(Press-News.org) Overfishing likely did not cause the Atlantic cod, an iconic species, to evolve genetically and mature earlier, according to a study led by Rutgers University and the University of Oslo - the first of its kind - with major implications for ocean conservation.
"Evolution has been used in part as an excuse for why cod and other species have not recovered from overfishing," said first author END
Overfishing of Atlantic cod likely did not cause genetic changes
Study suggests reducing fishing and addressing environmental changes would help cod recover
2021-04-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sex differences in brain in response to midlife stress linked to fetal stress exposures
2021-04-05
BOSTON - Men and women whose mothers experienced stressful events during pregnancy regulate stress differently in the brain 45 years later, results of a long-term study demonstrate.
In a unique sample of 40 men and 40 women followed from the womb into their mid-forties, the brain imaging study showed that exposure during fetal development to inflammation-promoting natural substances called cytokines, produced by mothers under negative stress, results in sex-associated differences in how the adult brain responds to negative stressful situations more than 45 years after ...
Biodiversity's healthy byproduct -- nutrient-rich seafood
2021-04-05
High levels of biodiversity in aquatic settings offers a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids crucial for human health, a range of nutrients that are lacking in ecosystems where the number of species have been reduced by overfishing, pollution, or climate change, researchers report April 5 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"What we found is that biodiversity is crucial to human health," said Yale's Joey Bernhardt, a G. Evelyn Hutchinson Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and co-author of the paper.
While humans can achieve their protein requirements even with seafood from less-diverse systems, ...
A diversity of wildlife is good for our health
2021-04-05
A growing body of evidence suggests that biodiversity loss increases our exposure to both new and established zoonotic pathogens. Restoring and protecting nature is essential to preventing future pandemics. So reports a new Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) paper that synthesizes current understanding about how biodiversity affects human health and provides recommendations for future research to guide management.
Lead author Felicia Keesing is a professor at Bard College and a Visiting Scientist at Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies. She explains, "There's a persistent myth ...
To intervene or not to intervene? That is the future climate question
2021-04-05
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Nine of the hottest years in human history have occurred in the past decade. Without a major shift in this climate trajectory, the future of life on Earth is in question, which poses a new question: Should humans, whose fossil fueled society is driving climate change, use technology to put the brakes on global warming?
Michigan State University community ecologist Phoebe Zarnetske is co-lead of the Climate Intervention Biology Working Group, a team of internationally recognized experts in climate science and ecology that is bringing science to bear on the question and consequences of geoengineering a cooler Earth.
The group's ...
For 80% of Americans with resolved drug problem, significant personal achievements
2021-04-05
BOSTON - Addiction is associated with social exclusion, loss of access to resources, and general disengagement from civic life. Now, a study recently published in the journal Psychology of Addictive Behaviors and led by David Eddie, PhD, of the Massachusetts General Hospital's Recovery Research Institute has found that the majority of Americans who have resolved an alcohol or other drug problem report achievements related to self-improvement, family engagement, and civic and economic participation since resolving their addiction. Additionally, it appears these achievements accumulate with time in addiction recovery.
Incorporating data from the Recovery Research Institute's landmark 2017 National Recovery Study, which indicated ...
Surprising disconnect between physical characteristics and genetic ancestry in certain
2021-04-05
A new study by Stanford University biologists finds an explanation for the idea that physical characteristics such as skin pigmentation are "only skin deep." Using genetic modeling, the team has found that when two populations with distinct traits combine over generations, traits of individuals within the resulting "admixed" population come to reveal very little about individuals' ancestry. Their findings were published March 27 in a special edition of the American Journal of Physical Anthropology on race and racism.
"When two founding groups first come together, a visible physical trait that differed between those founders initially carries information about the genetic ancestry of admixed individuals," says Jaehee Kim, a postdoctoral research fellow in biology at Stanford and first author ...
Understanding how cancer can relapse
2021-04-05
In the fight against cancers, activating mutations in the RAS family of genes stand in the way of finding viable treatment options. Now, scientists at the University of Missouri and Yale University have discovered that one of these mutations -- oncogenic RAS or RASV12 -- is also responsible for the regrowth of cancer cells following genotoxic therapy treatment, or drugs that cause damage to a cancer cell's DNA in order to eliminate it from the body.
"Most of our knowledge of how cells respond to DNA damage is mainly derived from studies looking at the single cell level," said Yves Chabu, an assistant professor in the MU College of Arts and Science. "Therefore, we don't know much about how tumor cells respond to DNA damage in the broader ...
How climate change affects Colombia's coffee production
2021-04-05
URBANA, Ill. ¬- If your day started with a cup of coffee, there's a good chance your morning brew came from Colombia. Home to some of the finest Arabica beans, the country is the world's third largest coffee producer. Climate change poses new challenges to coffee production in Colombia, as it does to agricultural production anywhere in the world, but a new University of Illinois study shows effects vary widely depending on where the coffee beans grow.
"Colombia is a large country with a very distinct geography. The Andes Mountains cross the country from its southwest to northeast corner. Colombian coffee is currently growing in areas with different altitude levels, and climate impacts will likely be very different for low ...
Contraceptive planning is essential to optimal health for women with heart disease
2021-04-05
Pregnancy can increase the risk of morbidity and mortality in women with cardiovascular disease; however, many cardiologists are not having pre-pregnancy contraception discussions with their patients of child-bearing age. There is a need to provide evidence-based guidance for contraceptive safety and effectiveness and pregnancy planning options for this high-risk patient group, according to a paper published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). This paper is one of a five-part JACC focus seminar series addressing a wide range of topics in the emerging cardio-obstetrics field.
Prior research has found that 68% of females have had sex at least once by the time they were 17, ...
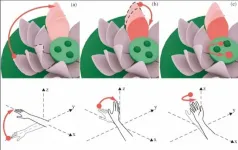
Amazing integration of technology and art: a 3D LotusMenu in your palm
2021-04-05
A recent study proposed a three-dimensional LotusMenu that can "bloom in the palm". With this menu, even if you are not Nezha, you can also control your own lotus.
The research paper is titled: "LotusMenu: A 3D Menu using Wrist and Elbow Rotation Inspired by Chinese Traditional Symbol". It's published in SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences recently, written by Associate Professor Lu Fei's human-computer interaction research team from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications. Based on the metaphor of the traditional lotus pattern, the researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
ACMG Foundation to present adaptive bikes to Baltimore-area children with genetic conditions at heartwarming “Day of Caring” event on March 13
Racial disparities in food insecurity for high- and low-income households
Incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest on a postholiday weekday
Prior authorization bans for buprenorphine alone may not improve treatment retention
When light boosts protein evolution
New model may predict preeclampsia in late pregnancy
[Press-News.org] Overfishing of Atlantic cod likely did not cause genetic changesStudy suggests reducing fishing and addressing environmental changes would help cod recover