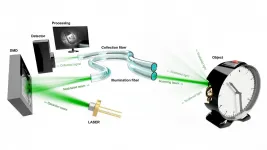
Using holographic endoscopes to observe distant objects
Endoscopes made of single-hair thin optical fibers can reconstruct images of macroscopic objects at larger imaging distances
2021-03-30
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, March 30, 2021 -- Scientists are developing tools to observe the biological machinery in in vivo animal models to be able to understand and better treat severe brain diseases like Alzheimer's disease and many other conditions. Holographic endoscopes attracted researchers' interest because of their potential to conduct minimally invasive observations inside the human body.
These tools can shed light on the biological processes occurring at the macromolecular and subcellular levels, which usually remain hidden from sight as most tissue is opaque to visible radiation. In APL Photonics, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the Leibniz Institute of Photonic Technology in Germany created a particularly narrow endoscope made of single hair-thin optical fibers that uses holographic methods to reconstruct images of macroscopic objects placed in front of the far end of the endoscope.
"We were positively surprised that the imaging quality was well-maintained at larger imaging distances, even for objects placed at a half meter from the endoscope," said author Ivo Leite. "We expected that the low number of photons collected in this range would give rise to much higher detection noise."
Efforts in imaging through multimode-fiber endoscopes previously focused on working distances typically smaller than 20 micrometers to resolve micrometer-scale details. This limits the field of view to the size of the fiber core.
The researchers brought the imaging operation to the observation of macroscopic objects, which can be placed far away from the endoscope. Researchers increased the imaging performance in terms of image definition to 100,000 pixels per image frame, an order of magnitude larger than previous holographic endoscopes and reaching the definition of modern video endoscopes.
Their efforts pave the way for bringing this class of minimally invasive endoscopes to clinical applications. The macroscopic imaging modality shown in this study will be essential to analyze biological samples at the tissue scale -- just as conventional clinical endoscopes do -- as well as to guide the instrument insertion.
Once a region of interest is identified, the hologram sequence displayed by the spatial light modulator can be updated to switch the imaging modality and perform observations at the cellular and subcellular levels.
"The potential for such flexibility in imaging operation through the same unmodified endoscope is a unique feature that, we believe, holographic endoscopes could soon offer," said author Tomas Cizmar.
The researchers' light control methods could be used to deliver practically any type of photonics tool through a hair-thin endoscope, which could have applications in a range of areas, such as optical transfection, subcellular laser surgery, and laser-assisted microfabrication.
INFORMATION:
The article "Observing distant objects with a multimode fiber-based holographic endoscope" is authored by Ivo T. Leite, Sergey Turtaev, Dirk E. Boonzajer Flaes, and Tomas Cizmar. The article will appear in APL Photonics on March 30, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0038367). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0038367.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
APL Photonics is the dedicated home for open access multidisciplinary research from and for the photonics community. The journal publishes fundamental and applied results that significantly advance the knowledge in photonics across physics, chemistry, biology and materials science. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/app.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-30
It makes evolutionary sense for long-lived animals to have complex social relationships - such as friends and enemies - researchers say.
Some species and individuals focus their energy on reproduction (live fast, die young), while "slow-living" animals prioritise survival and tend to live longer lives.
In the new paper, University of Exeter scientists argue that natural selection favours complex social structures among slow-living animals - meaning that knowing their friends and enemies is easier for animals with longer lifespans, and helps them live even longer.
Meanwhile, fast-lived species should only bother with such social relationships if it increases ...
2021-03-30
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated COVID-19 vaccine intentions among racially and ethnically diverse samples of health workers and the general population in the San Francisco Bay area.
Authors: Kevin Grumbach, M.D., of the San Francisco General Hospital and University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.1445)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-03-30
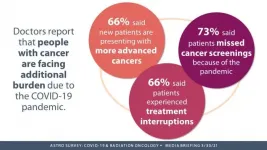
ARLINGTON, Va., March 30, 2021 -- Doctors who oversee cancer clinics say that new patients are arriving for treatment with more advanced disease than before the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new survey from the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). The national survey of radiation therapy practice leaders fielded this winter also indicates that treatment postponements and deferrals that were common a year ago have largely subsided and that clinics continue to use a variety of enhanced safety measures to protect their patients and staff.
"One year into the COVID-19 pandemic, we already see the consequences of pandemic-driven drops in cancer screening and diagnostics," said Thomas J. Eichler, MD, FASTRO, ...
2021-03-30
Boston - For decades, the power of the placebo effect was thought to lie in patients' belief that they were -- or at least, could be -- receiving a pharmacologically active treatment. A new study by physician-researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) suggests that patients don't need to be deceived to receive benefit from treatment with placebo.
In a randomized clinical trial published in the journal PAIN, researchers found participants with moderate to severe irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) who were knowingly treated with a pharmacologically inactive pill -- referred to as an honest or open-label placebo -- reported clinically meaningful improvements in their IBS symptoms. People who received the open-label placebo experienced improvements ...
2021-03-30
LAWRENCE -- Recent incidents of racial discrimination and violence against Asians and Asian-Americans in the United States have prompted critical discussions about how to talk about such biases with younger age groups. New research from the University of Kansas shows using critical race media literacy, or examining how race and gender are addressed in popular culture, can be an effective way to discuss those topics and engage students.
KU researchers published a study in which they observed an American teacher using critical race media literacy to discuss racism and sexism in superhero movies in English as a foreign language classes in a South Korean high school. They argued that successful implementation ...
2021-03-30
Through his role on the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, UVA Health's Li Li, MD, PhD, MPH, has helped develop new lung cancer screening guidelines that expand screenings to more high-risk patients.
The new guidelines are focused on Americans at higher risk because of their history of smoking, which is the leading cause of lung cancer. There are two significant changes in the new guidelines. For those who are still smoking or quit less than 15 years ago, a yearly screening using a low-dose computed tomography (CT) scan is now recommended:
beginning at age 50, instead of age 55.
for anyone who has smoked 20 pack-years in their lifetime, instead of 30 pack-years. A pack-year equals smoking a pack of cigarettes a day for a year.
The ...
2021-03-30
Physicists from the University of Sussex have developed an extremely thin, large-area semiconductor surface source of terahertz, composed of just a few atomic layers and compatible with existing electronic platforms.
Terahertz sources emit brief light pulses oscillating at 'trillion of times per second'. At this scale, they are too fast to be handled by standard electronics, and, until recently, too slow to be handled by optical technologies. This has great significance for the evolution of ultra-fast communication devices above the 300GHz limit - such as that required for 6G mobile phone technology - something that is still fundamentally beyond the limit of current electronics.
Researchers ...
2021-03-30
People are adept at discerning most of the different emotions that underlie screams, such as anger, frustration, pain, surprise or fear, finds a new study by psychologists at Emory University. Screams of happiness, however, are more often interpreted as fear when heard without any additional context, the results show.
PeerJ published the research, the first in-depth look at the human ability to decode the range of emotions tied to the acoustic cues of screams.
"To a large extent, the study participants were quite good at judging the original context of a scream, simply by listening to it through headphones without any visual cues," says Harold Gouzoules, Emory professor of psychology and senior author of the study. ...
2021-03-30
WHAT:
When variants of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) emerged in late 2020, concern arose that they might elude protective immune responses generated by prior infection or vaccination, potentially making re-infection more likely or vaccination less effective. To investigate this possibility, researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues analyzed blood cell samples from 30 people who had contracted and recovered from COVID-19 prior to the emergence of virus variants. They found that one key player in the immune response to SARS-CoV-2--the CD8+ T cell--remained active against the virus.
The research team was led by NIAID's Andrew Redd, Ph.D., and included ...
2021-03-30
Indigenous traditions often place land at the centre of their cultures. However, with more than half of Canada's Indigenous population now living in urban areas and Indigenous communities struggling to overcome legacies of colonialism defined by assimilation and land theft, that connection is getting frayed.
Elizabeth Fast, an associate professor of applied human sciences in the Faculty of Arts and Science, wanted to help Indigenous youth reconnect with their cultures in safe and accessible ways. Along with a youth advisory group composed of Indigenous youth (some of whom are also students), she has been organizing a series of land-based learning retreats ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Using holographic endoscopes to observe distant objects
Endoscopes made of single-hair thin optical fibers can reconstruct images of macroscopic objects at larger imaging distances