How to tame a restless genome
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) Short pieces of DNA--jumping genes--can bounce from one place to another in our genomes. When too many DNA fragments move around, cancer, infertility, and other problems can arise. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor & HHMI Investigator Leemor Joshua-Tor and a research investigator in her lab, Jonathan Ipsaro, study how cells safeguard the genome's integrity and immobilize these restless bits of DNA. They found that one of the jumping genes' most needed resources may also be their greatest vulnerability.
The mammalian genome is full of genetic elements that have the potential to move from place to place. One type is an LTR retrotransposon (LTR). In normal cells, these elements don't move much. But if something happens to allow them to move, say during sexual reproduction or in cancerous cells Joshua-Tor says:
"Sometimes they jump into very important spots, either genes themselves or in areas of the genome that is important for regulating genes."
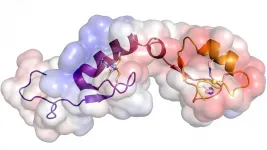
In this study, Joshua-Tor and Ipsaro examined a mouse protein called Asterix/Gtsf1 that immobilizes LTRs. To understand how this protein locks down LTRs, Ipsaro used several techniques, including cryo-EM, to take a closer look at the protein structure. Joshua-Tor says:
"Structure just informs us in many ways, like how things work. If you can see something, you have a way better idea of how it works."
Ipsaro found Asterix/Gtsf1 binds directly to a particular class of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA). tRNAs normally are part of the cell's protein manufacturing machinery. LTRs have borrowed that part of the protein-making machinery to replicate their genetic material. Asterix/Gtsf1 overrides what the LTRs are trying to do by freezing the otherwise mobile element in place, shutting down their ability to move. Ipsaro says:
"It's trying to copy and paste itself all over the genome. A part of it evolutionarily has depended on tRNA binding in order to replicate."
Instead of freezing the entire genome, scientists think Asterix/Gtf1 is using tRNAs to suppress small specific regions, like LTRs. Researchers are trying to figure out how cells protect themselves against these and other types of mobile genetic elements. They hope that someday they might tame an overly restless genome, preventing new mutations in the germline and in tumors.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - Research shows people turn to religion in times of fear and uncertainty - and March 2020 was one of those times.
To find the impact of religion during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, Landon Schnabel, the Robert and Ann Rosenthal Assistant Professor of Sociology in the College of Arts and Sciences, analyzed responses from 11,537 Americans surveyed March 19-24, 2020, shortly after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global health pandemic.
Religion protected mental health of members of several ...
2021-04-08
Image inpainting is a computer vision technique in which pixels missing from an image are filled in. It is often used to remove unwanted objects from an image or to recreate missing regions of occluded images. Inpainting is a common tool for predicting missing image data, but it's challenging to synthesize the missing pixels in a realistic and coherent way.
Researchers at the University of Tokyo have presented a frequency-based inpainting method that enables the use of both frequency and spatial information to generate missing image portions. Publishing in the Journal of Electronic Imaging (JEI), Hiya Roy et al. detail the technique in " END ...
2021-04-08
COLUMBUS, Ohio - It's one thing to decide among two or three snacks available at a friend's house. But what do people do when they're faced with a vending machine offering 36 different options?
A new study using eye-tracking technology suggests that the amount of time people spend looking at individual items may actually help them decide. Findings showed that people tended to choose snacks they spent more time looking at, sometimes even over snacks that they rated more highly.
"We could do pretty well predicting what people would choose based just ...
2021-04-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Avian brood parasites lay their eggs in the nests of other bird species, forcing the hosts to do the hard work of raising the unrelated young. A team of scientists wanted to simulate the task of piercing an egg - a tactic that only a minority of host birds use to help grasp and eject the foreign eggs. Their study offers insight into some of the physical challenges the discriminating host birds face.
The new findings appear in the Journal of Experimental Biology.
Take cowbirds, for example. Their eggs look nothing like the host birds' eggs, "yet most of their hosts do not reject the parasite eggs," said study co-author Mark Hauber, a professor of evolution, ecology and behavior at the ...
2021-04-08
Natural disasters have a way of bringing people together to rebuild. Now, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on April 8 have found that the same is true for rhesus macaques.
The study reports that after a major hurricane hit Puerto Rico, macaques living on Cayo Santiago Island became more tolerant of each other and sought new social connections. The findings are based on careful study of social connections among Cayo Santiago Island's macaques before and after Hurricane Maria, a devastating storm that left more than 3,000 people dead.
"The macaques ...
2021-04-08
Chest beating by mountain gorillas - rapidly beating their chests with their hands to produce a drumming sound - may convey information about their body size and allow identification of individuals, a study published in Scientific Reports suggests. These findings demonstrate how non-vocal behaviours may contribute to mountain gorilla communication.
Although it had previously been suggested that gorillas may beat their chests to convey information, the exact nature of that information was unclear. Edward Wright and colleagues observed and recorded 25 wild, adult male silverback gorillas monitored by the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund in Volcanoes National Park, Rwanda, between January 2014 and July 2016. Body size was determined from photographs ...
2021-04-08
Along the Tian Shan and Alay mountain ranges of Central Asia, sheep and other domestic livestock form the core economy of contemporary life. Although it was here that the movements of their ancient predecessors helped to shape the great trade networks of the Silk Road, domestic animals were thought to have come relatively late to the region. A new study, published today in the journal Nature: Human Behavior, reveals that the roots of animal domestication in Central Asia stretch back at least 8,000 years - making the region one of the oldest continuously inhabited pastoral landscapes in the world.
The domestication ...
2021-04-08
Ageing and age-related brain disease do not affect women and men in the same way. The adult brain constantly generates new brain cells called neurons from stem cells, a process called neurogenesis. This process is important for learning and cognitive function which declines as the brain ages. Neurogenesis has been extensively studied in animals, but most studies have looked at male animals, raising the question of whether age-related decline in neurogenesis affects both sexes in the same way. To address this, researchers Sally Temple, PhD (sallytemple@neuralsci.org), Kristen Zuloga, PhD (zuloagk@amc.edu) and colleagues at the NY Neural Stem ...
2021-04-08
Mutations in the DNA of the cell's energy 'factories' increases the chances of survival for people with bowel cancer, according to a study published today (Thursday) in Nature Metabolism.
Scientists funded by Cancer Research UK have found that patients with colorectal cancer, a common form of bowel cancer, had a 57 to 93% decreased risk of death from their cancer, depending on the presence and type of mitochondrial DNA mutations in their tumours.
The researchers hope that in the future, doctors could use this information to identify patients with more aggressive forms of bowel ...
2021-04-08
What The Study Did: This analysis evaluated in-hospital mortality rates for patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection over time and factors associated with changes were examined
Authors: Lyn Finelli, Dr.P.H., M.S., of Merck Research Labs in North Wales, Pennsylvania, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6556)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How to tame a restless genome





