Researchers realize synthetic gauge fields in single optomechanical resonator
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) The research team led by Prof. GUO Guangcan and Dr. DONG Chunhua from the University of Science and Technology of China realized synthetic gauge fields in a single optomechanical resonator by controlling geometric phase with the multimode interaction in the micro-resonator.
By engineering a Hamiltonian, uncharged particles or bosonic excitations can acquire a path-dependent phase which realizes a synthetic magnetic field. Such synthetic gauge field can improve the precision of quantum many-body simulation and control over bosons.
Previous works have realized synthetic gauge fields through coupled resonators, while this time the team realized synthetic gauge field in a single optomechanical resonator based on multimode interaction of microcavity.
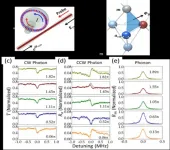
The team proposed to employ clockwise and counterclockwise driving lasers into the microcavity simultaneously, which realized the coherent coupling between optical photons and phonons and achieved complete control over the coupling phase.
In the experiment, researchers proved that the coupling transport of optical photons between multiple modes would obtain a path-dependent phase, which can realize the equivalent synthetic magnetic field of optical photons.
Thanks to the advantages of microcavity optical field modulation, the team further realized the time-varying canonical phase and demonstrated the synthetic electric field of optical photons in a single optomechanical resonator.
Higher dimensional synthetic gauge field is indicated by the experiment results, in consideration of the strong coherent optomechanical coupling interaction and coherent nonlinear optical effects in microcavities.
The study was published on Physics Review Letters.
The synthetic fields shown in this work shed light on the topological properties of optical photons and realization of chiral edge states and topological protection.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-01
Close to 60% of working adults who were hospitalized as a result of an injury had returned to their jobs after being discharged, according to a recent study in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery.
However, more than half of the patients in the study's sample were in medical debt, and close to a quarter forwent additional care to save money. Compared to those who were not injured, patients were also more likely to experience food insecurity, physical disability, and difficulty affording and accessing health care.
The research team, which included several Michigan Medicine physicians, ...
2021-04-01
GALVESTON, TEXAS -- A new research study leveraging a database from the largest equal access health system in the US, the Department of Veteran Affairs, offers insight into the outcome of specific treatment patterns for advanced bladder cancer patients. Lead author Dr. Stephen Williams of the University of Texas Medical Branch says it is one of the first comprehensive studies looking at both the outcomes and the costs of treating a potentially lethal and devastating type of bladder cancer.
The study was published today in JAMA Network Open, a ...
2021-04-01
Leesburg, VA, April 1, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting reveals increased rates of emphysema in marijuana smokers, compared to both non-smokers and tobacco-only smokers, as well as greater rates of paraseptal emphysema.
"Marijuana smoking is also associated with airways disease, including bronchial wall thickening, bronchiectasis, and bronchiolar mucoid impaction, in comparison to both the control group and tobacco-only group," wrote first author Luke Murtha of Ottawa Hospital in Canada.
Querying imaging reports on Ottawa Hospital's PACS, Murtha and colleagues identified three ...
2021-04-01
Leesburg, VA, April 1, 2021--A Scientific E-Poster to be presented at the 2021 ARRS Virtual Annual Meeting found the COVID-19 "Safer at Home" order resulted in a significant decline in radiology ordering utilization, outpatient consultations, and emergency department (ED) visits.
"There was a disproportionate impact in the outpatient setting, especially on screening and other nonessential imaging," wrote Evan Raff of Olive View-UCLA Medical Center, which "mirrors the impact that the order has had on clinical services, as reflected in outpatient consult volumes, ...
2021-04-01
Osaka, Japan - As the worldwide demand for electronic devices continues to grow, so too does the strain on the finite resources used in their production, such as metals and fossil fuels. In an effort to provide renewable alternatives, researchers from Osaka University have developed a nanocarbon material for electronics applications made from chitin derived from crab shells. Their findings are published in Journal of Materials Chemistry C.
Nanocarbon materials show significant promise for use in electronic devices. In particular, those with porous ...
2021-04-01
A team of researchers has sought to mitigate the mental health impacts of COVID-19 on adolescents by harnessing previous research on youth physical and mental health.
Their review also drew on the psychological stressors of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami on children. The results were published in the Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine on March 26, 2021.
"We combined past research on the psychological stress on children with present studies on the effects of COVID-19," said Junko Okuyama of the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at Tohoku University Hospital and lead author of the study. "We found ...
2021-04-01
WASHINGTON--Endocrine-disrupting chemicals may influence hormonal shifts during pregnancy as well as contribute to postpartum depression, according to a small study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Postpartum depression is a serious and common psychiatric disorder that affects up to 1 in 5 childbearing women. The cause of postpartum depression is not well understood, but hormonal changes during pregnancy have been found to be an important factor. Harmful chemicals such as bisphenols and phthalates that are found in plastics and personal care products are known to affect sex hormones.
"We found that phthalate ...
2021-04-01
Children and young adults who receive CAR T-cell therapy for the most common childhood cancer - acute lymphoblastic leukemia - suffer remarkably fewer relapses and are far more likely to survive when the treatment is paired with a subsequent stem cell transplant, a new study finds.
The research, with an average follow up of nearly five years, suggests that stem cell transplants offer long-term benefits for young patients who receive the cutting-edge immunotherapy. CAR T-cell therapy results in complete remission in 60%-100% of patients initially, but the relapse rate is high. However, among those who received a stem cell transplant after CARs, the relapse rate was less than 10% two years later.
"More than 50% of kids in other ...
2021-04-01
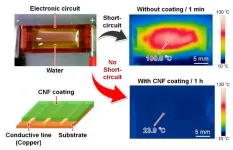
Osaka, Japan - Most electronic devices aren't waterproof, much to your irritation if a sprinkler suddenly sprays you while you're talking outside on your cellphone. Some electronics can be made at least water-resistant by, for example, using special glues to fuse outer components together. Flexible electronics are another story. Their sealant materials must be able to bend, yet with current technology it's inevitable that eventually such a sealant will crack or separate from the device--and there goes your water-resistant coating.
Researchers are determined to come up ...
2021-04-01
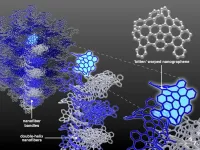
Nanographene is flexible, yet stronger than steel. With unique physical and electronic properties, the material consists of carbon molecules only one atom thick arranged in a honeycomb shape. Still early in technological development, current fabrication methods require the addition of substituents to obtain a uniform material. Additive-free methods result in flimsy, breakable fibers--until now.
An international team of researchers has developed self-assembling, stable and strong nanographene wires. The results were published on March 24 in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The team, led by Yasutomo Segawa, associate professor at the Institute for Molecular Science, part of the National Institutes of Natural Science in Japan, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers realize synthetic gauge fields in single optomechanical resonator