Serving size, satisfaction influence food waste on campus
Multicampus study identifies problem's causes and potential solutions
2021-04-02
(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (April 2, 2021) - Understanding what drives food choices can help high-volume food service operations like universities reduce waste, according to a new study.
Researchers have concluded that food waste in places like university cafeterias is driven by how much people put on their plates, how familiar they are with what's on the menu and how much they like - or don't like - what they're served.
Food waste has been studied often in households, but not so often in institutional settings like university dining commons. What drives food choices in these "all-you-care-to-eat" facilities is different because diners don't perceive personal financial penalty if they leave food on their plates.
Published in the journal Foods, "Food Choice and Waste in University Dining Commons -- A Menus of Change University Research Collaborative Study" was conducted by a team of experts from Rice University; the University of California, Davis; Stanford University; Lebanon Valley College; the University of California, Santa Barbara; and the University of California, Berkeley.
Co-author Eleanor Putnam-Farr, assistant marketing professor at Rice's Jones Graduate School of Business, is available to discuss the findings and potential impact with news media.
The researchers conducted student surveys during the 2019 spring and fall semesters to study foods types, diner confidence and diner satisfaction. They used photos taken by diners themselves before and after eating to measure how much food was taken and how much of it went to waste. "Diners were intercepted at their dining halls and asked if they wanted to participate in a study about food choices and satisfaction, but the objective of investigating food waste behavior was not disclosed," the authors wrote.
The study found the amount of food wasted didn't significantly differ among types of food. Instead, researchers discovered waste was related to the amount of food diners put on their plates, how satisfied they were with their meals and how often they went to the dining commons. If students were satisfied with their food, they tended waste less of it. And diners who visited the commons most often -- making them more familiar with the menus and more confident in their choices -- tended to waste less.
Mixed dishes, like sandwiches or stir-fry, took up a greater percentage of the surface area on surveyed plates than animal proteins or grains and starches. Those three types of food took up a greater area of the plates than fruits, vegetables or plant proteins. The amount of food wasted, however, did not significantly differ among the various food categories.
The mixed dishes and animal proteins that took up greater portions of the plate tended to be pre-plated by the commons staff or have a suggested serving size. The study's results showed that greater amounts of food taken by diners correlated with the item being pre-plated or served by others.
The authors recommend future research on the topic uses their multicampus approach -- which enabled them to study food choice among a large and diverse group -- to better understand what causes food waste and find out if it can be reduced by interventions such as posting signs that encourage healthier choices.
INFORMATION:
To schedule an interview with Putnam-Farr, or for more information, contact Avery Franklin, media relations specialist at Rice, at averyrf@rice.edu or 713-348-6327.
Related materials:
Paper: https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/10/3/577.
Putnam-Farr bio: https://business.rice.edu/person/eleanor-putnam-farr.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
This news release can be found online at news.rice.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-02
A personalized tumor cell vaccine strategy targeting Myc oncogenes combined with checkpoint therapy creates an effective immune response that bypasses antigen selection and immune privilege, according to a pre-clinical study for neuroblastoma and melanoma. The neuroblastoma model showed a 75% cure with long-term survival, researchers at Children's National Hospital found.
Myc is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that help manage cell growth and differentiation in the body. When Myc mutates to an oncogene, it can promote cancer cell growth. The Myc oncogenes are ...
2021-04-02
James McKerrow, MD, PhD, dean of the Skaggs School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at University of California San Diego, has long studied neglected tropical diseases -- chronic and disabling parasitic infections that primarily affect poor and underserved communities in developing nations. They're called "neglected" because there is little financial incentive for pharmaceutical companies to develop therapies for them.
One of these neglected diseases is Chagas disease, the leading cause of heart failure in Latin America, which is spread by "kissing bugs" carrying the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. These parasites produce an enzyme called cruzain that helps ...
2021-04-02
A novel mechanism has been identified that might explain why a rare mutation is associated with familial Alzheimer's disease in a new study by investigators at the University of Chicago. The paper, published on April 2 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, characterizes a mutation located in a genetic region that was not previously thought be pathogenic, upending assumptions about what kinds of mutations can be associated with Alzheimer's Disease.
Alzheimer's, a neurodegenerative disease that currently affects more than 6 million Americans, has ...
2021-04-02
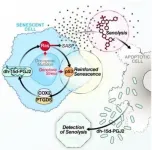
Buck Institute researchers have discovered and are developing a novel, non-invasive biomarker test that can be used to measure and track performance of senolytics: a class of drugs that selectively eliminate senescent cells. The discovery is expected to play a major role in efforts to develop treatments that would battle a myriad of chronic age-related conditions that range from arthritis to lung disease to Alzheimer's disease and glaucoma. This biomarker is a unique signaling lipid metabolite, normally exclusively intracellular, but is released when senescent cells are forced to die. This metabolite is detectible in blood and urine, making non-invasive ...
2021-04-02
Gasoline, the primary transportation fuel, contains hydrocarbons with 5-11 carbons (C5-11) and is almost derived from petroleum at present.
Gasoline can also be produced from non-petroleum syngas. Nonetheless, achieving high conversions of syngas to C5-11 with excellent selectivity and stability remains a challenge.
A research group led by Prof. LIU Zhongmin and Prof. ZHU Wenliang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences realized highly efficient and selective conversion of syngas to gasoline-range liquid hydrocarbons over a dual-bed catalyst.
The study was published in Chem Catalysis on April 2.
This dual-bed catalyst, (CZA +Al2O3)/N-ZSM-5(97), consists ...
2021-04-02
Up to one in five employees at an academic medical institution are considering leaving their professions due to the strains of coping with the pandemic in their own lives, according to a new University of Utah Health study. Individuals who had caregiving responsibilities were among those most likely to contemplate leaving or reducing hours.
The findings suggest that retaining highly trained doctors, nurses, and scientists in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic could be the next great health care challenge.
"It's sobering to learn that, during a time of economic recession, at least one-fifth of our workforce were considering leaving their jobs because of the severe levels of stress they were experiencing," says Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., the study's senior author and professor ...
2021-04-02
SAN FRANCISCO, CA (April 2, 2021) -- In recent years, advancements in DNA sequencing have exposed a large amount of hidden diversity in reef-building corals: species that appear identical to one another but are genetically distinct. Typically ignored as they are invisible to the naked eye, a team of researchers at the California Academy of Sciences and The University of Queensland, along with over a dozen international collaborators, is taking a more holistic approach to understand these hidden species by investigating overlooked ecological differences that have wide-ranging implications for the vulnerability and resilience of reef-building corals. The team hopes that their findings, ...
2021-04-02
What The Study Did: This survey study examined the career development, productivity, childcare needs and likelihood of leaving the workforce among employees at an academic medical center during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3997)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
2021-04-02
What The Study Did: Researchers compared rates of health maintenance organization (HMO) enrollment, by race and ethnicity, for children with commercial and public coverage with the use of national survey data.
Authors: Alon Peltz, M.D., M.B.A., M.H.S., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.4162)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-04-02
Extended surges in the South and West in the summer and early winter of 2020 resulted in regional increases in excess death rates, both from COVID-19 and from other causes, a 50-state analysis of excess death trends has found. Virginia Commonwealth University researchers' latest study notes that Black Americans had the highest excess death rates per capita of any racial or ethnic group in 2020.
The research, publishing Friday in the Journal of the American Medical Association, offers new data from the last 10 months of 2020 on how many Americans died during 2020 as a result of the effects of the pandemic -- beyond the number of COVID-19 deaths alone -- and which states and racial groups were hit hardest.
The rate of excess deaths -- or deaths above the number that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Serving size, satisfaction influence food waste on campus
Multicampus study identifies problem's causes and potential solutions