(Press-News.org) Children who regularly snore have structural changes in their brain that may account for the behavioral problems associated with the condition including lack of focus, hyperactivity, and learning difficulties at school. That is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), which was published today in the journal Nature Communications.
The research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) and nine other Institutes, Centers, and Offices of the National Institutes of Health.
To conduct study, the researchers examined MRI images collected from more than 10,000 children aged 9 to 10 years enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the largest long-term study of brain development and child health in the US. UMSOM researchers are co-investigators in this ongoing study.
They found that children who snored regularly (three or more times per week), as reported by their parents were more likely to have thinner gray matter in several regions in the frontal lobes of their brain. These areas of the brain are responsible for higher reasoning skills and impulse control. The thinner cortex in these regions correlated with behavioral disturbances associated with sleep disordered breathing, a severe form of which is called sleep apnea. These behavioral problems include a lack of focus, learning disabilities, and impulsive behaviors. The snoring condition causes disrupted sleep throughout the night due to interrupted breathing and reduction in oxygen supply to the brain.
"This is the largest study of its kind detailing the association between snoring and brain abnormalities," said study lead author Amal Isaiah, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Otorhinolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery and Pediatrics at UMSOM. "These brain changes are similar to what you would see in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Children have loss of cognitive control which is additionally associated with disruptive behavior."
Up to 10 percent of American children have obstructive sleep disordered breathing, and a significant percentage are misdiagnosed as having ADHD and treated with stimulant medications.
Dr. Isaiah offered this advice to parents: "If you have a child who is snoring more than twice a week, that child needs to be evaluated. We now have strong structural evidence from brain imaging to reinforce the importance of diagnosing and treating sleep disordered breathing in children."
The condition can be treated with tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy, considered the first line of treatment of children with symptoms of snoring, breathing pauses during sleep, and mouth breathing.
"We know the brain has the ability to repair itself, especially in children, so timely recognition and treatment of obstructive sleep disordered breathing may attenuate these brain changes. More research is needed to validate such mechanisms for these relationships which may also lead to further treatment approaches," said study co-author Linda Chang, MD, MS, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine who is a co-principal investigator on the ABCD study.
The researchers plan to conduct a follow-up study to determine whether children who continued to snore experienced worsening brain findings on their MRI.
"For the first time, we see evidence on brain imaging that measures the toll this common condition can take on a child's neurological development," said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine. "This is an important finding that highlights the need to properly diagnose snoring abnormalities in children."
INFORMATION:
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 45 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs; and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has more than $563 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 student trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System ("University of Maryland Medicine") has an annual budget of nearly $6 billion and an economic impact more than $15 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity, is an innovator in translational medicine, with 600 active patents and 24 start-up companies. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
Past Global Changes Horizons is a scientific review of why the study of Earth's history is important, and uses comics, pictures, and drawings that support short papers with strong messages about past sciences and how to prepare for a changing future. Articles cover different environments across the planet, from caves to oceans, and from Antarctica to the Rift valley in Africa.
Each of the 18 contributions addresses a scientific question and includes appealing and understandable figures or images, without sacrificing scientific rigor. Tips and suggestions for further research and discussion topics are also included, meaning Horizons is ...
Growing more legumes, like beans and lentils, is potentially a more sustainable and nutritious approach to European agriculture, shows a new study in END ...
PITTSBURGH, April 13, 2021 - What can vaccine proponents, clinicians and public health communicators learn from "anti-vaxxers?" A lot, according to new guidance for pro-vaccination social media events written by University of Pittsburgh health scientists.
The five-part guidelines, published today in the journal Vaccine, arose from an analysis of a grassroots pro-vaccination campaign organized last year by popular physician and social media personality Zubin Damania, M.D., colloquially known as "ZDoggMD." Unexpectedly, more than three-quarters of the tweets associated with the ...
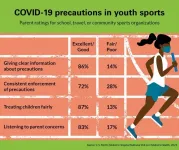
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- For young athletes, the new normal on soccer fields and basketball courts means temperature checks before practice, wearing masks through games and a sparse in-person fan base.
But that hasn't kept children and teens from playing. Close to a fourth of parents say their child has participated in school, travel, or community sports during the fall or winter months, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at the University of Michigan.
And while the majority of parents give their child's sports organization high marks for communication about safety protocols, one in four rate their sports ...
Hamilton, ON (April 13, 2021) - Ontario doctors are still hesitant to prescribe medical cannabis to patients suffering long-term pain 20 years after it was first introduced, says a new study carried out at McMaster University.
Physicians surveyed said their main concerns relate to possible ill-effects and a lack of understanding regarding their effectiveness as painkillers.
Of particular concern among doctors were potentially harmful effects on cognitive development, a possible worsening of existing mental illnesses in patients and the drug's effects in older adults, which may include dizziness or drowsiness.
Meanwhile, the ...
As the foremost economic zone in China, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) region has recently been experiencing more frequent haze events, resulting in dramatic damages to human and ecosystem health.
Anthropogenic aerosol emissions play a key role in affecting the formation of haze events. However, aside from local sources of pollution, some studies have found that external and preceding climate drivers, such as Arctic sea ice and subtropical western Pacific sea surface temperature, are also influential factors. However, most research has mainly been confined to analyzing the effects on haze pollution in the Northern Hemisphere, with few considering the Southern Hemisphere.
"We found that the December sea surface temperature ...
Scientists found six sex chromosomes in the Odorrana swinhoana frog species endemic in Taiwan, giving new insights into how complex XY systems evolve.
The discovery was a surprise to the international research team led by Associate Professor Ikuo Miura of Hiroshima University's Amphibian Research Center. In 1980, the first reported instance of multiple sex chromosome systems in amphibians was found in the Taiwanese brown frog Raina narina -- a synonym for O. swinhoana -- which had a male-specific translocation between two chromosomes. Its sex chromosomes could be described as ?X1Y1X2Y2-?X1X1X2X2.
The ...
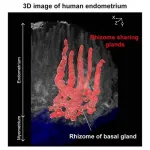
Niigata, Japan- New insights into the three-dimensional (3D) morphology of the human uterine endometrium could advance our understanding of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration and fertilized egg implantation while clarifying the pathogenesis of menstrual disorders, infertility and endometrium-related diseases such as adenomyosis, endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer.
The endometrial glands are comprised of complicated winding and branching structures, and conventional 2D imaging techniques have been unable to adequately assess their shape. This limitation has prevented elucidation of the mechanisms of endometrial regeneration during the menstrual cycle and the location of endometrial progenitor cells. Recent developments in 3D tissue-clearing imaging ...
A Korean research team succeeded in developing a technology generating various vibration using LED light signals. The technology allows various tactile sensations by area and reduction in size by considerably lowering the cost of light source, and these are expected to be applied to many industries including automobile and electronics.
The Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, or ETRI for short, announced that it succeeded in developing a technology to implement various vibrations using LED. This technology was widely recognized as published on the cover of the February 10 issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces1), a leading ...
Researchers have answered key questions to help prevent damage and improve the safety of hydraulic systems used for pipelines, water turbines and other applications.
The work, led by engineers at the University of Waterloo, investigates a phenomenon known as cavitation, or the formation and collapse of destructive gas-filled bubbles resulting from rapid pressure changes in liquids.
Cavitation is behind a well-known party trick that involves shattering the bottom of a liquid-filled bottle by striking its open top with the palm of your hand.
"The growth and collapse of cavitation bubbles are fascinating," said Zhao Pan, a professor of mechanical and mechatronics engineering who led the research. ...