Parkinson's discovery points to possible future treatment approaches
More than 20 years after the discovery of the parkin gene linked to young-onset Parkinson's disease, researchers at The Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa may have finally figured out how this mysterious gene protects the brain
2021-04-07
(Press-News.org) More than 20 years after the discovery of the parkin gene linked to young-onset Parkinson's disease, researchers at The Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa may have finally figured out how this mysterious gene protects the brain.
Using human and mouse brain samples and engineered cells, they found that the parkin protein works in two ways. First, it acts like a powerful antioxidant that disarms potentially harmful oxidants in the brain, including dopamine radicals. Second, as the brain ages and dopamine radicals continue to build up, parkin sequesters these harmful molecules in a special storage site within vulnerable nerve cells, so they can continue to function normally throughout our lifespan.
In people with mutations in both copies of the parkin gene, these protective effects are missing, and as a result Parkinson's develops before the age of 40 years. If confirmed, the results could point the way towards the development of new treatments.
"If we could deliver antioxidants or a healthy copy of the parkin gene into the brains of people with these mutations, this could help slow down or even halt early-onset Parkinson's," said co-corresponding author and scientific project manager Dr. Julianna Tomlinson.
"What we don't know yet is whether such an approach could also benefit individuals with late-onset Parkinson's that is not linked to the parkin gene," added co-corresponding author Dr. Michael Schlossmacher, neurologist and Director of Neuroscience at The Ottawa Hospital. "We are eager to investigate this."
INFORMATION:
Dr. Schlossmacher is also a professor at the University of Ottawa Brain and Mind Research Institute and holds the Bhargava Family Research Chair in Neurodegeneration at The Ottawa Hospital.
This research was possible because of a large team effort, with important contributions from several graduate students, including Jacqueline Tokarew, Daniel El-Kodsi, Nathalie Lengacher and Travis Fehr.
Drs. Schlossmacher, Tomlinson and John Pezacki of the Department of Chemistry at uOttawa were recently awarded a new project grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to continue this work. They are also making their unique research tools available around the world through a partnership between BioLegend and the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-07
CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. -- If, as the saying goes, less is more, why do we humans overdo so much?
In a new paper featured on the cover of Nature, University of Virginia researchers explain why people rarely look at a situation, object or idea that needs improving -- in all kinds of contexts -- and think to remove something as a solution. Instead, we almost always add some element, whether it helps or not.
The team's findings suggest a fundamental reason that people struggle with overwhelming schedules, that institutions bog down in proliferating red tape, and, of particular ...
2021-04-07
Mobility tracking using cell phone data showing greater movement of people is a strong predictor of increased rates of COVID-19, according to new data in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"This study shows that mobility strongly predicts [severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2] SARS-CoV-2 growth rate up to 3 weeks in the future, and that stringent measures will continue to be necessary through spring 2021 in Canada," writes Dr. Kevin Brown, Public Health Ontario, with coauthors.
Until Canadians are widely vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2, nonpharmaceutical public health interventions such as physical distancing and limiting social contact will be the main population-based means of controlling the spread of the virus.
"Mobility ...
2021-04-07
While studying genetic diversity in bumblebees in the Rocky Mountains, USA, researchers from Uppsala University discovered a new species. They named it Bombus incognitus and present their findings in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Bumblebees are vital for agriculture and the natural world due to their role in plant pollination. There are more than 250 species of bumblebee, and they are found mainly in northern temperate regions of the planet. Alarmingly, many species are declining due to the effects of climate change, and those with alpine and arctic habitats are particularly threatened. However, the full diversity of bumblebee ...
2021-04-07
The hormone auxin is of central importance for the development of plants. Scientists at the University of Bayreuth and the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Tübingen have now developed a novel sensor that makes the spatial distribution of auxin in the cells of living plants visible in real time. The sensor opens up completely new insights into the inner workings of plants for researchers. Moreover, the influences of changing environmental conditions on growth can now also be quickly detected. The team presents its research results in the journal Nature.
The effects of the plant hormone auxin were first described ...
2021-04-07
Ants react to social isolation in a similar way as do humans and other social mammals. A study by an Israeli-German research team has revealed alterations to the social and hygienic behavior of ants that had been isolated from their group. The research team was particularly surprised by the fact that immune and stress genes were downregulated in the brains of the isolated ants. "This makes the immune system less efficient, a phenomenon that is also apparent in socially isolating humans - notably at present during the COVID-19 crisis," said Professor Susanne Foitzik, who headed up the study at Johannes ...
2021-04-07
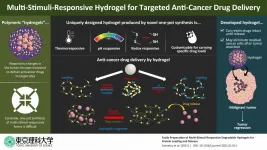
Cancer therapy in recent times relies on the use of several drugs derived from biological sources including different bacteria and viruses, among others. However, these bio-based drugs get easily degraded and therefore inactivated on administration into the body. Thus, effective delivery to and release of these drugs at target tumor sites are of paramount importance from the perspective of cancer therapy.
Recently, scientists have discovered unique three-dimensional, water-containing polymers, called hydrogels, as effective drug delivery systems (DDSs). Drugs loaded into these hydrogels remain relatively stable owing to the network-like structure and organic tissue-like consistency of these DDSs. Besides, drug release from hydrogels can ...
2021-04-07
By Karina Ninni | Agência FAPESP – A multidisciplinary research group affiliated with the Department of Physical Education’s Human Movement Laboratory (Movi-Lab) at São Paulo State University (UNESP) in Bauru, Brazil, measured step length synergy while crossing obstacles in patients with Parkinson’s disease and concluded that it was 53% lower than in healthy subjects of the same age and weight. Step length is one of the main variables affected by the disease.
Synergy, defined as combined operation, refers in this case to the capacity of the locomotor (or musculoskeletal) system to adapt movement while crossing an obstacle, combining factors such as speed and foot position, for example. Improving synergy in Parkinson’s patients while they ...
2021-04-07
You might not think an animal made out of stone would have much to worry about in the way of predators, and that's largely what scientists had thought about coral. Although corallivores like parrotfish and pufferfish are well known to biologists, their impact on coral growth and survival was believed to be small compared to factors like heatwaves, ocean acidification and competition from algae.
But researchers at UC Santa Barbara have found that young corals are quite vulnerable to these predators, regardless of whether a colony finds itself alone on the reef or surrounded by others of its kind. The research, led by doctoral student Kai Kopecky, appears in the journal Coral Reefs.
Kopecky and his co-authors ...
2021-04-07
Unusual diseases are medical mysteries that fascinate us, and one such disease is multiple system atrophy, or MSA. This rare neurological disorder causes failures in the proper functioning of the body's autonomic system (processes that are not under our conscious control, such as blood pressure, breathing, and involuntary movement). The resulting symptoms can look like two other types of neurodegenerative disease: Parkinson's disease and cerebellar ataxia. In fact, MSA can be separated into a parkinsonism subtype or a cerebellar subtype based on whether the resultant movement-related ...
2021-04-07
Within multicellular organisms, cells build connections with each other forming cell layers that cover the surfaces of tissues and organs and separate structures in the body. For example, the skin forms a mantle around the entire organism, and the layer of cells lining the blood vessels creates a boundary between the bloodstream and tissues. Special connections between neighbouring cells ensure that these cellular barriers are, on the one hand, stable and tight - thus protecting the body and organs against pathogens - while, on the other hand, they remain permeable to specific substances or migrating cells. This is how the cells allow dissolved ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Parkinson's discovery points to possible future treatment approaches
More than 20 years after the discovery of the parkin gene linked to young-onset Parkinson's disease, researchers at The Ottawa Hospital and the University of Ottawa may have finally figured out how this mysterious gene protects the brain