Researchers devise more efficient, enduring CAR gene therapy to combat HIV
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) FINDINGS
A UCLA research team has shown that using a truncated form of the CD4 molecule as part of a gene therapy to combat HIV yielded superior and longer-lasting results in mouse models than previous similar therapies using the CD4 molecule.
This new approach to CAR T gene therapy -- a type of immunotherapy that involves genetically engineering the body's own blood-forming stem cells to create HIV-fighting T cells -- has the potential to not only destroy HIV-infected cells but to create "memory cells" that could provide lifelong protection from infection with the virus that causes AIDS.
BACKGROUND
CAR therapies have emerged as a powerful immunotherapy for various forms of cancer and show promise for treating HIV-1, the more prevalent of the two main forms of the virus. However, current applications of these therapies may not impart long-lasting immunity. Researchers have been seeking a T cell-based therapy that can respond to malignant or infected cells that may reappear months or years after treatment.
In a previous study, the UCLA researchers described the creation of blood-forming stem cells that carry genes for chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs. Once these genetically engineered stem cells are transplanted into the body, they form specialized infection-fighting white blood cells known as CAR T cells that specifically seek out and kill cells infected with HIV.
METHOD
Because HIV binds to CD4 molecules in order to infect cells in the body, the researchers previously created a CAR molecule containing part of the CD4 molecule to hijack that interaction. When HIV would bind to the CD4 section of the CAR molecule on T cells, other regions of the CAR molecule would signal the cell to become activated and kill the virus. That molecule, however, contained two parts, or "domains," that still had the potential to allow HIV infection.
For the new study, the researchers removed those domains while adding another one that makes the cells resistant to infection and allows for a more efficient and longer-lasting cell response against HIV than before.
While the previous approach allowed for the continuous production of new HIV-fighting T cells that persisted for more than two years, these cells were essentially inactivated until they encountered HIV in the body. The improved CAR therapy engineers the body's immune response to HIV rather than waiting for the virus -- or parts of the virus -- to induce a response, in much the same way vaccines prime one's immune system to respond against a virus. The new approach also leads to the production of a significant number of "memory" T cells, that are capable of more potently and quickly responding to reactivated HIV.
IMPACT
The findings provide critical insights into the types of CAR molecules and approaches that are suitable for CAR therapies using blood-forming stem cells and that allow for optimal function and persistence of CAR T cells after development. The findings could influence the field of immunotherapy focused on engineering T cells with CAR molecules that are able to persist and form immunologic memory, and that can recognize and kill virus-infected or cancerous cells.
INFORMATION:
AUTHORS
Study authors included Anjie Zhen, Mayra Carrillo, Wenli Mu, Valerie Rezek, Heather Martin, Philip Hamid, Irvin Chen, Dr. Otto Yang, Jerome A. Zack and Scott Kitchen, all of UCLA.
JOURNAL
The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS Pathogens.
FUNDING
The study was funded by amfAR, The Foundation for AIDS Research; the National Institutes of Health; the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine; and UPLIFT: UCLA Postdocs' Longitudinal Investment in Faculty.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
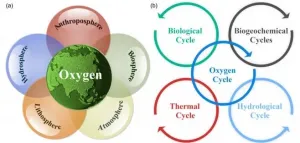
As an essential material for the survival and reproduction of almost all aerobic organisms, oxygen is closely related to the formation and development of complex organisms. A recent review provides a systematic overview of the latest advances in the oxygen cycle at different spatial and temporal scales and the important role that oxygen plays in shaping our current habitable Earth.
Professor Jianping Huang from Lanzhou University is the corresponding author of the review entitled "The oxygen cycle and a habitable Earth", which is the cover article of the 64(4) of SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences in 2021.
Based ...
2021-04-02
BOSTON - In the first study to use whole genome sequencing (WGS) to discover rare genomic variants associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD), researchers have identified 13 such variants (or mutations). In another novel finding, this study establishes new genetic links between AD and the function of synapses, which are the junctions that transmit information between neurons, and neuroplasticity, or the ability of neurons to reorganize the brain's neural network. These discoveries could help guide development of new therapies for this devastating neurological condition. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), the Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center report these findings in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
Over ...
2021-04-02
Bottom Line: Among patients at high risk of melanoma, those who received routine skin cancer screening and education about skin self-exams were significantly more likely to be diagnosed with thinner and earlier stage melanomas.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Michael Sargen, MD, a dermatologist and clinical fellow in the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH)
Background: "Whole-body screening for melanoma is currently routine for individuals at high ...
2021-04-02
The Tibet ASγ experiment, a China-Japan joint research project on cosmic-ray observation, has discovered ultra-high-energy diffuse gamma rays from the Milky Way galaxy. The highest energy detected is estimated to be unprecedentedly high, nearly 1 Peta electronvolts (PeV, or one million billion eV).
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out across the Milky Way (see Fig.1).
Scientists believe these gamma rays are produced by the nuclear interaction between cosmic rays escaping from the most powerful galactic sources ...
2021-04-02
A dangerous toxin has been witnessed - for the first time - releasing into the air from pond scum, research published in the peer-reviewed journal Lake and Reservoir Management today shows.
Not only is pond scum - otherwise known as algal bloom - an unsightly formation which can occur on still water across the world, it can also prove dangerous to wildlife and humans.
For the first time, scientists have now detected the presence of the algal toxin anatoxin-a (ATX)which is also known as 'Very Fast Death Factor', in the air near a Massachusetts pond with large algal blooms.
ATX can cause a range of symptoms at acute doses, including loss of coordination, muscular twitching and respiratory paralysis, and has been linked to the deaths of livestock, waterfowl and dogs from ...
2021-04-02
Researchers from University of Queensland, University of Melbourne, and Universidad Finis Terrae published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that studies consumer resistance to a nationwide plastic bag ban implemented in Chile in 2019.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "How Do I Carry All This Now?': Understanding Consumer Resistance to Sustainability Interventions" and is authored by Claudia Gonzalez-Arcos, Alison M. Joubert, Daiane Scaraboto, and Jörgen Sandberg.
As environmental crisis challenges accelerate, governments are searching for solutions to reduce the negative impacts of economic activity. One popular measure has been to ban disposable plastic ...
2021-04-02
A palliative care doctor has suggested that studying Shakespeare's plays could help medical students connect more closely with their patients. Writing in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Dr David Jeffrey, of the Department of Palliative Medicine at the University of Edinburgh, investigates how the playwright's empathic approach - the ability to understand and share the feelings of another - can enhance the patient-doctor relationship.
Dr Jeffrey writes that the idea that emotions are disruptive and need to be controlled is deeply ingrained in medical education and practice, contributing to doctors distancing from patients. The coronavirus pandemic, with ...
2021-04-02
Fewer than half of inmates in jails and prisons surveyed in a study by the CDC and University of Washington said they would accept a COVID-19 vaccine, while the majority either said they wanted to wait before getting the vaccine or would refuse one.
"This is a population already at risk for COVID-19, and outbreaks among incarcerated people can worsen inequities in COVID-19 outcomes as well as contribute to spread in the surrounding community," said lead author Dr. Marc Stern, affiliate assistant professor of health services in the UW School of Public Health. "So culturally and health-literacy informed interventions are needed to help them feel more confident about getting vaccinated."
The study conducted by CDC researchers ...
2021-04-02
As the COVID-19 pandemic lingers, researchers have found associations between certain lifestyle factors and a person's risk of getting infected. While it has already been established that those with Type II diabetes and a high body mass index (BMI) are at greater risk of experiencing hospitalizations and other severe complications related to COVID-19, they are also at greater risk of getting symptomatic infection in the first place. That is the finding of a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine that was published today in the journal PLoS ONE.
Using data from the UK Biobank of 500,000 British volunteers over age 40, the researchers examined ...
2021-04-02
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- All too often, patients with high levels of antibodies face major challenges getting a transplant. These highly sensitized patients have a much higher risk of death while waiting for suitable organs they are less likely to reject. But there is new hope for highly sensitized patients in need of a combined heart and liver transplant, thanks to an innovative surgical approach at Mayo Clinic.
Traditionally, surgeons transplant the heart first, followed by the liver. But Mayo Clinic heart transplant team decided to reverse the order for highly sensitized patients in the hopes that the liver would absorb some of the patient's antibodies, removing them from circulation and lowering ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers devise more efficient, enduring CAR gene therapy to combat HIV