Black women are dying of COVID-19 at rates higher than men in other racial/ethnic groups
GenderSci Lab publishes first analysis of sex-disparity in COVID-19 mortality across racial groups, emphasizing the specific vulnerability of Black women.
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) A new paper in the Journal of General Internal Medicine published by the GenderSci Lab at Harvard University shows that Black women are dying at significantly higher rates than white men, and that disparities in mortality rates among women of all races are greater than those between white women and white men.
The study is the first to quantify the inequities in COVID-19 mortality looking at both race and sex group.
"This analysis complicates the simple narrative that men are dying at greater rates of COVID-19 than women," said lead author Tamara Rushovich, Harvard Ph.D. candidate in population health sciences and lab member at the GenderSci Lab.
Results show that the common belief that men with COVID-19 fare more poorly than women varies in magnitude across social groups defined by race/ethnicity.
Key findings of the study include:
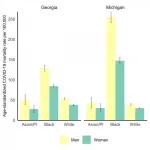
Black women have COVID-19 mortality rates that are almost 4 times higher than that of white men and 3 times higher than that of Asian men, as well as higher than white and Asian women.
Black men have far higher mortality rates than any other sex and racial group, including over 6 times higher than the rate among white men.
The disparity in mortality rates between Black women and white women is over 3 times the disparity between white men and white women.
The disparity between Black men and Black women is larger than the disparity between white men and white women.
It is well understood that racism and social inequities, not genetics, are responsible for racial disparities in COVID-19 mortality. However, many researchers focus on differences in biology to explain the sex disparity in COVID-19 mortality. This paper's findings challenge the sole focus on biology as an explanation for sex differences in COVID-19 mortality and argue that societal factors related to gender in combination with racism and socioeconomic stratification are important explanatory factors.
INFORMATION:
This study used census data and publicly available data from Michigan and Georgia, the only two states reporting data disaggregated by age, race, and sex, to calculate and compare COVID-19 mortality rates.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
The adult human body produces hundreds of billions of blood cells every day. This essential process unavoidably leads to the appearance of mutations in the DNA of the progenitor cells. These are known as somatic mutations because they are acquired, not inherited. While most of these mutations are innocuous, occasionally a mutation gives affected cells a competitive advantage that allows them to expand progressively, generating clonal populations of blood cells. This phenomenon is known as clonal hematopoiesis.
Now, a team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) and the Hospital Universitario Virgen de Arrixaca in Murcia has discovered that the presence of these acquired mutations in blood cells increases ...
2021-04-06
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. ACP Best Practice Advice: Shorter course of antibiotics may be appropriate for some common infections
HD video soundbites of ACP's president discussing the paper are available to download at http://www.dssimon.com/MM/ACP-antibiotics-paper.
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7355
Free ...
2021-04-06
Researchers at the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center (HUG-CELL), hosted by the University of São Paulo's Institute of Biosciences (IB-USP) in Brazil, have developed a technique to reconstruct and produce livers in the laboratory.
The proof-of-concept study was conducted with rat livers. In the next stage of their research, the scientists will adapt the technique for the production of human livers in order in future to increase the supply of these organs for transplantation.
The study was supported by FAPESP and is reported in an article published in Materials Science and Engineering: ...
2021-04-05
PITTSBURGH, April 5, 2021 - "Near-poor" Americans--people just above the federal poverty level but still well below the average U.S. income--who rely on Medicare for health insurance face high medical bills and may forgo essential health care, according to new research led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health. This is due to a coverage "cliff" in Medicaid, which supplements Medicare for people with incomes below poverty but excludes individuals above the federal poverty threshold, including the near-poor.
In a report published today in the April issue of the journal Health Affairs, the authors describe the effects of this cliff and propose solutions to fix it, with the aim of lessening barriers to care among near-poor people ...
2021-04-05
PHILADELPHIA-- Approximately 6.5 million people are under correctional supervision in the United States on any given day. Justice-involved individuals (people currently or recently in prison or jail, on probation or parole, or arrested) experience higher rates of substance use disorders than the general population. In fact, among people with opioid use disorder (OUD), more than half have reported contact with the criminal justice system.
Numerous clinical studies have shown that medications for OUD -- specifically, methadone or buprenorphine -- lead to superior outcomes for retention in treatment, reduced illicit opioid use, and decreased opioid-related overdose rates and serious acute care compared with treatments that ...
2021-04-05
PHILADELPHIA-- While the emergency department (ED) functions as an integral part of the United States healthcare safety net by handling all medical complaints regardless of insurance status, ED visits are expensive, and many are for lower-acuity conditions that may be amenable to care in other settings. Previous research has suggested that greater availability of urgent care centers - freestanding facilities with extended hours that staff emergency physicians, primary care physicians, or nurse practitioners, and focus on a broad range of lower acuity complaints, like rash, muscle strain, bronchitis, and urinary tract infection - helps decrease ED visits, but whether the centers reduce or increase net spending for patients ...
2021-04-05
Even before the pandemic made telehealth a hot topic, people with minor urgent health needs had started to turn to companies that offer on-demand video chats with physicians that they don't normally see.
Insurers and employers even started buying access to this direct-to-consumer form of virtual care, hoping it might reduce in-person care, including emergency department visits.
But a new University of Michigan study casts some doubt on whether that will actually happen.
Published in the April issue of Health Affairs, the study finds that patients who had an on-demand ...
2021-04-05
In a new study, researchers found nearly half of those who share explicit images of others without permission feel remorse after the fact and 24% try to deflect blame onto victims. Amy Hasinoff, a researcher at the University of Colorado Denver, joined Danish researcher Sidsel K. Harder, to take a deeper dive into the issue of sexual abuse and image sharing.
Hasinoff and Harder looked at how people who shared explicit images online spoke to police officers about the harmful acts they committed. While looking over cases where the image-sharer was caught and convicted, ...
2021-04-05
People with ovarian cancer frequently receive aggressive end-of-life care despite industry guidelines that emphasize quality of life for those with advanced disease, according to a recent study.
In fact, by 2016, ICU stays and emergency department visits in the last month of life had become more common for people with ovarian cancer than they were in 2007, the earliest year from which researchers analyzed data.
The proportion of non-Hispanic Black people who turned to the emergency department for care was even higher -- double that of non-Hispanic whites. Black people were also nearly twice as likely to undergo intensive treatment, including ...
2021-04-05
One day, humankind may step foot on another habitable planet. That planet may look very different from Earth, but one thing will feel familiar -- the rain.
In a recent paper, Harvard researchers found that raindrops are remarkably similar across different planetary environments, even planets as drastically different as Earth and Jupiter. Understanding the behavior of raindrops on other planets is key to not only revealing the ancient climate on planets like Mars but identifying potentially habitable planets outside our solar system.
"The lifecycle of clouds is really important when we think about planet habitability," said Kaitlyn Loftus, a graduate student in the Department ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Black women are dying of COVID-19 at rates higher than men in other racial/ethnic groups
GenderSci Lab publishes first analysis of sex-disparity in COVID-19 mortality across racial groups, emphasizing the specific vulnerability of Black women.


