Curbing coronavirus spread in enclosed spaces means better masks, adequate ventilation
Findings show leakage of airborne droplets escaping from masks even when just breathing
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, April 6, 2021 -- With research increasingly showing the COVID-19 virus is transmissible via smaller droplets suspended in air, there is a growing concern current public health guidelines of mask wearing and social distancing are insufficient in combating its spread in indoor environments, like prisons, hospitals, and meatpacking plants, where people tend to be in close quarters.
Most research has focused on coughing and sneezing. But studies on how simply breathing might contribute to airborne spread of the virus are rare.
In AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar show social distancing is equally important as mask wearing when people indoors are just breathing or participating in normal conversation, even when there is no risk of coughing or sneezing. They also found mask leakage in the same scenario presents a notable challenge in preventing the virus's spread.
"Our findings show the need for good ventilation systems that take into account the 5 to 10% of aerosolized particle leakage that occurs in each breathing cycle as a way to reduce droplet concentration in enclosed spaces," author Venugopal Arumuru said. "There also is a need for mask design innovation to reduce side and bottom droplet leakage while providing adequate face comfort."
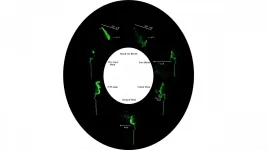
In an experimental setup, a mechanical breathing simulator was connected to a mannequin standing at 5 feet 8 inches tall to simulate regular breath and slightly longer breath typical of healthy adults standing still or involved in moderate activity, like walking, talking, or participating in assembly work. The researchers evaluated the efficacy of various mask types, mask-shield combinations, and only face shield use.
A fog generator was filled with a mixture of water and glycerin to emulate the consistency of saliva droplets in the diameter range of 1-10 micrometers to reflect airborne transmissibility. Droplet exposure was illuminated and captured by video camera.
The researchers found that with no face covering, droplets from breathing can travel up to 4 feet in five seconds. A commercial five-layered mask was found to provide the best protection, with full front-of-face protection and minimal leakage below the chin. A commercial N-95 mask impedes droplet leakage in front, but leakage in gaps between the mask and nose was significant.
Leakage from the front of the surgical mask was evident, although adding a face shield increased droplet restriction.
"However, the noticeable droplets settling below the shield is concerning, and pairing surgical masks with shields is not adequate in hospitals and other places where strict social distancing guidelines are difficult to follow," Arumuru said.
INFORMATION:
The article "Breathing, virus transmission and social distancing - An experimental visualization study" is authored by Venugopal Arumuru, Jangyadatta Pasa, Sidhartha Sankar Samantaray, and Vaibhavsingh Surendrasingh Varma. The article will appear in AIP Advances on April 6, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0045582). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0045582.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences--applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/adv.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
Spain is among the five countries in the world with the highest levels of social acceptance of LGBTIQ+ people and rights, and was the third country in the world to legalize same-sex marriages, in 2005. In 2019, 3.1% of marriages were between same-sex couples (INE 2020). In this context, it would seem consistent that sexual orientation should not determine wage inequalities. But is this really so? What is the relationship between sexual orientation and wages?
The study, recently published in Journal of Family Issues, found a significant correlation ...
2021-04-06
The Tibetan Plateau, known as "the roof of the world", has warmed more rapidly than global average in the past decades. The observed warming of the Tibetan Plateau since 1960s can be attributed to human activities, particularly greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, the Plateau may warm faster in the future than climate models projected, according to a study recently published in Environmental Research Letters.
The Tibetan Plateau contains the largest volumes of ice outside the Arctic and Antarctic, feeding water to dozens of major Asian rivers. However, the rapid warming of the "Water Tower of Asia" has significantly affected regional hydrological cycle and ecosystem services, leading to remarkable glacier retreat and geohazard ...
2021-04-06
New research led by the universities of Kent and Warwick has found that, contrary to previous beliefs, adolescents born preterm have the same levels of self-esteem and overall wellbeing as those born full-term.
Preterm birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks of gestation, has been previously found to be associated with an increased risk for lower academic achievement, higher mental health problems and increased difficulties in social relationships compared to those born full-term. This new study, co-led by Dr Ayten Bilgin (Kent) alongside colleagues from Warwick, demonstrates that in contrast, preterm birth ...
2021-04-06
A total of 108 women participated in the research from the first weeks of pregnancy to delivery, having recorded their stress levels before, during, and after conception (via the concentration of cortisol in hair) and performed different psychological tests
A study carried out by scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) has revealed that women who experience stress both before becoming pregnant and during conception are almost twice as likely to have a girl as a boy.
Researchers from the Mind, Brain and Behaviour Research Centre (CIMCYC), the Department of Pharmacology (Faculty of Pharmacy), and the Faculty of Psychology have analysed the levels of cortisol (a steroid hormone that is released in response to stress) ...
2021-04-06
Cuckoo wasps - also called emerald wasps - are some of the most beautiful insects we have, with colourful exteriors that shine like jewels. However, these beauties have also created a lot of headaches.
"Normally we distinguish insects from each other by their appearance, but cuckoo wasps are so similar to each other that it makes it difficult," says Frode Ødegaard.
Ødegaard is an insect researcher at the NTNU (Norwegian University of Science and Technology) University Museum and belongs to the European research group that has now ...
2021-04-06
New research suggests Ireland's increasing populations of Sika deer may be linked to local outbreaks of TB infection in cattle.
Although TB infection rates have decreased in general in recent decades, county-level data shows a correlation between higher Sika numbers and higher local TB infections - with County Wicklow a particular hotspot.
The research, conducted by researchers from Trinity College Dublin and the National Parks and Wildlife Service and supported by the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine, has major implications for controlling TB. It has ...
2021-04-06
Is there a way to chemically manipulate small, confined areas on cellular surfaces? Scientists have developed a microfluidic probe to send a flow of free radicals on live cells and track the outcome using fluorescence imaging. As outlined in the journal Angewandte Chemie, this approach makes it possible for the first time to generate a reaction zone of free radicals with controlled size and concentration for subcellular research.
Free radicals are important stimulants for cells. When live cells are exposed to radicals, they develop intense reactions that can lead to cell ...
2021-04-06
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have experimentally demonstrated a novel cancer diagnosis technique based on the scattering of circularly polarized light. Computational studies revealed that this technique can detect the progression of precancerous lesions and early cancer. This method can be implemented using an endoscope equipped with spin-LEDs--devices that emit circularly polarized light.
Most cancers of the digestive system emerge in the surface layer first and then progress into deeper layers. While surface layer carcinomas can be readily treated using an endoscope, carcinomas that have advanced onto deeper layers need surgical intervention to prevent them from metastasizing to lymph nodes or other organs. Thus, accurate measurements of the depth of cancer ...
2021-04-06
Amsterdam, April 6, 2021 - The rarity of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) means that promising new treatments may be tested in only a limited spectrum of patients before approval. Investigators evaluated a newly approved drug, onasemnogene abeparvovec, in a broader spectrum of patients in order to obtain expanded data on its side effects profile. They report in the Journal of Neuromuscular Diseases that the drug is associated with an immune response against the adeno-associated viral vector and needs careful monitoring, but showed no long-term adverse effects.
In recent years, the availability of a growing number of drug treatments has significantly ...
2021-04-06
New Orleans, LA - A study led by Edward Wojcik, PhD, Associate Professor of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine, identified how microcephaly (abnormally small heads) and blindness may develop in Zika-infected fetuses, as well as a new way to potentially prevent these neurodevelopmental defects. The results are published online in iScience, available here.
The mechanism by which Zika virus disrupts neuronal development and results in congenital Zika syndrome was unknown. Because of similarities between Zika syndrome and a recognized congenital genetic disease (Kinesin-5) known to cause microcephaly and retinopathies in developing infants, the research team studied both, looking for similarities. They discovered a direct link, the first ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Curbing coronavirus spread in enclosed spaces means better masks, adequate ventilation
Findings show leakage of airborne droplets escaping from masks even when just breathing