-generated music recommendations were for mainstream and non-mainstream music listeners. They used a dataset containing the listening histories of 4,148 users of the music streaming platform Last.fm who either listened to mostly non-mainstream music or mostly mainstream music (2,074 users in each group). Based on the artists music users' listened to most frequently, the authors used a computational model to predict how likely music users were to like the music recommended ...