Exercise, healthy diet in midlife may prevent serious health conditions in senior years
Journal of the American Heart Association report
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 31, 2021 -- Following a routine of regular physical activity combined with a diet including fruits, vegetables and other healthy foods may be key to middle-aged adults achieving optimal cardiometabolic health later in life, according to new research using data from the Framingham Heart Study published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
Cardiometabolic health risk factors include the metabolic syndrome, a cluster of disorders such as excess fat around the waist, insulin resistance and high blood pressure. Presence of the metabolic syndrome may increase the risk of developing heart disease, stroke and Type 2 diabetes.
Researchers noted it has been unclear whether adherence to both the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans and their 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans - as opposed to only one of the two - in midlife confers the most favorable cardiometabolic health outcomes later in life. The physical activity guidelines recommend that adults achieve at least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of vigorous physical activity per week, such as walking or swimming. The dietary guidelines, which were updated in January 2021, offer suggestions for healthy eating patterns, nutritional targets and dietary limits.
In an analysis of data from participants of the Framingham Heart Study, which began more than 70 years ago in Framingham, Massachusetts, investigators examined data from 2,379 adults ages 18 and older and their adherence to the two guidelines. They observed that meeting a combination of the two recommendations during midlife was associated with lower odds of metabolic syndrome and developing serious health conditions as participants aged in their senior years in 2016-2019 examinations.
"Health care professionals could use these findings to further promote and emphasize to their patients the benefits of a healthy diet and a regular exercise schedule to avoid the development of numerous chronic health conditions in the present and in later life," said corresponding author Vanessa Xanthakis, Ph.D., FAHA, assistant professor of medicine and biostatistics in the Section of Preventive Medicine and Epidemiology at Boston University School of Medicine in Boston. "The earlier people make these lifestyle changes, the more likely they will be to lower their risk of cardiovascular-associated diseases later in life."
Study participants were selected from the third generation of the Framingham Heart Study. Participants (average age 47, 54% women) were examined between 2008 and 2011. Researchers evaluated physical activity using a specialized device known as an omnidirectional accelerometer. The device, which tracks sedentary and physical activity, was worn on the participant's hip for eight days. Researchers also collected dietary information from food frequency questionnaires to measure the kinds and levels of food and nutrients consumed.
In this investigation, researchers observed that among all participants, 28% met recommendations of both the physical activity and dietary guidelines, while 47% achieved the recommendations in only one of the guidelines. Researchers also observed that:
participants who followed the physical activity recommendations alone had 51% lower odds of metabolic syndrome;
participants who adhered to the dietary guidelines alone had 33% lower odds; and
participants who followed both guidelines had 65% lower odds of developing metabolic syndrome.
"It is noteworthy that we observed a dose-response association of adherence to diet and physical activity guidelines with risk of cardiometabolic disease later in life," Xanthakis said. "Participants who met the physical activity guidelines had progressively lower risk of cardiometabolic disease as they increased adherence to the dietary guidelines."
All study participants were white adults, therefore, the findings cannot be generalized to people in other racial or ethnic groups. Additional studies with a multiethnic participant sample are needed, researchers said.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Joowon Lee, Ph.D.; Maura E. Walker, Ph.D.; Maximillian T. Bourdillon, M.D., Nicole Spartano, Ph.D.; Gail T. Rogers, M.A.; Paul F. Jacques, D.Sc.; and Ramachandran S. Vasan, M.D.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, the Evans Medical Foundation and Boston University School of Medicine.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link:
https://newsroom.heart.org/news/exercise-healthy-diet-in-midlife-may-prevent-serious-health-conditions-in-senior-years?preview=fc9ffd2e312b36e5d9441e420e2593a6
After March 31, 2021, view the manuscript online.
About Metabolic Syndrome
Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes
2018 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans
2021-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Healthy living
Follow AHA/ASA news on Twitter @HeartNews
Follow news from the Journal of the American Heart Association @JAHA_AHA
Statements and conclusions of studies published in the American Heart Association's scientific journals are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association's policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers are available here, and the Association's overall financial information is available here.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public's health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
More research is needed on the environmental impact of sunscreen on the world's coral reefs, scientists at the University of York say.
The concerns over the number of cases of cancer as a result of overexposure to UV solar radiation, has led to extensive production and use of skin protection products. The chemical compounds used in these products, however, can enter the environment at the points of manufacture as well as through use by the consumer.
It is already understood that UV-filter compounds have toxic effects on marine organisms, but research in this area ...
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON, DC - March 31, 2021 -- Nearly 20% of Americans, or more than 46 million adults, say they did not seek treatment for a health problem in the last year due to cost, and an equal number say that if they needed some form of healthcare today they would not be able to afford it, according to a new West Health-Gallup survey. The findings come as Americans struggle through a year-plus long pandemic that has claimed over 550,000 lives and put millions of people out of work.
Americans who found themselves unemployed were about twice as likely ...
2021-03-31
The era of big data has inundated nearly all scientific fields with torrents of newly available data with the power to stimulate new research and enable inquiry at scales not previously possible. This is particularly true for ecology, where rapid growth in remote sensing, monitoring, and community science initiatives has contributed to a massive surge in the quantity and kinds of environmental data that are available to researchers.
Writing in BioScience, a team led by US Department of Agriculture ecologist Sarah McCord states that the volume of the data is only part of the story. Just as important, they say, is the quality of the data. According to the newly published article, "Big data has magnified both the burden and the complexity of ensuring ...
2021-03-31
GENEVA, LAUSANNE, 31 March 2021: Cocaine is a highly addictive substance that, in the long term, can have adverse effects on health and wellbeing. There are around 18 million cocaine users globally, according to a UN report. Understanding how cocaine modifies brain networks could reveal potential targets for therapies to treat addiction and other neuropsychological disorders.
A new study published today in the journal Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience by a team of researchers from the University of Lausanne and the Wyss Center for Bio and Neuroengineering reveals that during cocaine withdrawal, neurons in a brain area associated with depression connect ...
2021-03-31
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 31, 2021)--Menopause typically signals the end of a woman's ability to become pregnant. However, in a small new study, a novel approach of administering platelet-rich plasma and gonadotropins near the ovarian follicles is showing promise in restoring ovarian function. Study results are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
As more women look to build their careers before pursuing motherhood, the average age of conceiving a child continues to be pushed back. For some of these women, however, their hope of becoming pregnant is cut short by the onset of early menopause, which is described as the cessation of ovarian function ...
2021-03-31
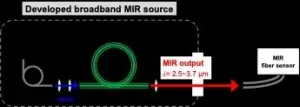
A research team of the National Institutes of Natural Sciences, National Institute for Fusion Science and Akita Prefectural University have successfully demonstrated a broadband mid-infrared (MIR) source with a simple configuration. This light source generates highly-stable broadband MIR beam at 2.5-3.7 μm wavelength range maintaining the brightness owing to its high-beam quality. Such a broadband MIR source facilitates a simplified environmental monitoring system by constructing a MIR fiber-optic sensor, which has the potential for industrial and medical applications.
In the MIR wavelength region, there are many strong absorption lines of molecules ...
2021-03-31
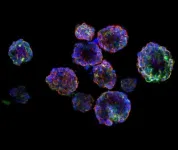
A*STAR's Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has teamed up with Singapore Institute of Advanced Medicine Holdings Pte Ltd (SIAMH) to establish the first of its kind in-vitro patient-derived 3D organoid models of Nasopharyngeal Cancer (NPC).
The study was published in Frontiers in Oncology on 23 February 2021. It is the first direct experimental evidence to predict optimal Radiation Treatment (RT) boost dose required to cause sufficient damage to recurrent hypoxic (low oxygen level) NPC tumour cells, which can be further used to develop dose-painting algorithms in clinical practice.
Two patient-derived xenograft (PDX) ...
2021-03-31
Researchers from Loyola Marymount University, San Diego State University, Indian Institute of Management, and Iowa State University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how effective marketplace participation by subsistence consumers requires knowledge and skills that relate to what, how, and why to participate.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Marketplace Literacy as a Pathway to a Better World: Evidence from Field Experiments in Low-Access Subsistence Marketplaces" and is authored by Madhu Viswanathan, Nita Umashankar, Arun Sreekumar, and Ashley Goreczny.
Success for marketers looking to emerging markets for growth is inextricably ...
2021-03-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Bangladesh's floating gardens, built to grow food during flood seasons, could offer a sustainable solution for parts of the world prone to flooding because of climate change, a new study has found.
The study, published recently in the Journal of Agriculture, Food and Environment, suggests that floating gardens might not only help reduce food insecurity, but could also provide income for rural households in flood-prone parts of Bangladesh.
"We are focused here on adaptive change for people who are victims of climate change, but who did not cause climate ...
2021-03-31
PULLMAN, Wash. -- Nature's strongest material now has some stiff competition. For the first time, researchers have hard evidence that human-made hexagonal diamonds are stiffer than the common cubic diamonds found in nature and often used in jewelry.
Named for their six-sided crystal structure, hexagonal diamonds have been found at some meteorite impact sites, and others have been made briefly in labs, but these were either too small or had too short of an existence to be measured.
Now scientists at Washington State University's Institute for Shock Physics created hexagonal diamonds large enough to measure ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Exercise, healthy diet in midlife may prevent serious health conditions in senior years
Journal of the American Heart Association report