Scientists launch 'herculean' project creating atlas of human genome variants
2021-04-01
(Press-News.org) SEATTLE (April 1, 2021) - An international consortium of geneticists, biologists, clinicians, mathematicians, and other scientists is determined to take the study of the human genome to the next level - creating a comprehensive atlas of genetic variants to advance the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of disease.
"This Herculean undertaking is unprecedented," said Dr. Matthew Hurles, a geneticist at the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Cambridge, England. "Indeed, the scientific community has an increasingly comprehensive catalog of functional DNA elements in the human genome, but that catalog remains incomplete. We have collectively characterized the functional impact of less than 1% of genetic variation in the 1 to 2 percent of our DNA."
Hurles and Dr. Doug Fowler, a member of the Brotman Bata Institute for Precision Medicine (BBI) and professor of Genome Sciences at the University of Washington's UW Medicine, want to increase those percentages significantly.
They are founding members of the Atlas of Variant Effects (AVE) Alliance and co-authors of a white paper outlining what may be the most ambitious task over the past 30 years since the Human Genome Project.
AVE, along with BBI and the Center for the Multiplexed Assessment of Phenotype, is co-hosting the fourth annual "Mutational Scanning Symposium." The event will bring together global experts performing leading edge research in precision medicine, functional genomics, protein science, and variant interpretation and prediction and will be held virtually for three days beginning on Monday, April 5. Those interested in participating in the free symposium may learn more at https://www.varianteffect.org/aveevents/mutational-scanning-symposium.
The launch of the AVE alliance and the consortium's effort to create the atlas of human genome variants are key issues to be covered at the meeting. The atlas will also examine technology development, data generation, data analysis, data coordination and sharing, and clinical and biological translation.
"We've never known so much about naturally occurring variation in the human genome and now is the time to seize the opportunity to understand what that variation means for human health," said Anna L. Gloyn, DPhil, professor of pediatrics at the Stanford University School of Medicine and an AVE Executive Committee member.
The initial efforts of members of the AVE Alliance will focus on quantifying the functional impact of single nucleotide variants at the genomic loci, primarily human protein-coding genes, that offer the greatest and most immediate clinical utility.
"The ultimate goal is to develop a systematic, extensive understanding of the functional impact of variants in human, model organism and pathogen genomes," Fowler said.
"However, the field of variant effect mapping is already yielding major impacts. We believe and expect that a coordinated and phased approach with others globally could be transformative. The first major, 'real world' impact of the atlas of variant effects is expected to be improved genetic diagnosis and precision medicine."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Hurles, Fowler, and Gloyn, the AVE Executive Committee founding members are: David J. Adams, Wellcome Sanger Institute; William C. Hahn, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Debora S. Marks, Harvard Medical School; James T. Neal, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; Fritz Roth, University of Toronto; Alan F. Rubin, University of Melbourne; and Lea M. Starita, BBI and University of Washington.
CONTACT:
Dean R. Owen, Director of Communications
The Brotman Baty Institute for Precision Medicine at the University of Washington's School of Medicine
dean1227@uw.edu; +1.253.906.8645
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-01
Exposure to antibiotics in utero and infancy can lead to an irreversible loss of regulatory T-cells in the colon-a valuable component of the immune system's response toward allergens in later life - after only six months, a Rutgers researcher found.
The study was published in the journal mBio.
It is already known that the use of antibiotics early in life disrupts the intestinal microbiota - the trillions of beneficial microorganisms that live in and on our bodies - that play a crucial role in the healthy maturation of the immune system and the prevention of ...
2021-04-01
Video games offer students obvious respite from the stresses of studies and, now, a study from a University of Ottawa medical student has found they could benefit surgical skills training.
Arnav Gupta carries a heavy course load as a third-year student in the Faculty of Medicine, so winding down with a game of Legend of Zelda always provides relief from the rigorous of study. But Zelda may be helping improve his surgical education, too, as Gupta and a team of researchers from the University of Toronto found in a paper they recently published in the medical journal ...
2021-04-01
East Hanover, NJ. April 1, 2021. A team of New Jersey researchers has shown that changes in perceptual certainty and response bias, two central metrics of signal detection theory (SDT), correlate with changes in cognitive fatigue. They also show that SDT measures change as a function of changes in brain activation. This finding was reported in Frontiers in Psychology on January 15, 2021, in the open access article "Using Signal Detection Theory to Better Understand Cognitive Fatigue" (doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.579188).
The authors are Glenn Wylie, DPhil, Brian Yao, PhD, and John DeLuca, PhD, of Kessler Foundation, and Joshua Sandry, PhD, of Montclair State ...
2021-04-01
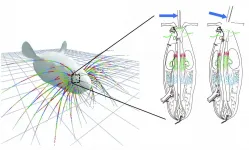
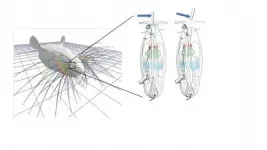
Researchers have developed a new mechanical model that simulates how whiskers bend within a follicle in response to an external force, paving the way toward better understanding of how whiskers contribute to mammals' sense of touch. Yifu Luo and Mitra Hartmann of Northwestern University and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
With the exception of some primates, most mammals use whiskers to explore their environment through the sense of touch. Whiskers have no sensors along their length, but when an external force bends ...
2021-04-01
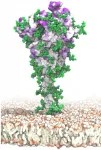
A new, detailed model of the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reveals previously unknown vulnerabilities that could inform development of vaccines. Mateusz Sikora of the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt, Germany, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
SARS-CoV-2 is the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. A key feature of SARS-CoV-2 is its spike protein, which extends from its surface and enables it to target and infect human cells. Extensive research has resulted in detailed static models of the spike protein, but these models do not capture the flexibility of the spike protein itself nor the movements of protective glycans--chains ...
2021-04-01
Six genetic variants add up to determine the risk of several blood cancers in pre-disposed dog breeds, according to a study by Benoît Hédan at the University of Rennes and colleagues, publishing April 8th in the open-access journal PLOS Genetics. The results confirm a known tumour-suppressor gene as a risk factor for histiocytic sarcoma -- a rare and aggressive blood cancer that affects both dogs and humans -- as well as identifying four new genetic loci associated with the disease.
The researchers sequenced genomic DNA extracted from blood samples from Bernese mountain dogs, Rottweilers, flat-coated retrievers, and golden retrievers, including ...
2021-04-01
Memory loss is common after general anesthesia, particularly for events occurring immediately before surgery--a phenomenon called retrograde amnesia. But a new study publishing on April 1st 2021 in the open access journal PLOS Biology, led by Simon Wiegert at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf in Germany, shows that changes in the hippocampus--the part of the brain used to make new memories--differ depending on which general anesthetic is used. Consequently, their effects on memory formation also differ.
Understanding how different anesthetics affect the brain, particularly the hippocampus, is therefore important for both clinicians with human patients and experimental scientists who work with animals. Wiegert and his team recorded brain activity from the hippocampus ...
2021-04-01
Achuta Kadambi, an assistant professor at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering, published a column in the journal Science about how medical devices can be fundamentally biased -- not just in dataset representation as has been widely reported, but from a deeper root: the laws of physics.
Kadambi described how the inherent physics behind medical devices could vary across race and gender. He cited several examples of potential physics-based bias. For example, recent research has shown that a pulse oximeter -- a medical device typically placed on a fingertip that uses infrared and light beams to measure oxygen saturation of the blood and the pulse rate -- is more likely to miss low levels in people with darker skin.
What motivated Kadambi to write this piece stemmed from ...
2021-04-01
A group of scientists from the University of Koblenz-Landau, Germany, has shown that for plants and insects the applied pesticide toxicity in agriculture has substantially increased between 2004 and 2016. In a paper published in the current issue of Science, the authors show that this pattern is even relevant in genetically modified (GM) crops that were originally designed to reduce pesticide impacts on the environment.
"We have taken a large body of pesticide use data from the US and have expressed changes of amounts applied in agriculture over time as changes in total applied pesticide toxicity," says lead author Ralf Schulz, professor for environmental sciences in Landau. "This provides a new view on the potential ...
2021-04-01
We know your cat's whiskers are handsome -- but you can't even see the cool part.
The base of the whisker, which is responsible for sending touch signals to the brain, is hidden inside the follicle, a deep pocket that embeds the whisker within the skin. Because this section of the whisker is obscured, understanding precisely how whiskers communicate touch to the brain has been a longstanding mystery.
In a new study, an interdisciplinary team of researchers at Northwestern University has developed the first mechanical simulation of the whisker inside the follicle. By combining their new model with new anatomical observations, the researchers discovered that when whiskers touch an object, they ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists launch 'herculean' project creating atlas of human genome variants